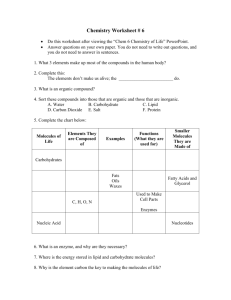
Biomolecules
advertisement

Organic Molecules and Biomolecules • Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of living organisms • Inorganic Chemistry is the chemistry of nonliving things • Organic molecules are defined as molecules containing both carbon and hydrogen. • Biomolecules are organic compounds found in living things. • There are only 4 categories of biomolecules- carbohydrates, Carbon • Carbon only has 4 electrons in its outer shell. • To fill its outer shell to 8, carbon usually combines with C, H, N, O. P, S which are the elements that make up most of the weight of living things. • Because carbon can combine with up to 4 other elements, it makes it the perfect building block for biomolecules. Hydrocarbons • Long chains of C-C bonds with the only other element being hydrogen. Octane Hydrocarbons • Carbon is also capable of forming double and triple bonds with itself. This makes the molecule less flexible and influences the function of the molecule Functional Groups • Functional groups are specific combinations of bonded atoms that always react in the same way, regardless of the carbon skeleton they are attached to. • The functional group of a biomolecule is actually more important than the carbon skeleton it is attached to. Isomers • Organic molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different arrangement of elements. • Ex: C3H6O3 Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are universally used as an immediate energy source and they play structural roles for a variety of organisms. • Carbohydrates have a carbon to hydrogen to oxygen ratio of 1:2:1 • Carbs include single sugar molecules and chains of sugars. Monosaccharides • Monosaccharides are only a single sugar molecule called a simple sugar. • They can have a carbon backbone of 3 to 7 carbons • Examples: Glucose and Ribose Disaccharides • Disaccarides contains 2 monsaccharides that have joined during a dehydration reaction. Polysaccharides • Polymers of monosaccharides. • When an organism needs energy, the polysaccharide is broken down to release simple sugar molecules. • The helical shape of the polysaccharides helps expose the sugar linkages to enzymes when they break them down. Polysaccharides • Plants store glucose as starch. Potatoes store starch during winter until energy is needed to grow in the spring. Polysaccharides branch at the 6th carbon of the monomer. (No main carbon chain) Polysaccharides • Animals store glucose are glycogen. Our liver cells store glycogen until energy is needed. The storage and release of glycogen is controlled by hormones. Polysaccharides • Polysaccharides are used as storage molecules because they are not soluble in water and are much larger than simple sugars. Polysaccharides • Polysaccharides can be used as structural molecules as well. • Ex: Cellulose, Chitin, and peptidoglycan Cellulose in plants. Cellulose is the most abundant carbohydrate and organic molecule. Animals cannot digest the bonds between the glucose monomers. • Chitin in animals and fungi. Found in fungal cell walls and exoskeletons of crabs. Chitin cannot be digested by animals. Lipids • There are a variety of organic compounds classified as lipids: • • • • • Fats- butter, lard Oils – cooking oils Phospholipids- plasma membrane Steroids- medicines Waxes- candles, polishes Triglycerides • Fats and Oils contain 2 subunits: fatty acids and glycerol. • Fatty acids contain an long hydrocarbon chain and a – COOH (carboxyl functional group) Most contain 16 or18 carbons • Fatty acids can be saturated, containing no double bonds between carbons, or unsaturated, having double bonds between carbons. Triglycerides • Glycerol is a 3-carbon compound with 3 –OH (hydroxyl groups) • -OH makes it polar, so therefore can mix with water. Triglycerides • The –COOH of fatty acids and the –OH of glycerol undergo a dehydration reaction and result in a fat molecule and 3 molecules of water Phopholipids • Like triglycerides, but the third fatty acid contains a phosphate group. This causes the fatty acid to become polar and be the polar “head” Steroids • Steroids are different from fats and have skeletons of 4 fused carbon rings. Each type of steroids differ based on the type of functional group attached to the carbons. • Cholesterol is a primary component to the cell membrane and is a precursor of several other steroids. Waxes • In waxes, long chain fatty acids bone with long chain alcohols. Proteins • Proteins are of primary importance to the structure and function of cells. • Some functions include: • Metabolism, Support, transport, defense, regulation, and motion. Peptides