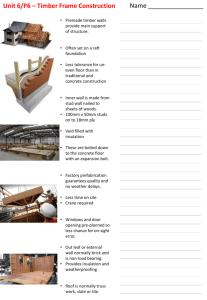
Document
advertisement

Chapter IV - Timber Structures Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural I. GENERAL PROVISIONS 1.3.2 The fulfillment of the essential requirements of mechanical resistance and stability of the structure and of a part of the essential requirement of fire protection related to preservation of the load-bearing capacity of a timber structure in the case of fire during a certain period determined by a special regulation (hereinafter: resistance to fire), is attained with a timber structure that has the technical characteristics and meets the requirements laid down in this Regulation. 1.1 1.1.1 This Technical Regulation (hereinafter referred to as the Regulation), in compliance with the fulfillment of the essential requirements for construction works, defines the technical characteristics for load bearing timber structures in buildings (hereinafter referred to as timber structures), the requirements for the design ,execution, usability, maintenance and other requirements for timber structures, and technical characteristics and other requirements for construction products intended to be incorporated into the timber structure (hereinafter referred to as construction products). 1.4 1.4.1 Construction products made of timber to which this Regulation applies are: - Wood products (structural timber beams and wood based panels) - Mechanical fasteners - Adhesives - Prefabricated elements - Wood protection products, 1.1.2 This regulation also applies to components of the building that are not integral parts of timber structures (non-structural elements - wood panels, wooden bulkheads, fences, fill, etc.) i.e., elements of timber structure that do not affect the mechanical resistance and stability of the building as a whole. - Other construction products for which requirements have been prescribed in Appendixes of this Regulation because of their installation along with the products from subparagraphs 1 to 5 of this paragraph. 1.5 1.1.3 This regulation does not apply to final coatings of structural and non -structural parts of the buildings (coatings of ceiling, flooring, and walls) and wood products that serve as thermal, acoustic or other insulation. 1.5.1 Timber structures and construction products to which this regulation applies shall have the technical characteristics and meet all other requirements laid down in this Regulation. 1.2 1.5.2 Integral parts of a timber structures (bracings, foundations, etc.) and construction products that are incorporated in them, and which are not covered by this Regulation, must, in addition to provisions of this Regulation, fulfill the provisions of a special regulation which governs such Structures, 1.2.1 Design, execution, maintenance and usage of building shall be such as to fulfill the requirements laid down in this Regulation 1.3 1.3.1 The timber structure is part of the building complex. 110 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural II. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF A TIMBER STRUCTURE and 2.1.2 of this Regulation, it is considered that the building meets the essential requirement of mechanical resistance and stability, and fulfills the specified resistance to fire. 2.1 2.1.1 The technical characteristics of a timber structure must be such that during the life of a building, while complying with the execution and maintenance specified in the design documentation of the timber structure, it withstands usual exploitation and environmental effects, so that during its execution and use, foreseeable impacts on a building do not cause: - Collapse of a whole or part of the work, - Major deformations to an inadmissible degree, - Damage to other parts of the construction works or to fittings or installed equipment as a result of a major deformation of the load bearing construction, - Damage by an event to an extent disproportionate to the original cause, 2.2.2 When, in accordance with special regulations, the additional protection of a timber structure is necessary in order to meet the requirements of fire resistance (linings, sprinkler installation etc.), that protection shall be an integral part of the technical design documentation of the timber structure. 2.3 2.3.1 Technical characteristics of the timber structure must be such that, in addition to fulfilling the requirements of this Regulation, requirements of other specific regulations are also fulfilled which are necessary for fulfillment of other essential requirements for the building. 2.1.2 Technical characteristics of a timber structure, along with the requirements of Paragraph 2.1.1, must be such that in the event of an outbreak of fire, the load-bearing capacity of structure or part of it is preserved for a period of time defined in a special regulation. 2.4 2.4.1 A timber structure shall, after the reconstruction of a building, have the technical characteristics as prescribed in paragraph 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 and paragraph 2.3.1 of this Regulation. 2.1.3 Technical characteristics of a timber structure referred to in paragraph 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 are accomplished by designing and constructing the timber structure in accordance with the provisions of this Regulation. 2.4.2 As an exception to paragraph 2.4.1, a timber structure must after reconstruction and adaptation of the building, which does not significantly affect the technical properties of the timber structure, have at least minimum of technical characteristics that it had before reconstruction and adaptation (hereinafter referred to as pre-existing technical characteristics). 2.1.4 Preservation of technical characteristics of a timber structure referred to in paragraphs 2.1.1 and 2.1.2 is achieved by the maintenance of a timber structure in accordance with the provisions of this Regulation. 2.2 2.4.3 It is considered that the reconstruction of a building should not affect significantly the technical characteristics of a timber structure if 2.2.1 If a timber structure has technical characteristics stipulated in paragraphs 2.1.1 111 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural the pre-existing technical characteristics related to the mechanical resistance and the stability of the building are satisfactory and if they do not change more than 10 percent (eg. change of values of resultant forces in sections, etc.). solution in design documentation of the timber structure. 2.5.6 Protection of a timber structure is specified in more detail in Appendix E of this Regulation. 2.4.4 The provision of paragraph 2.4.2 of this Article does not apply: - To multiple reconstructions of a building which change the pre-existing technical characteristics of a steel structure as a whole or in part, which characteristics are related to the mechanical resistance and the stability of the building, - To reconstruction of a building whose timber structure is damaged so that a danger is present to the lives and health of people, environment, nature, other buildings and things, or the stability of the ground on the surrounding land. III. CONSTRUCTION PRODUCTS FOR TIMBER STRUCTURES 3.1 3.1.1 Construction products are produced in production plants (factories) outside of construction sites, unless specified otherwise in this Regulation for certain construction products. 2.5 3.1.2 An exception to paragraph 3.1.1 of this Regulation, the prefabricated elements of a timber structure (hereinafter: prefabricated elements) may be fabricated on a construction site for the needs of that construction site. 2.5.1 Technical characteristics of protection of timber structures must ensure fulfillment of the requirements set on series of paragraphs 2.1 of this Regulation. 3.1.3 The construction site, in addition to being the place as defined by the Construction Law, implies, within the meaning of paragraph 3.1.2 of this Regulation, a production plant in which the prefabricated elements, applying suitable construction technology, are produced or fabricated for needs of a given construction site in accordance with the technical design documentation of a timber structure. 2.5.2 The protection of a timber structure must be conducted in such way as to ensure the attainment of technical characteristics of protection referred to in paragraph 2.5.1 of this Regulation. 2.5.3 If the protection is conducted in accordance to standards indicated in Appendix E of this Regulation, it is considered that the attainment of the protection characteristics referred to in paragraph 2.5.1 of this Regulation is ensured. 3.2 3.2.1 A construction product produced in a production plant (factory) outside of construction site may be incorporated into a timber structure if it fulfills the requirements laid down in this Regulation and if a certificate of conformity was issued for it in accordance with the provisions of a special regulation. 2.5.4 It is allowed to use other standards in addition to those indicated in Appendix E of this Regulation if the same level of compliance is attained. 2.5.5 The protection of a timber structure is considered to be an integral part of a technical 112 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural 3.2.2 Prefabricated elements fabricated on the construction site for needs of that construction site may be incorporated into a timber structure if their usability is proven in accordance with the technical design documentation of a timber structure and this Regulation. must fulfill are laid down in Appendixes of this Regulation for: - Wood products– in Appendix A, - Mechanical fasteners – in Appendix B, - Adhesives – in Appendix C, - Prefabricated elements– in Appendix D, and - Wood protection products – in Appendix E. 3.2.3 In the case of non-compliance of the construction product with technical specifications for that product and/or the technical design documentation of a timber structure, the producer of a construction product or the contractor constructing the timber structure must immediately stop the production/ installation of that product and undertake measures for the determination and removal of the faults which caused the lack of conformity. 3.3.2 Certifications of conformity of products that are not covered by standards or deviate significantly from standards indicated in Appendixes A to E referred to in paragraph 3.3.1 of this Regulation are to be conducted according to technical specifications for such products. 3.3.3 Certifications of conformity, in terms of paragraph 3.3.1 and 3.3.2 of this Regulation, cover the activities of assessing conformity of construction products and, depending on the specified assessment system, issuing the certificate of factory production control or issuing the certificate of conformity of construction products. 3.2.4 If there is non-conforming delivery of a construction product, the manufacturer or importer must inform, without delay, all buyers, distributors, authorized legal person that took part in certifying the conformity and the Ministry of Trade and Industry. 3.2.5 The manufacturer or the importer and distributor of the construction product are obliged to undertake corresponding measures to maintain the technical properties of a construction product during handling, storing and transport, as is the contractor constructing the timber structure during transport, handling, storing and installation of a construction product. IV. DESIGN OF TIMBER STRUCTURES 4.1 4.1.1 Timber structures must be designed in such way that during execution of work and service life of the building, all impacts on the timber structure must be predicted, resulting from the method and sequence of construction, from foreseeable conditions of normal use of the building and foreseeable impacts of the environment on the building. 3.3 3.3.1 Specific properties, attestations, certifications of conformity and marking of construction products, testing of construction products, and specifics during design and construction, necessary control procedures and other requirements that construction products 4.1.2 Technical design documentation of timber structure, in accordance with this Regulation, must prove that the building will, during its construction and the designed usage life, fulfill the essential requirement of mechanical resistance and stability, fire resistance and 113 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural other essential requirements in accordance with relevant regulations. 4.3.2 The application of other rules for designing of timber structures which differ from the rules laid down in the European standards indicated in Appendix “F” of this Regulation is allowed, if it is proven that by applying those rules the requirements of this Regulation are fulfilled at least at the level specified in European standards in Appendix “F”. 4.1.3 If not specified otherwise, with this or other regulations, the service life of the building referred to in paragraph 4.1.1 of this Regulation must be at least 50 years. 4.2 4.3.3 Appendix “F” referred to in paragraph 4.3.1, specifies in more detail the designing of timber structures. 4.2.1 The mechanical resistance and stability and also fire resistance of the building are to be proven in the technical design documentation, with calculations of load-bearing capacity and serviceability of the timber structure for foreseeable actions and impacts on the building. 4.4 4.4.1 Glued timber must have a water content corresponding to the technical instructions of the adhesive manufacturer but not less than 9% and not more than 15% provided that the maximum difference between the water content of elements to be bonded must be ± 2%. 4.2.2 As an exception to paragraph 4.2.1 of this Regulation, fire resistance does not have to be proven if by a special regulation is not determined the period during which the ultimate limit state of the load-bearing capacity of the timber structure must be preserved during fire. 4.4.2 Initial imperfections in the middle of a linear element, i.e. the deviation from the direction of the axis of the linear element, and the slender beams where buckling may occur as in the frame, must not be greater than 1/500 of the length for glued laminated timber or 1/300 for structural timber. 4.2.3 The calculations referred to in paragraph 4.2.1 of this Regulation are to be conducted by suitable calculation procedures that, when necessary, may be complemented by tests, in which all relevant parameters must be included. 4.5 4.2.4 Calculation models and other models must be such that, when the appropriate entry parameters are used and the modeling is carried out correctly, correspond to the behavior of the structure during construction and use. 4.5.1 It is not allowed incorporation of various types of fasteners in one joint, unless they have the same or similar mechanical properties. 4.5.2 It is not allowed to use different types of adhesives in construction of a single element of timber structure. 4.3 4.5.3 As an exception to paragraph 4.5.1, it is allowed the use of nails and screws when making glued joints, but only for tightening of glued joint, and not as bearing fasteners. 4.3.1 Design of timber structures, shall be done according to European Standards specified in Appendix "F" of this Regulation. 114 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural 4.5.4 It is not allowed installation in timber structures, of structural timber indicated in Appendix "A" with water content greater than 22%. foreseeable actions and impacts, and calculation of certain parts of the timber structure for all stages of transportation, handling, execution and usage of building, - Calculation of global stability of the structure, 3. In the program of quality control and quality assurance of timber structures: - Technical properties that construction products must possess in order to be installed in the timber structure, including adequate information for labeling of construction products, according to provisions of this Regulation, - Tests and procedures to prove the usability of construction products that are manufactured at the site for the purposes of that construction site, - Control of construction products incorporated into the steel structure that has to be conducted before their incorporation: Test methods, for verification of load bearing capacity and serviceability of timber structures, including traditional fasteners and staples. - Conditions for execution of works and other requirements that must be fulfilled during the execution of timber structure which affect the attainment of the designed and specified technical characteristics of timber structure and fulfillment of essential requirement of that building, - Other conditions relevant for the fulfillment of requirements laid down in this Regulation and special regulations, and, - Water content of elements of timber structure before incorporation in timber structure and water content of timber structure before junction with the other parts of the building. 4.5.5 It is not allowed installation in timber structures of timber elements that are not protected by preventive care processes in a manner to prevent re-wetting the timber during transport, processing, intermediate storage, assembly and use, avoiding direct contact with the water and soil, proper stacking and covering of timber elements. 4.6 4.6.1 Design documentation - a technical design documentation of timber structure, which is an integral part of the main project design of the building shall include in particular: 1. in the technical description - A description of the impacts from the purpose and usage of building, and environmental influence on the properties of the timber structure, - The data from the previous researches and data from other surveys and studies that can affect the properties of the timber structure, - A description of a timber structure, including foundation, - A description of method for execution of timber structure and installation of certain construction products, - Exposure class of timber structural parts, including steel and concrete components, - A description of the measures for structural protection, measures for chemical protection and special care if such is needed. 2. In the calculation of mechanical resistance and stability - Information on the predictable actions and their impact on the structure of building, - Information on the ground for foundation and earthquake zone, - Calculation of load bearing capacity and serviceability of the timber structure for the 4.6.2 Requirements from item 3, paragraph 4.6.1, depending on conditions, procedures and other circumstances of execution, may be elaborated in more detail in the execution project design documentation of the timber structure. 115 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural 4.7 V. EXECUTION AND SERVICEABILITY OF TIMBER STRUCTURES 4.7.1 In addition to conditions laid down in paragraphs 4.1 to 4.6 of this Regulation, project design of a timber structure in which the execution of the timber structure is elaborated must contain technical solutions for: - Elements of the timber structure and ways of their production or fabrication, - Incorporation of elements into a timber structure, including the calculation and required properties of connections of the elements with other elements of the timber structure, - Transfer and transport of elements of a timber structure (points of support and suspension and description of lifting systems, position of elements during transfer and transport, transport path, and other), and the designed weight and permitted weight tolerances of elements of the timber structure, - Arrangement of props, necessary supports systems and other measures to ensure stability and prevent damage to elements of the structure during transport, incorporation and connection of elements of the structure. 5.1 5.1.1 Execution of buildings that contain a timber structure must be such that the timber structure has technical characteristics and fulfills other requirements laid down in this Regulation, in accordance with the technical solution of the building and conditions for execution given in the project design, and so that it ensures the preservation of such properties and serviceability of the building during its life. 5.1.2 When executing a timber structure, contractor is obliged to follow the requirements of project design of timber structure and technical instructions for incorporation and usage of construction products and comply with the provisions of this Regulation. 5.2 5.2.1 When taking over a construction product produced outside the construction site, the contractor has to determine: - Whether the construction product was delivered with the mark in accordance with a special regulation and if the data in the documentation with which the construction product was delivered match the data in the mark, - Whether the construction product was delivered with technical instructions for incorporation and use, - Whether the properties, including the useful life of the construction product and data relevant for its incorporation, usage and impact on properties and duration of a timber structure are in accordance with properties and data specified in the main project design. 4.8 4.8.1 In addition to conditions laid down in paragraphs 4.1 to 4.6 of this Regulation, the project design for reconstruction or renovation of a building, in which the timber structure is changed, must necessarily contain data on determined pre-existing technical characteristics of a timber structure 4.8.2 Pre-existing technical characteristics of a timber structure shall be determined by checking the documentation of the building, tests, calculations and other appropriate ways. 5.2.2 The facts determined in accordance with paragraph 5.2.1 shall be recorded in accordance 116 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural with a special regulation on conducting daily progress reports, whereas the documentation with which the construction product was delivered is saved among the proofs about the conformity of construction products that the contractor must have at the construction site. technical characteristics and fulfills the requirements laid down in the project design and in this Regulation. 5.5.2 Conditions for execution of a timber structure are specified with a program of control and quality assurance that is an integral part of the main project design of the timber structure, at least in accordance with the provisions of Appendix “G” of this Regulation. 5.3 5.3.1 Specified properties and usability of a construction product produced at the construction site are determined in the way specified in the project design and in this Regulation. 5.5.3 If the technical solution of a timber structure and conditions in which execution work is being performed and other circumstances that could affect technical characteristics of a timber structure are such that they are not encompassed within the provisions of Appendix “G” of this Regulation, then in the program of control and quality assurance, such special conditions of execution must be specified which fulfill the requirements of paragraph 5.5.1. 5.3.2 Data attesting the usability and attained properties of the construction product from paragraph 5.3.1 must be recorded by the contractor in accordance with a special regulation on conducting daily progress reports. 5.4 5.4.1 It is forbidden to incorporate a construction product which: - Is delivered without a mark in accordance with a special regulation, - Is delivered without technical instruction for incorporation and use, - Does not have the properties required by project design or its useful life has expired, or whose data relevant for incorporation, use and impact on properties and durability of the timber structure are not in accordance with the data specified in the main project design. 5.5.4 Appendix “G” referred to in paragraphs 5.5.2 and 5.5.3 of this Article specifies in more detail execution and maintenance of timber structures. 5.6 5.6.1 It is considered that a timber structure has the technical properties foreseen by the project design and that it is usable if: - Construction products are incorporated in a timber structure in a specified way and have a certificate of conformity according to paragraph 3.2.1 of this Regulation, or proofs of usability according to paragraph 3.2.2 of this Regulation, - Conditions of execution and other circumstances which could affect the technical characteristics of a timber structure are in accordance with the requirements of project design, - The timber structure has proofs concerning load-bearing capacity and serviceability determined in examination by test load, when it 5.4.2 The incorporation of a construction product, i.e., the continuation of work must be allowed by supervising engineer, which is recorded in accordance with a special regulation on conducting daily progress reports. 5.5 5.5.1 Construction of a timber structure must be such that the timber structure has the 117 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural is prescribed as mandatory or required by project design, and if for checking of these facts exists formal records or documentation. specified in the project design of the building and in regulations in accordance with which the timber structure was constructed are fulfilled. 5.6.2 It is considered that the serviceability of a timber structure is proven if the conditions in paragraph 5.6.1 and in paragraph 5.5 of this Regulation have been fulfilled. 6.2 6.2.1 Maintenance of a timber structure implies: - Regular inspections of a timber structure, in periods and in the way specified in the project design of the building, this Regulation or a special regulation passed in accordance with the Construction Law, -special inspections of a timber structure after exceptional event or when an inspection body requires it, - conducting works in which the timber structure remains in the condition, or is returned to the condition specified in the project design of the building and this Regulation or a regulation in accordance with which the timber structure was constructed. 5.7 5.7.1 If it is determined that the timber structure does not possess properties foreseen in its design, additional verification must be carried out to prove that the timber construction fulfills the requirements of this Regulation. 5.7.2 Proof from paragraph 5.7.1 is considered a part of the as build design. 5.7.3 In the case that it is confirmed that the attained technical characteristics of the timber structure do not fulfill the requirements of this Regulation, it is necessary to produce project design for rehabilitation of a timber structure. 6.2.2 Fulfillment of specified conditions for maintenance of a timber structure is documented in accordance with the requirements of project design of the building and: - Reports on inspections and testing of a timber structure, - Records on maintenance work, - In other suitable way, if not otherwise specified in this Regulation or other regulation passed in accordance with the provisions of Construction Law. VI. MAINTENANCE OF TIMBER STRUCTURES 6.1 6.1.1 Maintenance of a timber structure must be such that during the life of the building its technical characteristics remain preserved and the requirements specified in the project design of the building and in this Regulation are fulfilled, as well as other essential requirements that the building must fulfill in accordance with a special regulation. 6.3 6.3.1 It is permitted to use for maintenance works, only those construction products which fulfill prescribed conditions and for which a certificate of conformity is issued in accordance with a special regulation, or for which usability is proved in accordance with project design of the building and this Regulation. 6.1.2 Maintenance of a timber structure that is constructed in accordance with regulations that were valid earlier must be such that during the life of the building its technical characteristics remain preserved and the requirements 118 Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Section 2 – Structural 6.3.2 By the maintenance of the building or by any other way the technical characteristics and fulfillment of specified requirements for timber structures must not be endangered. 6.4.1 While performing maintenance work on timber structures, the provisions of this Regulation that concern the execution of timber structures apply. 6.4 119 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX A WOOD PRODUCTS A.1 SCOPE A.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 3.3.1 of this Regulation, are specified technical characteristics and other requirements for wood products that are integral parts of timber structures and/or prefabricated elements from Appendix D to this Regulation, and the manner of certifying the conformity of wood products unless specified differently in this Regulation. A.1.2 Technical characteristics and other requirements and certifying of conformity of wood products are determined or conducted in accordance with the standards stated in item A.6 of this Appendix, standards to which those standards indicate and the provisions of this Appendix, and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation. A.1.3 Wood products, within the meaning of item A.1.1 of this Appendix, are products produced in a production plant (factory) for such kind of a product, and encompass: a) Solid timber (sawn and carpentry timber) set out in article A.2.1.5 subparagraph a) to b) of this Regulation, b) Glued laminated timber set out in article A.2.1.6 and structural products based on timber (ex. LVL) c) wood-based panels set out in paragraph A.2.1.7, subparagraphs a) to g) of this Regulation. A.2 SPECIFIC PROPERTIES, CERTIFICATION OF CONFORMITY AND MARKING A.2.1 Specified properties A.2.1.1 Technical properties of solid timber must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of solid timber and depending on the type of solid timber must be specified in accordance with the standards of series SK EN 14081 or standards SK EN 14544, standard SK EN 385, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Annex. A.2.1.2 Technical properties of structural products made of wood must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of structural products made of wood and depending on the type of structural products made of wood must be specified in accordance with the standards of series SK EN 14080 or standards SK EN 14374, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Annex. A.2.1.3 Technical properties of wood-based panels must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of wood based panels and depending on the type of wood based panels must be specified in accordance with the standards SK EN 13986, SK EN 14279 respectively SK EN 634-1, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Annex. A.2.1.4 Technical properties of wood products must be specified in the project design of a timber structure. 120 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures A.2.1.4.1 Regardless of conditions of use of a timber structures, for solid timber, glued laminated timber and structural products made of wood in the project design of timber structure must be specified following properties: a) Bending strength b) Tensile strength c) Modulus of elasticity d) Bonding quality e) Swelling and shrinking f) Durability A.2.1.4.2 Regardless of conditions of use of a timber structures, for wood based panels, in the project design of timber structure must be specified following properties: g) Characteristic values of strength perpendicular to surface (bending, shear, compression, tension) h) Modulus of stiffness (perpendicular and parallel to surface) i) Characteristic values of strength parallel to surface (bending, shear, compression, tension) j) Density k) Adhesives, percentage of adhesives and quality of internal bonding l) Linear expansion (swelling)- for veneer panels linear expansion should be defined in both directions m) Mechanical durability (hazard class) n) Moisture content A.2.1.4.3 For wooden based panels which correspond to class of serviceability 2 and 3, beside properties specified in paragraph A.2.1.4.2 in project design of timber structure must be specified also characteristics of water vapor permeability. A.2.1.4.4 For wooden based panels intended for external use, beside properties specified in paragraph A.2.1.4.2, in project design of timber structure must be specified also characteristics of thermal conductivity. A.2.1.4.5 For buildings that under a special regulation belong to the group of demanding buildings, for all types of wood products in the project design of timber structures must be specified properties of fire resistance. A.2.1.4.6 In spaces where the release of formaldehyde could have an impact on health (residence spaces for people, animal, spaces where food is stored etc.), for structural timber which is jointed with other timber or is continued through adhesives (structural finger jointed solid timber), for beams and panels based on wood, in project design of timber structure must be specified formaldehyde emission. A.2.1.5 Structural timber is produced as a) Structural timber with rectangular cross-section b) Structural timber with round cross-section A.2.1.6 Glued laminated timber and other wood based structural products (ex. LVL) A.2.1.7 Wood based panels are produced as: a) Solid wood panels (surface appearance hardwood or softwood) 121 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures b) Glued laminated veneer panels (LVL) - panels with longitudinal veneers and panels with max. 20% transverse orientation veneers. c) Panels with crossover orientation of veneers. d) Oriented Strand Boards (OSB) e) Particleboards f) Cement bonded particleboards g) Fibreboards (hardboards, medium boards, soft boards, MDF medium density fibreboard) A.2.2 Certification of conformity . A.2.2.1 Certification of conformity of structural timber from item A.2.1.5 of this Appendix depending on the type of structural timber is conducted in accordance with the procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of series of standard SK EN 14081, or procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 14544, and provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. A.2.2.2 Certification of conformity of laminated timber from item A.2.1.6 of this Appendix depending on the type of laminated timber is conducted in accordance with the procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 14080, or procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 14374, and provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. A.2.2.3 Certification of conformity of wood-based panels from item A.2.1.7 of this Appendix depending on the type of wood based panels is conducted in accordance with the procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 13986, and provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. A.2.3 Marking A.2.3.1 A timber product produced in accordance with a technical specification is marked on the bill of lading and on a product in accordance with that specification. The mark must contain the reference to that specification, in accordance with a special regulation. A.3 TESTING A.3.1 Taking of samples, preparation of samples and testing of wood products, depending on the type of a product, is conducted in accordance with the standards to which the corresponding standard from item A.6 refers. A.3.2 Instead of testing according to item A.3.1 of this Appendix, for botanical type of woods and country of origin determined by tables 1 and 2 of standard SK EN 1912, strength class can be determined visually or by testing equipment according to standard SK EN 14081-1, and standards to which this standard refers. A.4 CONTROL BEFORE INCORPORATION A.4.1 Timber product produced in accordance with technical specification for which the Conformity is confirmed as laid down in this Appendix and the certificate of conformity is issued, may be incorporated in the element of the timber structure if it conforms to the requirements from the project design of timber structure. 122 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures A.4.2 immediately before the incorporation of timber product appropriate supervisory activities must be conducted as laid down in Annex H of this Regulation. A.4.3 In case of suspicion on properties of wood products, before incorporation appropriate tests must be conducted according to standards to which the corresponding standard from item A.6 refers. A.5 MAINTAINING OF PROPERTIES A.5.1 Producer and distributor of a timber product and the contractor employed are obliged to undertake appropriate measures to maintain the properties of a timber product during handling, transport, trans-shipment, storing and incorporation according to technical instructions of a producer. A.6 LIST OF STANDARDS A.6.1 Standards for structural timber SK EN 14081-1:20XX SK EN 14081-2:20XX SK EN 14081-3:20XX SK EN 14081-4:20XX SK EN 14544:20XX SK EN 385:20XX Timber structures - Strength graded structural timber with rectangular cross section - Part 1: General requirements Timber structures - Strength graded structural timber with rectangular cross section - Part 2: Machine grading - Additional requirements for initial type testing Timber structures - Strength graded structural timber with rectangular cross section - Part 3: Machine grading- additional requirements for factory production control Timber structures - Strength graded structural timber with rectangular cross section - Part 4: Machine grading - Grading machine settings for machine controlled systems Timber structures - Structural timber with round cross-section – Requirements Finger jointed structural timber. Performance requirements and minimum production requirements A.6.2 Standards for wood based load bearing elements SK EN 14080:20XX Timber structures. Glued laminated timber. Requirements A.6.3 Standards for wood-based panels SK EN 13986:20XX SK EN 14279:20XX SK EN 14374:20XX SK EN 634-1:20XX Wood-based panels for use in construction. Characteristics, evaluation of conformity and marking Laminated veneer lumber (LVL). Definitions, classification and specifications Timber structures. Structural laminated veneer lumber. Requirements Cement-bonded particle boards. Specification. General requirements 123 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX B MECHANICAL FASTENERS B.1 SCOPE B.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 3.3.1 of this Regulation, technical characteristics and other requirements are specified for mechanical fasteners in timber structures, and the way of certifying their conformity unless specified differently in this Regulation. B.1.2 Technical characteristics and other requirements and certifying of conformity of mechanical fasteners are determined or conducted in accordance with the standards stated in item B.6, standards to which those standards indicate and the provisions of this Appendix, and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation. B.1.3 Mechanical fasteners, within the meaning of item B.1.1 of this Appendix, are dowel type fasteners stated in item B.2.1.4, (a) to e)), of this Appendix and special performance connectors stated in item B.2.1.5, a) to b), produced in a production plant (factory) for such kind of a product. B.2 SPECIFIC PROPERTIES, CERTIFICATION OF CONFORMITY AND MARKING B.2.1 Specified properties B.2.1.1 Technical properties of dowel type fasteners must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of dowel type fasteners in timber structure and must be specified in accordance with the standard SK EN 14592, standards to which this standard indicate, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. B.2.1.2 Technical properties of special performance connectors must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of special performance connectors in timber structure and must be specified in accordance with the standards SK EN 14545and SK EN 912, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. B.2.1.3 Technical properties of mechanical fasteners must be specified in the project design of timber structure. B.2.1.3.1 In the project design of timber structure must be specified corrosion protection depending on the type of timber connector and classes of serviceability as outlined in Appendix E. B.2.1.4 Types of dowel type fasteners are: a) b) c) d) e) nails screws dowels bolts and nuts staples B.2.1.4 Types of connectors are: 124 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures a) Punched metal plate fasteners b) Timber fasteners c) Nail plates B.2.2 Certification of conformity B.2.2.1 Certification of conformity of dowel type fasteners from item B.2.1.4 of this Appendix is conducted in accordance with the procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 14592, provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. B.2.2.2 Certification of conformity of connectors from item B.2.1.5 of this Appendix is conducted in accordance with the procedure and criteria of Appendix ZA of standard SK EN 14545, criteria of standard SK EN 912, provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. B.2.3 Marking B.2.3.1 Mechanical fasteners produced in accordance with a technical specification are marked on the bill of lading and on packaging in accordance with provisions of that specification. The mark must contain the reference to that specification, in accordance with a special regulation. B.3 TESTING B.3.1 Taking of samples, preparation of samples and testing of mechanical fasteners, depending on a kind of a timber connector, is conducted in accordance with standards to which the corresponding standard from item B.6 refers. B.4 CONTROL BEFORE INCORPORATION B.4.1 Mechanical fasteners produced in accordance with standards in item B.6 of this Appendix for which the conformity is confirmed in the way laid down in this Appendix and the certificate of conformity is issued, may be incorporated in the timber structure or the elements of the timber structure if they conform with the requirements of the project design of that timber structure. B.4.2 Before the incorporation of mechanical fasteners appropriate supervisory activities are conducted as laid down in Appendix H to this Regulation. B.5 MAINTAINING OF PROPERTIES B.5.1 The producer and distributor of mechanical fasteners and the contractor employed are obliged to undertake appropriate measures to maintain the properties of a product during handling, transport, trans-shipment, storing and incorporation according to technical instructions of a producer. 125 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures B.6 LIST OF STANDARDS B.6.1 Standards for dowel type fasteners SK EN 14592:20XX Timber structures. Dowel-type fasteners. Requirements B.6.2 Standards for connectors SK EN 14545:20XX SK EN 912:20XX Timber structures. Connectors. Requirements Timber fasteners. Specifications for connectors for timbers 126 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX C ADHESIVES C.1 SCOPE C.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 3.3.1 of this Regulation, technical characteristics and other requirements are specified for adhesives used in timber structures, and the way of certifying their conformity, unless specified differently in this Regulation. C.1.2 Technical characteristics and other requirements and certifying of conformity of adhesives are determined or conducted in accordance with the standards stated in item C.6, standards to which these standards indicate and the provisions of this Appendix, and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation C.1.3 Adhesives, within the meaning of item C.1.1 of this Appendix, are stated in item C.2.1.8, (a) to b)), of this Appendix produced in a production plant (factory). C.2 SPECIFIC PROPERTIES, CERTIFICATION OF CONFORMITY AND MARKING C.2.1 Specified properties C.2.1.1 Technical properties of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (a)), must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of adhesive and must be specified in accordance with standard SK EN 301,and standards to which this standard indicates, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. C.2.1.2 Technical properties of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (b)), must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of adhesive and must be specified in accordance with standard SK EN 12436, and standards to which this standards indicates, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. C.2.1.3 Technical properties of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (c)), must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of adhesive and must be specified in accordance with standard SK EN 15425, and standards to which this standards indicates, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. C.2.1.4 Technical properties of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.2, (a)), must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of adhesive and must be specified in accordance with standard SK EN 12765, and standards to which this standards indicates, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. C.2.1.5 Technical properties of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.2, (b)), must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of adhesive and must be specified in accordance with standard SK EN 204, and standards to which this standards indicates, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. 127 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures C.2.1.6 Technical characteristics of adhesives determines contractor employed or manufacturer of prefabricated elements in accordance with the requirements set out in project design or technical specification , for timber structure or prefabricated element. C.2.1.7 For casein adhesives except for the technical properties specified in standard SK EN 12436, it is obligatory to test the resistance to delaminating and the resistance to the effects of wood. C.2.1.8 According to intended purpose adhesives are categorized as: a) Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures b) Wood adhesives for non-structural application (formwork, partitions, fences, fill-in etc.) C.2.1.8.1 Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures are: a) Phenolic and amino plastic b) Casein c) One component polyurethane C.2.1.8.2 Wood adhesives for non-structural application are: a) Thermosetting (phenolic, amino- plastic, epoxy ) b) Thermoplastic C.2.2 Certification of conformity C.2.2.1 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.8 depending on type, is conducted in accordance with the provisions from items C.2.2.1.1, C.2.2.1.2, C.2.2.1.3, C.2.2.1.4, C.2.2.1.5, provisions of this Appendix and provisions of special regulation. C.2.2.1.1 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (a)) is conducted according to standard SK EN 301, standards to which this standard indicate, by application of conformity systems 1, 3, or 4 for properties related to requirements in case of fire and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation, and conformity systems 2+ for all other properties. C.2.2.1.2 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (b)) is conducted according to standard SK EN 12436, standards to which this standard indicate, by application of conformity systems 1, 3, or 4 for properties related to requirements in case of fire and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation, and conformity systems 2+ for all other properties. C.2.2.1.3 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.8.1, (c)) is conducted according to standard SK EN 15425, standards to which this standard indicate, by application of conformity systems 1, 3, or 4 for properties related to requirements in case of fire and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation, and conformity systems 2+ for all other properties. C.2.2.1.4 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.7.2, (a)) is conducted according to standard SK EN 12765 by application of conformity system 3. 128 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures C.2.2.1.5 Certification of conformity of adhesives from item C.2.1.7.2, (b)) is conducted according to standard SK EN 204 by application of conformity system 3. C.2.3 Marking C.2.3.1 Adhesive produced in accordance with technical specification, are marked on the bill of lading and on packaging in accordance with provisions of those specifications. The mark must contain the reference to that specification, in accordance with a special regulation. C.3 TESTING C.3.1 Taking of samples, preparation of samples and testing of adhesives, depending on type of adhesive, is conducted in accordance with standards to which the corresponding standard from item C.6 of this Annex refers, for certain type of adhesive. C.4 CONTROL BEFORE INCORPORATION C.4.1 Adhesives produced in accordance with technical specification for which the conformity is confirmed in the way laid down in this Appendix and a certificate of conformity is issued, may be incorporated in the timber structure if they conform to the requirements of the contractor of timber structure or manufacturer of prefabricated elements. C.4.2 Before incorporation of adhesives it is necessary to make a visual check of color, viscosity, appearance of sediments, presence of blobs etc. C.4.3 Before the incorporation, appropriate supervisory activities are to be Conducted as laid down in Appendix H to this Regulation C.5 MAINTAINING OF PROPERTIES C.5.1 The producer and distributor of adhesives and the contractor employed are obliged to undertake appropriate measures to maintain the properties of a product during handling, transport, transshipment, storing and incorporation according to technical rules and instructions of a producer. C.6 LIST OF STANDARDS C.6.1 Standards for adhesives for load-bearing timber structures SK EN 12436:20XX SK EN 301:20XX SK EN 15425:20XX Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures. Casein adhesives. Classification and performance requirements. Adhesives, phenolic and amino plastic, for load-bearing timber structures - Classification and performance requirements. Adhesives: One component polyurethane for load bearing timber structures. Classification and performance requirements C.6.1 Standards for wood adhesives for non-structural application 129 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures SK EN 12765:20XX Classification of thermosetting wood adhesives for non-structural applications SK EN 204:20XX Classification of thermoplastic wood adhesives for non-structural applications 130 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX D PREFABRICATED ELEMENTS D.1 SCOPE D.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 3.3.1 of this Regulation, technical characteristics and other requirements are specified for prefabricated elements used in timber structures (hereinafter: prefabricated elements), unless specified differently in this Regulation. D.1.2 Prefabricated element within the meaning of item D.1.1 is the element produced or fabricated at the place different from its final place in the structure, at a construction site for needs of that construction site or in a production plant for production of prefabricated elements, from- timber products produced in accordance with the Appendix A, fasteners produced in accordance with the Appendix B, adhesives produced in accordance with the Appendix C, wood preservatives produced in accordance with Appendix E and other products. D.1.3 Technical characteristics and other requirements, verification of usability respectively certifying of conformity of prefabricated elements are determined respectively conducted in accordance with item D.1.3.1 and D.1.3.2 of this Appendix, and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation. D.1.3.1 Technical characteristics and other requirements, and verification of usability of a prefabricated element fabricated in accordance with a project design of a timber structure are determined and conducted in accordance with that project design. D.1.3.2 Technical characteristics and other requirements, and certifications of conformity of a prefabricated element produced in accordance with technical specification (standard or technical approval) are determined and conducted in accordance with that specification. D.2 SPECIFIC PROPERTIES, CERTIFICATION OF CONFORMITY AND MARKING D.2.1 Specified properties D.2.1.1 Technical properties of prefabricated elements must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose in the structure, and must be specified in accordance with the standard SK EN 14732, and depending from type of prefabricated element also according to standards SK EN 14250 or SK EN 13377, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. D.2.1.2 Technical properties of timber products, fasteners, adhesives and preservatives of which the prefabricated element is fabricated respectively produced must be specified in accordance with Appendixes A, B, C, or E of this Regulation. D.2.1.3 Technical properties of other products except those from paragraph D.2.1.2, of which the prefabricated element is fabricated respectively produced must be specified in accordance with relevant standards for those types of products. D.2.1.4 Prefabricated element is fabricated or produced for: 131 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures a) Structural use (element of a partially prefabricated timber structure, element of a prefabricated timber structure or as a separate structure). b) Non-structural use (formwork, partition, fence, infill). D.2.1.5 Technical properties of prefabricated elements must be specified in a project design of a timber structure, and in case of a prefabricated element produced in accordance with technical specification, they shall be specified in the technical specification for that element. D.2.2 Verification of usability and certification of conformity D.2.2.1 Verification of usability of a prefabricated element fabricated in accordance with a project design of a timber structure is conducted in accordance with the project design of a timber structure and provisions of this Appendix, and includes the requirements for: A) contractor’s fabrication control and testing of a prefabricated element, and b) Supervision of a production plant and supervision of contractor’s fabrication control of manufacturing of prefabricated element, in the way appropriate for the attainment of technical characteristics of a timber structure in accordance with this Regulation. D.2.2.2 Certification of conformity of a prefabricated element produced in accordance with technical specification is conducted in accordance with provisions of that specification, and provisions of this Appendix also a special regulation. D.2.3 Marking D.2.3.1 Prefabricated element fabricated in accordance with the project design of a timber structure is marked on a bill of lading and on the element itself in accordance with the mark from the project design. D.2.3.2 Prefabricated element produced in accordance with a technical specification is marked on a bill of lading and on the element itself in accordance with provisions of that specification. The mark must contain the reference to that specification, in accordance with a special regulation. D.3 TESTING D.3.1 Prefabricated element fabricated in accordance with the project design of a timber structure is tested in accordance with that project design. D.3.2 Prefabricated element produced in accordance with technical specification is tested in accordance with that specification. D.4 DESIGN D.4.1 Prefabricated element is designed in accordance with provisions of Appendix F respectively Appendix G, and the provisions of this Regulation. D.4.2 Design of a prefabricated element must prove technical characteristics and behavior in all phases of the foreseen usage life of the element, i.e., for the phases of fabrication, transfer, storing, transport to the construction site, incorporation, use, maintenance and disassembly. 132 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures D.5 EXECUTION, FABRICATION AND PRODUCTION D.5.1 When executing a timber structure with prefabricated elements the rules laid down in Appendix H of this Regulation must be applied correspondingly, and: - Details related to all phases of the foreseen usage life of elements, - Details related to constituent materials of joints and standards that certify the conformity of those materials, - Details related to use and maintenance, specified in the design of a timber structure and/or technical instruction for incorporation and use. D.5.2 During fabrication of prefabricated element the provisions of Appendix H of this Regulation are applied correspondingly. D.5.3 when producing a prefabricated element the rules specified in corresponding technical specification for that product must be followed. D.6 CONTROL BEFORE INCORPORATION D.6.1 Prefabricated element fabricated in accordance with a project design of a timber structure may be incorporated in a timber structure if the conformity of timber products, fasteners, adhesives and preservatives is certified and if the usability of a prefabricated element is proven in the way determined in the project design of a timber structure and this Appendix. D.6.2 Prefabricated element produced in accordance with technical specification for which the conformity was certified in the way determined in this Appendix and the certificate of conformity was issued, may be incorporated in a timber structure if it conforms with the requirements of the project design of that timber structure. D.6.3 Immediately before the incorporation of a prefabricated element appropriate supervisory activities are conducted as laid down in Annex I of this Regulation. D.7 LIST OF STANDARDS D.7.1 Standards for prefabricated elements Pr EN 14732:20XX SK EN 14250:20XX SK EN 13377:20XX Timber structures: Prefabricated wall, floor and roof elements. Requirements Timber structures. Product requirements for prefabricated structural members assembled with punched metal plate fasteners Prefabricated timber formwork beams. Requirements, classification and assessment 133 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX E PRESERVATION OF TIMBER STRUCTURES E.1 SCOPE E.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with Article 2.5 of this Regulation, are specified technical characteristics and other requirements for preservation of timber structures and wooden preservatives, and the way of certification of conformity of wooden preservatives, unless specified differently in this Regulation. E.1.2 Technical characteristics and other requirements for preservation of timber structures and wooden preservatives, and certification of conformity of wooden preservatives are determined, respectively conducted, depending on the type of preservation respectively wooden preservatives, in accordance with provisions of this Appendix, standards to which it indicates and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation. E.1.3 Preservation of timber structure within the meaning of item E.1.1 includes building-physics, structural, organizational and chemical measures of preservation from atmospheric actions, actions of interior climate, seepage and other sources of water, also biological and fire actions in order to preserve essential requirements of mechanical resistance and stability and fire resistance of timber structure. E.2 TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PRESERVATION OF WOODEN STRUCTURES E.2.1 Technical characteristics of preservation of timber structures must be such that during service life of the building through regulated respectively design determined execution and maintenance of preservation of timber structure, it withstands all impacts of normal use of the building and impacts of the environment, so that during its execution and use, foreseeable impacts on a building do not cause losing of technical characteristics of timber structure. E.2.2 Technical characteristics of preservation of timber structures must be such that, depending on the class of exposure specified according to relevant provisions of series of standards SK EN 335, provide equilibrium moisture content during service life of the building, with a provision that moisture content insures protection against fungi, as a causative agent of decay, and enables dimensional stability, without inducing by that permanent deformations. E.2.3 Technical characteristics of preservation of timber structures regarding resistance to fire must be harmonized with the requirements of special regulations, and at least with requirements of standards indicated by Appendix “F” respectively Appendix “G” of this Regulation E.2.4 Preservation of timber structure must encompass preservation of all components of timber structure separately (wooden, metallic, etc), as well as preservation of timber structure as a whole. E.2.5 By preservation of individual components of timber structure should not adversely affect other components of structure. E.2.6 Corrosion protection of metallic fasteners which form an integral part of timber structure is conducted according to provisions of a special regulation, and in accordance with relevant provisions of 134 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures standards SK EN 1992, SK EN 1993, also examples of minimal specification for protection against corrosion of metal fasteners for different service classes given in standard SK EN 1995-1-1 table 4.1. E.3 PRODUCTS FOR PRESERVATION OF TIMBER STRUCTURES E.3.1 Specified properties, certification of conformity and marking E.3.1.1 Specified properties E.3.1.1.1 Technical properties of products for preservation must fulfill general and special requirements essential for the end purpose of products for preservation and must be specified in accordance with the standards stated in item E.6, standards to which these standards indicate, as well as the provisions of this Appendix. E.3.1.1.2 Types of products for preservation are: a) agents for protection against abiotic causes of degradation ( atmospherics, hydrolysis, shrinking, swelling, warping, surface discoloration caused by UV radiation, cracking and splitting, wear, abrasion ), b) Agents for protection against biotic causes of degradation (insects; bacteria; fungi that cause mold, decay and discoloration; marine borers), c) Fire protection agents. E.3.1.1.3 Technical characteristics of preservatives must be specified in project design of timber structure. E.3.1.1.4 For preservatives from E.3.1.1.2,(a)), technical characteristic of water-repellency must be specified in project design of timber structure. E.3.1.1.5 For preservatives from E.3.1.1.2,(b)), technical characteristic of effectiveness against actions of biotic agents of degradation, must be specified in a project design of timber structure, for those biotic agents of degradation which are, depending on the class of use defined in standard SK EN 335-1, occur in timber structure. E.3.1.1.6 For preservatives from E.3.1.1.2, (c)), technical characteristics of reaction to fire must be specified in project design of timber structure, related to resistance to fire foreseen in project design for timber structure. E.3.1.2 Certification of conformity E.3.1.2.1 Certification of conformity of preservatives from item E.3.1.1.2 is conducted depending on the types of preservatives, in accordance with provisions of item E.3.1.2.1.1, item E.3.1.2.1.2, item E.3.1.2.1.3, also provisions of this Appendix and a special regulation. E.3.1.2.1.1 Certification of conformity of preservatives from item E.3.1.1.2,(a)), depending on the type of preservative, is conducted for characteristics of preservatives against abiotic agents according to reference standards from item E.6 by application of system of conformity attestation 4 according to special regulation. 135 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures E.3.1.2.1.2 Certification of conformity of preservatives from item E.3.1.1.2,(b)), depending on the type of preservative, is conducted for characteristics of preservatives against biotic agents according to reference standards from item E.6 by application of system of conformity attestation 3 according to special regulation. E.3.1.2.1.3 Certification of conformity of preservatives from item E.3.1.1.2,(c)), depending on the type of preservative, is conducted for characteristics of fire protection according to relevant standards from item E.6 by application of system of conformity attestation 1+ according to special regulation. E.3.1.3 Marking of wooden preservatives E.3.1.3.1Wooden preservatives, produced in accordance with relevant standards from item E.6, are marked on the bill of lading and on packaging in accordance with provisions of those specifications. The mark must contain the reference to that standard, in accordance with a special regulation. E.3.2 Testing of wooden preservatives E.3.2.1 Taking of samples, preparation of samples and testing of wooden preservatives from item E.3.1.1.2, depending on their type, is conducted in accordance with relevant standards from item E.6 and standards to which these standards indicate. E.3.3 Control of wooden preservatives before incorporation E.3.3.1 Wooden preservative produced in accordance with technical specifications for which the conformity is confirmed in the way laid down in this Appendix and the certificate of conformity is issued, may be incorporated in a timber structure if they conform to the requirements of the project design of that timber structure. E.3.3.2 Before the incorporation of wooden preservative appropriate supervisory activities must be conducted as laid down in Appendix H of this Regulation. E.3.4 Maintaining properties E.3.4.1 Producer and distributor of wooden preservatives and the contractor employed are obliged to undertake appropriate measures to maintain the properties of a product during handling, transport, trans-shipment, storing and incorporation according to technical rules and instructions of a producer. E.4 DESIGN FOR PRESERVATION OF TIMBER STRUCTURES E.4.1 Design, calculation and execution E.4.1.1 For basis of design for preservation of timber structures in part of fire protection are applied relevant standards from Appendix “F”, respectively Appendix “G” of this Regulation and standards to which these standards indicate, unless specified differently in this Regulation. 136 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures E.4.1.2 During design of preservation of timber structures, in a part of preservation from: weathering; actions of interior climate; actions of seepage and other sources of water, and biological attacks; provisions of items E.4.1.2.1, E.4.1.2.2, E.4.1.2.3 and E.4.1.2.4 of this Appendix must be applied accordingly. E.4.1.2.1 During design of building physics measures of preservation of timber structures in particular must be paid attention to: - Reduce to minimum possible degree impact of rainfall and damping of structural elements either from environment or from other parts of that structure (ex. eaves, edges, lintels) - Disable the contact of elements of the structure with the ground, earth, or other materials and media that can cause excessive moisture (e.g. elevation of elements of the structure from the soil, sheathing etc.) - Long-term protection from weathering of those elements of timber structures that are exposed to rainfall and also enabling their simple replacement. - Allow as much air flow and easy access to elements of timber structures in order to perform regular checkups. E.4.1.2.2 During design of constructional measures of preservation of timber structures in particular must be paid attention to: - Ensure runoff of water from wooden surfaces and as short as possible water and snow retention on exposed surfaces (surface treatment, rounding corners of beams, etc.) - Prevent the penetration of rain water into the cross section (covering, coating, sealing, etc.) - Allow as much as possible air flow and drying of all parts of structure. E.4.1.2.3 During design of organizational measures of preservation of timber structures in particular must be paid attention to: - Providing such technical solutions that will during exploitation of the building, by permanent or temporary ventilation prevent the timber structure to be exposed to the air with relative humidity greater than 80% in indoor spaces. - Determine method of repair of preservation of timber structures which (preservation) is damaged during transport, processing, storing and assembly of the timber structure - Determine, in accordance with a special regulation, requirements for the management of construction waste generated by replaced parts of the structure during maintenance or removal of the structure. E.4.1.2.4 During design of chemical measures of preservation of timber structures in particular must be paid attention to: - Prevention of surface degradation due to damping and solar radiation by application of surface veneering. - Determine the type and procedure for application of protective coating taking into account the type of wood, purpose, class of exposure according to the relevant provisions of a series of standards SK EN 335, aesthetics, durability according to the relevant provisions of standard SK EN 1995-1-1, SK EN 3501:20XX, SK EN 350-2:20XX, SK EN 460:20XX, SK ENV 1099:20XX and paragraphs C.3., C.4. and C.5. of standard SK EN 14080, protection of the surface after the application, purpose, subsequent exposure to wetting, impact of corrosion on metallic parts, impact on the environment, maintenance of the structure, method of assembly, previous undertaken protection measures, emissions of formaldehyde, etc. 137 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures - Determine procedures for applying the final coat into elements of timber structure, when these elements are preventively protected in the production plant, if it is provided by technical solution of timber structure that the final coat will be applied on site. E.4.1.3 During design of protective measures from items E.4.1.2.1, E.4.1.2.2, and E.4.1.2.4 it is necessary give priority to building-physics and constructive measures of protection, while the chemical protective measures apply: - When by building-physics and constructive measures of preservation cannot be achieved the required level of preservation. - If climate and other conditions are particularly conducive to the development of biotic agents of degradation (insects and fungi in humid and / or warmer climate attack more, which is also favored by the proximity of the forest; microclimate, etc.) E.4.1.4 During design of preservation of timber structures must be taken into account also possible adverse effects of measures of preservation and / or preservatives on fulfilling technical characteristics of timber structure from paragraph 2.1 of this Regulation. E.4.2 Technical characteristics of wooden preservatives E.4.2.1 Technical properties of construction products that are integral parts of preservation of timber structure must be specified in the project design of timber structure according to provisions of item E.3.1 of this Appendix. E.5 EXECUTION OF PRESERVATION OF TIMBER STRUCTURES E.5.1 Execution, supervisory activities and control procedures at a construction site E.5.1.1 During transport, processing, storage, incorporation and use, it is necessary to prevent the wetting of timber, avoiding direct contact with water or soil, proper stacking of elements and covering. E.5.1.2 Elements of timber structures should be fold up in stacks that are covered, apart from each other and exposed to constant ventilation. When stored in the open space, glued laminated timber intended to be incorporated into the structure, must be embedded in structure in shortest possible time. E.5.1.3 It is not permitted preventive preservation (impregnation) by application of chemical preservatives at construction site. E.5.1.4 The provision of item E.5.1.3 do not apply to the case of applying the final coats when this is determined by project design of timber structure, also on repair of preservation which is necessary because of eventual damage of protection during transport, processing, and assembly of elements of the timber structure. E.5.1.5 In the case of execution of works from item E.5.1.4 must be prevented the emission of hazardous substances into the environment and implement adequate work protection measures. E.5.1.7 Before applying pesticides is necessary to clean the surface of the structural element according to the requirements of the project in accordance with the technical instructions. 138 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures E.5.1.6 During application of preservative coating it is necessary to comply with all manufacturers’ instructions and requirements of the project design of timber structure. E.5.1.7 Before application of preservative coatings it is necessary to clean the surface of the element of the structure according to the requirements of project design and in accordance with the manufacturer’s technical instructions. E.5.1.8 For preservation of elements of the structure with glued joints it is not allowed application of preservative coatings (veneers) which chemically react with the used glue. E.5.1.9 During execution of timber structure should be managed, in accordance with requirements of a special regulation, with the waste material of preservative coatings. E.5.1.10 On construction site it is necessary to conduct appropriate supervisory activities and control procedures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “G” of this Regulation. E.5.2 Usability of preservation E.5.2.1 During usability assessment of protection of timber structure must be taken into account: a) Written records in the construction diary regarding characteristics and other data on the protection of timber structures, b) Proof of usability (test results, records of the implemented procedures, etc.) that the contractor provides during implementation of procedures for protection of timber structure, c) Execution conditions and other circumstances which according to construction diary and other documentation that contractor must have at a construction site, also documentation that a manufacturer of building products must have may influence the technical characteristics of the protection of timber structures. E.5.3 Subsequent assessment of characteristics of preservation treatment E.5.3.1 For preservation treatment that does not have technical characteristics foreseen in project design or the same cannot be affirmed due to lack of required documentation, technical characteristics of protection of timber structure must be determined by subsequent testing and subsequent calculations. E.5.3.2 In order to determine the technical characteristics of protection treatment of timber structures according to item E.5.3.1 of this Appendix, it is necessary to collect relevant information about the protection treatment of timber structures and the circumstances of its execution to the extent and degree that enable assessing the degree of compliance with the essential requirements of mechanical resistance and stability , fire resistance and other essential requirements for the structure according to provisions of special regulations. 139 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures E.5.4 Maintenance of preservation treatment E.5.4.1 Activities for maintenance of preservation treatment of timber structure must be conducted in accordance with provisions of this Appendix and relevant standards from item E.6, as well as with adequate application of provisions of other Appendixes of this Regulation. E.5.4.2 Regular visual inspections for the purpose of maintenance of protection treatment of timber structure are conducted in accordance with requirements specified in the project design of the structure, or at least once a year. E.5.4.3 Determination of condition of preservation treatment of timber structure in relation to designed characteristics for the purpose of maintenance of protection treatment of timber structures must be conducted at least every 5 years. E.5.4.4. Methods of performing regular inspections in order to maintain the protection treatment of timber structure is determined in project design of the structure, and includes at least: a) visual inspection, which includes determination of the degree of damage of protection treatment as well as eventual damages to timber structure that are essential for the preservation of technical characteristics of protection treatment. b) Determination of condition of protection treatment, if on the basis of visual inspection described in sub-item a) are doubts on fulfilling of characteristics of protection treatment. E.6 LIST OF STANDARDS E.6.1 List of standards related to durability of wood SK EN 335-1:20XX SK EN 335-2:20XX SK EN 335-3:20XX SK EN 350-1:20XX SK EN 350-2:20XX SK EN 460:20XX SK EN 14080:20XX SK CEN/TS 1099:20XX Durability of wood and wood-based products. Definitions of use classes. General Durability of wood and wood-based products. Definition of use classes. Application to solid wood Hazard classes of wood and wood-based products against biological attack. Application to wood-based panels Durability of wood and wood-based products. Natural durability of solid wood. Guide to the principles of testing and classification of natural durability of wood Durability of wood and wood-based products. Natural durability of solid wood. Guide to natural durability and treatability of selected wood species of importance in Europe Durability of wood and wood-based products. Natural durability of solid wood. Guide to the durability requirements for wood to be used in hazard classes Timber structures. Glued laminated timber. Requirements Plywood. Biological durability. Guidance for the assessment of plywood for use in different use classes 140 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures E.6.2 List of standards related to wood preservatives SK EN 351-1:20XX SK EN 599-1:20XX SK EN 599-2:20XX SK EN 15228:20XX SK EN 927-1:20XX SK EN 927-2:20XX SK EN ISO 4618:20XX SK EN 13501-1:20XX SK EN 1995-1-2:20XX Durability of wood and wood-based products. Preservative-treated solid wood. Classification of preservative penetration and retention Durability of wood and wood-based products. Efficacy of preventive wood preservatives as determined by biological tests - Part 1: Specification according to use class Durability of wood and wood-based products. Performance of preventive wood preservatives as determined by biological tests - Part 2: Classification and labelling Structural timber. Structural timber preservative treated against biological attack Paints and varnishes - Coating materials and coating systems for exterior wood - Part 1: Classification and selection Paints and varnishes - Coating materials and coating systems for exterior wood - Part 2: Performance specification Paints and varnishes. Terms and definitions E.6.3 List of standards related to fire protection Fire classification of construction products and building elements. Classification using test data from reaction to fire tests. Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures - Part 1-2: General - Structural fire design 141 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX F DESIGN OF TIMBER STRUCTURES F.1 SCOPE F.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 4 of this Regulation, rules for designing of timber structures of buildings are specified, unless specified differently in this Regulation. F.1.2 The provisions of this Appendix refer to designing of timber structures of buildings considering also basis of design and actions on structures, geotechnical design and design of structures resistant to earthquakes. F.2 DESIGN, CALCULATION AND EXECUTION F.2.1 Rules for designing of timber structures are specified with Kosova/European standards in sequences SK EN 1990, SK EN 1991, SK EN 1995, SK EN 1997 and SK EN 1998, with national features given in nationally determined parameters within particular standards, and Kosova/European standards indicated by these standards. F.2.2 For basis of design and actions on timber structures, the Kosova/European standards in sequences SK EN 1990, SK EN 1991 and SK EN 1995 apply, including the associated nationally determined parameters, and standards indicated by standards in these sequences. F.2.3 For design of timber structures related to earthquake resistance, the Kosova/European standards in sequence SK EN 1998 apply, including the associated nationally determined parameters, and standards indicated by standards in this sequence. F.2.4 For design of timber structures, the Kosova/European standards in sequence SK EN 1995 apply, including the associated nationally determined parameters, and standards indicated by standards in this sequence. F.2.5 For geotechnical design the Kosova/European standards in sequence SK EN 1997 apply, including the associated nationally determined parameters, and standards indicated by standards in this sequence F.2.6 If in accordance with paragraph 4.2.2 of this Regulation calculation of resistance to fire according to SK EN 1995-1-2 is not conducted, a timber structure of a building designed in accordance with provisions of this Appendix must satisfy general principles of protection from fire. F.3 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES OF TIMBER PRODUCTS, MECHANICAL FASTENERS, ADHESIVES, PREFABRICATED ELEMENTS F.3.1 Technical properties of wood products are specified in the design of timber structures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “A” of this Regulation F.3.2 Technical properties of mechanical fasteners are specified in the design of timber structures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “B” of this Regulation 142 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures F.3.3 Technical properties of adhesives are specified in the design of timber structures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “C” of this Regulation F.3.4 Technical properties of prefabricated elements of structure are specified in the design of timber structures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “D” of this Regulation F.3.5 Technical properties of preservation of timber structure and wooden preservatives are specified in the design of timber structures in accordance with provisions of Appendix “E” of this Regulation F.4 LIST OF STANDARDS F.4.1 Standards for design and calculation Eurocode 0: Basis of Structural design SK EN 1990:20XX:Eurocode 0. Basis of structural design. Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures SK EN 1991-1-1:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Densities, self-weight, imposed loads for buildings. SK EN 1991-1-2:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Actions on structures exposed to fire. SK EN 1991-1-3:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Snow Loads SK EN 1991-1-4:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Wind actions. SK EN 1991-1-5:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Thermal actions. SK EN 1991-1-6:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Actions during execution. SK EN 1991-1-7:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. General actions. Accidental actions. SK EN 1991-3:20XX Eurocode 1. Actions on structures. Actions induced by cranes and machines. *(No National Annex published for any of SK EN 1991 series) Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures SK EN 1995-1-1:20XX Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures - Part 1-1: General Common rules and rules for buildings SK EN 1995-1-2:20XX Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures - Part 1-2: General Structural fire design. SK EN 1995-2:20XX Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures - Part 2: Bridges *(No National Annex published for any of SK EN 1995 series) Eurocode 7: Geotechnical Design 143 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures SK EN 1997-1:20XX SK EN 1997-2:20XX Eurocode 7. Geotechnical design. General rules Eurocode 7. Geotechnical design. Ground investigation and testing *(No National Annex published for any of SK EN 1997 series) Eurocode 8: Design of structures for earthquake resistance SK EN 1998-1:20XX Eurocode 8. Design of structures for earthquake resistance. General rules, seismic actions and rules for buildings SK EN 1998-2:20XX Eurocode 8. Design of structures for earthquake resistance. Bridges SK EN 1998-3:20XX Eurocode 8. Design of structures for earthquake resistance. Assessment and retrofitting of buildings SK EN 1998-4:20XX Eurocode 8. Design of structures for earthquake resistance. Silos, tanks and pipelines SK EN 1998-5:20XX Eurocode 8. Design of structures for earthquake resistance. Foundations, retaining structures and geotechnical aspects *(No National Annex published for any of SK EN 1998 series) 144 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures APPENDIX G EXECUTION AND MAINTENANCE OF TIMBER STRUCTURES G.1 SCOPE G.1.1 In this Appendix, in accordance with paragraph 5.5 of this Regulation, technical and other requirements and conditions for execution of timber structures and supervisory activities and control procedures in the execution of timber structures are specified, as well as maintenance of timber structures, unless specified differently in this Regulation. G.1.2 Technical and other requirements and conditions from item G.1.1 of this Appendix are determined, i.e., execution and maintenance of timber structures is conducted in accordance with standards from item G.4.1 and G.4.2 of this Appendix, standards indicated by these standards and provisions of this Appendix and in accordance with provisions of a special regulation. G.1.3 On execution and maintenance of timber structures are also applied the corresponding standards for execution and maintenance of other kinds of products used in timber structures in accordance with rules for those products, except those to which Appendixes A, B, C, D, and E of this Regulation refer. G.2 EXECUTION, SUPERVISORY ACTIVITIES AND CONTROL PROCEDURES AT A CONSTRUCTION SITE G.2.1 Execution G.2.1.1 Elements of timber structures are constructed, from wooden products produced in accordance with Appendix “A”, mechanical fasteners produced in accordance with Appendix “B”, adhesives produced in accordance with Appendix “C”, wooden preservatives produced in accordance with Appendix “E”, and from other products, or as prefabricated elements produced in accordance with Appendix “D”, in accordance with the design of a timber structure and provisions of this Appendix. G.2.1.2 Before assembly of elements of timber structure, contractor must: - Inspect every bill of lading and marking of: wooden products, mechanical fasteners, adhesives, wooden preservatives and other construction products, which will be used, - Visual control of: wooden products, packaging of mechanical fasteners, adhesives, wooden preservatives and packaging of other construction products to determine possible damage, - Determine the moisture content of wood and prefabricated products. G.2.1.3 Moisture content of wooden products shall be determined immediately prior to assembly of elements of timber structure in accordance with the standards SK EN 13183-1 and SK EN 13183-2. G.2.1.4 Prior to the commencement of work for assembly of elements of timber structure, control tests of construction products must be conducted in case of suspicion. G.2.1.5 Elements of timber structure must be marked with a direction of assemblage if it is not clear from their shape. 145 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures G.2.1.6 Elements of timber structure, products referred to in Appendixes "A", "B", "C" and "E" of this Regulation and other products which are incorporated into the timber structure must be transported and stored until the moment of assemblage, in a manner as is determined in the design of timber structure and manufacturers technical instructions. G.2.1.7 During transport to the construction site and at the construction site as well as during incorporation it is necessary to comply with all requirements of the design of timber structure and ensure that wooden products and prefabricated elements are not brought into the position which is non-compliant with the design that could result in the exceeding stress in comparison to those during service, loss of stability or rollover of element. G.2.1.8 Tailoring of wooden products, by rule is conducted in covered and especially for that reason prepared platform or table, on which structure is drawn with all the details and cambers in actual size with the use of precision tools. G.2.1.9 As an exception from item G.2.1.8 in a case of simple elements of timber structures (roof rafters, etc) or elements of the timber structure that can be jointed during incorporation at the final position, the platform for tailoring of timber products doesn’t need to have drawn on it the structure in its actual size. G.2.1.10 During tailoring of timber products, the remaining parts which will be incorporated must be appropriately stored and labeled so that there is no confusion about the type and category of product. G.2.1.11 In truss girders it is necessary to check the ends of individual elements of truss for bumps and cracks and the elements that do not meet the criteria of incorporation to throw out. G.2.1.12 Holes, slots and notches for fasteners must be performed with such precision so to ensure joint properties determined by design. G.2.1.13 It is considered that the criteria from item G.2.1.12 is fulfilled if holes for fasteners are performed simultaneously on all elements of the same joint provisionally compounded in final position. G.2.1.14 Embedment of fasteners shall be conducted in such temporary position of elements of structure which ensures the completion of designed camber. G.2.1.15 During execution, timber structure must be secured from actions during execution (including actions from equipment used during execution or procedures of execution) as well as wind actions or unfinished structure in accordance with the design of timber structure. G.2.1.16 All temporary fixings and restraints must be provided in the timber structure until timber structure is not constructed to that extent which allows their safe removal. G.2.2 Gluing of timber joints G.2.2.1 Gluing on construction site is permitted only under controlled conditions, in accordance with technical instructions of manufacturer of adhesive, requirements from design of timber structure and provisions of this Appendix. 146 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures G.2.2.2 Gluing can be performed on elements whose surface is already prepared (dried, degreased, clear from dust etc.) in accordance with the project design and technical instructions of manufacturer. G.2.2.3 During execution of glued joints it is forbidden to repair uneven surfaces with the sandpaper. G.2.2.4 During execution of glued joints, moisture content of timber elements in the place of joint must be controlled just before bonding in accordance with the relevant standards from item G.4.1 of this Appendix. G.2.2.5 Maximum difference of moisture content of timber elements in the joint shall be not more than 2% compared to moisture content determined by design. G.2.2.6 All joints must be executed with adhesives of same origin, as well as adhesive with which is executed bonding of layers of timber in case of laminated timber. G.2.2.7 Adhesive must be prepared and applied in the manner and in the timeframe determined by manufacturer’s technical instruction. G.2.2.8 Glued joints must be treated according to the technical instructions of the manufacturer. G.2.2.9 pressing during gluing must be evenly distributed throughout the joint. G.2.2.10 Pressing must be applied in accordance with the manufacturer's technical instructions and in no case shall be less than 50 N/cm2. G.2.2.11 Pressing time must match the characteristics of the used adhesive and microclimate conditions in which the bonding is performed. G.2.2.12 During bonding is not allowed moving of elements. G.2.2.13 Control of glued joint and bond strength must be also done in bonded elements after completion of bonding, which is done by examination of test samples made on same terms and conditions as primary bonded structure or by taking test samples from primary structure by appropriate application of standard series SK EN 15416 and of series SK EN 302 (1-4). G.2.3 Assembly of elements of timber structure G.2.3.3 General G.2.3.1.1 Rules specified in item G.2.3.2 shall be applied accordingly to each part of timber structure fabricated on construction site out of final position. G.2.3.2 Installation of prefabricated element G.2.3.2.1 Prefabricated elements fabricated or produced under the provisions of Appendix “D” of this Regulation shall be mounted in timber structure according to design of timber structure and/or technical instruction for installation and use of prefabricated elements and provisions of this Regulation. 147 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures G.2.3.2.2 Handling, storage and preservation of prefabricated elements should be in accordance with the requirements of design of timber structures, relevant technical specifications for that prefabricated element and provisions of this Appendix. G.2.3.2.3 Contractor shall, prior to the installation on timber structure, check whether fabricated or produced prefabricated element (including the moisture content of the element determined at time of installation) is in accordance with the requirements of design of timber structure, and whether the handling and storage of prefabricated elements led to its damage, deformation or other changes that would affect the technical properties of timber structure. G.2.3.2.4 Supervising engineer just before the installation of prefabricated element in timber structure, must: a) Check whether for the prefabricated element, made according to design of timber structure, usability has been assessed in accordance with design. b) Check whether for the prefabricated element produced according to technical specification is issued certificate of conformity and whether the prefabricated element complies with the requirements of the project design of timber structure, c) Check whether the prefabricated element is placed in accordance with the design of timber structure and Appendix "D" of this Regulation, respectively with technical instructions for installation and use, d) Document the findings of all carried out tests by record in construction diary. G.2.4 Serviceability of timber structures G.2.4.1 During prove of serviceability of timber structure should be taken into account: a) Records in the construction diary on the properties and other information on construction products embedded in the timber structure, b) Results of supervision activities and control procedures which in accordance with this Regulation must be conducted before incorporation of construction products in the timber structure, c) Serviceability proof (test results, records of implemented procedures, etc.) which contractor has provided during execution of timber structure d) Results of examination with test load of timber structure or any of its part, e) Conditions of execution and any other circumstances which according to construction diary and any other documentation which contractor must keep in construction site, as well as documentation which producer of construction product must have may influence technical properties of timber structure. G.2.4.2 Examination by test load is conducted in order to evaluate the behavior of structure in relation to designed assumptions. By test load are examined timber structures for which this test is foreseen in design, if there is a suspicion and if it is specified by this Appendix. G.2.4.3 Examination from item G.2.4.2 must be conducted according to design of timber structure, appropriate application of standards from item G.4 of this Appendix and provisions of this Regulation. G.2.4.5 Examination from item G.2.4.2 is obligatory to conduct for cantilevered structures projecting more than 15 m, girder beams spanning more than 30m and arch structures with length of arch more than 60m. 148 Section 2 – Structural Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures G.2.5 Subsequent prove of technical properties of timber structure G.2.5.1 For timber structures that do not have the technical properties foreseen in design or the same cannot be identified due to lack of required documentation, must by subsequent examination and subsequent calculations determine technical properties of timber structure. G.2.5.2 In order to determine technical properties of timber structure according to item G.2.5.1 of this Appendix, it is necessary to collect relevant information’s of timber structure to that extent and degree that allows assessment of the degree of compliance with the essential requirements of mechanical resistance and stability, fire resistance and other essential requirements for the building according to provisions of special regulations. G.3 MAINTENANCE OF TIMBER STRUCTURES G.3.1 Actions within the maintenance of timber structures must be conducted according to provisions of this Appendix and standards referred to in this Appendix, as well as with appropriate application of other provisions of this Regulation. G.3.2 Frequency of regular inspections in order to maintain a timber structure are carried out in accordance with the requirements of design of timber structure, but not less then: a) 6 months for persevered parts of timber structure that serve for drainage (gutters, etc), respectively according to Appendix “E” of this Regulation b) 1 year for the parts of timber structure which are exposed to frequent changes of moisture content. c) 3 years for the parts of timber structure which are located in areas with difficult conditions of air flow. d) 10 years for the parts of timber structure which are located in areas with good ventilation. G.3.3 Methods of inspections are specified in design of timber structure, and include at least: a) Visual inspection, which includes determination of position and size of crack formation or expansion of biological attack (fungi and/or insects), as well as other damage relevant for maintaining of mechanical resistance and stability of the building. b) Determination of condition of preservative coating of elements of timber structures c) Determination of value of deflection of the main structural elements of timber structure in case of general actions, if based on the visual inspection described in subparagraph a) there is a suspicion in fulfilling the essential requirement of mechanical resistance and stability of building. d) Determination of moisture content G.3.4 Documentation referred to in item G.3.2 and G.3.3 and also other documentation regarding maintenance of timber structure shall be permanently kept by the owner of the building. G.4 LIST OF STANDARDS G.4.1 Standards for execution and maintenance SK EN 1995-1-1:20XX Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures - Part 1-1: General Common rules and rules for buildings 149 Section 2 – Structural SK CEN/TS 12872:20XX SK EN 13183-1:20XX SK EN 13183-2:20XX SK EN 594:20XX SK EN 595:20XX SK EN 596:20XX SK EN 1195:20XX SK EN 302-1:20XX SK EN 302-2:20XX SK EN 302-3:20XX SK EN 302-4:20XX SK EN 205:20XX SK EN 15416-1:20XX SK EN 15416-2:20XX SK EN 15416-3:20XX Unified Construction Code of Republic of Kosovo Chapter IV – Timber Structures Wood-based Panels - Guidance On The Use Of Load-bearing Boards in Floors, Walls and Roofs Moisture content of a piece of sawn timber. Determination by oven dry method Moisture content of a piece of sawn timber. Estimation by electrical resistance method Timber structures. Test methods. Racking strength and stiffness of timber frame wall panels Timber structures. Test methods. Test of trusses for the determination of strength and deformation behavior. Timber structures. Test methods. Soft body impact test of timber framed walls Timber structures. Test methods. Performance of structural floor decking Adhesives for load bearing timber structures. Test methods. Determination of bond strength in longitudinal tensile shear strength Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures. Test methods. Determination of resistance to delamination. Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures. Test methods. Determination of the effect of acid damage to wood fibers by temperature and humidity cycling on the transverse tensile strength Adhesives for load-bearing timber structures. Test methods. Determination of the effects of wood shrinkage on the shear strength Adhesives. Wood adhesives for non-structural applications. Determination of tensile shear strength of lap joints Adhesives for Load Bearing Timber Structures - Test Methods Part 1: Static Load Test of Single Bond line Specimens In Compression Shear Adhesives for load bearing timber structures other than phenolic and amino plastic. Test methods. Static load test of multiple bond line specimens in compression shear Adhesives for Load Bearing Timber Structures Other than Phenolic and amino plastic - Test Methods - Part 3: Creep Deformation Test at Cyclic Climate Conditions with Specimens Loaded in Bending Shear 150