File - Ms. Davis' Domain
advertisement

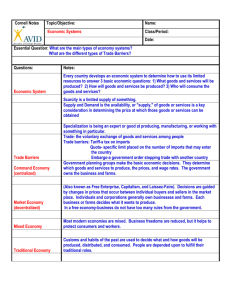
SS6E5A ECONOMIC SYSTEMS ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Traditional Economy Command Economy WHAT WILL HOW IT WILL BE WHO WILL BE PRODUCED PRODUCED PRODUCE IT Farm Goods/Livestock Gathering; Hand Work Family or group What is determined to be important by the government Amounts determined by the government Government workers Market Economy Determined by demand Determined by both makers and sellers Individuals and groups Mixed Economy Determined by demand but government may regulate some pricing or production Determined by makers and sellers but government may regulate safety Private individuals may own some business and factories EXAMPLES In a traditional economy, there are very few industries and citizens barter and trade goods produced. In a command economy, central planners make production, consumption, and distribution decisions. This economic system is most closely associated with a communist country. In a market economy the producers and consumers control production, consumption, and distribution of goods. Market economies may also be referred to as Free Markets or Free enterprise. This economic system is most often associated with democratic governments Mixed economy is most associated with democratic governments. ECONOMIC CONTINUUM Command N. Korea Market Peru Brazil Based on your knowledge of economic systems, the diagram above shows that most economies are: United States a. Market b. Mixed Supply and demand and competition help to drive a market economy. Competition in a free market almost always benefits consumers. Barter-to exchange goods or services in return for other goods or services; the practice or system of exchanging goods and services Currency exchange systems are required to facilitate trade between international countries. c. Pure d. Command SS6E5A ECONOMIC SYSTEMS COUNTRY ITALY GERMANY GEORGRAPHY Slightly larger than Arizona. Italy’s distinct shape (the boot) makes it one of the most recognizable countries in the world. Being a peninsula, the majority of the country is surrounded by the crystal blue Mediterranean Sea leading to nearly 8000 km (nearly 5000 miles) of stunning white sand beaches. At 137,847 square miles, Germany is just a little bit smaller than the state of Montana. TOPOGRAPHY Mostly rugged and mountainous; some plains, coastal lowlands CLIMATE The Northern part of Italy has hot summers and cold winter, although the temperature rarely drops below freezing during the daytime. The South enjoys mild winters and long, dry, hot Summers. Mountain areas such as the Alps and the Apennines have long; cold winters long and short, cool summers. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Italy was worth 2194.75 billion US dollars in 2011, according to a report published by the World Bank. With its irregular, elongated shape, Germany provides an excellent example of a recurring sequence of landforms found the world over. A plain dotted with lakes, moors, marshes, and heaths retreats from the sea and reaches inland, where it becomes a landscape of hills crisscrossed by streams, rivers, and valleys. The average January daytime temperature is 3°C (38°F) and in July is 22°C (72°F). Extremes commonly reach -10°C (5°F) in winter and 35°C (95°F) in the summer months. GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT (GDP) NATURAL RESOURCES Italy lack natural resources such as coal and iron. Major exporter of olive oil, tomatoes, and other farm products. 3.158 trillion of International dollars Germany’s Ruhr Valley region is rich in iron ore, but not in natural resources. Must import much of its energy (Large amounts of natural gas from Russia). Skilled work force. Based on the data above and your knowledge of economics, an abundance of natural resources in a country has a big impact on its: a. Geography b. GDP c. Topography d. Climate Gross Domestic Product (GDP) refers to the value of the total amount of goods and service produced in a country in a year. A nation must produce goods and services to support a growing economy. Production- This is the making of goods and services. The four factors of production are the ingredients, or elements, needed for production to occur. Entrepreneurs- These are the people who bring natural resources, labor resources, and capital resources together to produce goods and services. Investments in Human Resources- Workers are needed with the appropriate knowledge, skills and expertise to make goods or provide services. (education and training) Investment in Capital Resources- Machines, factories, and supplies are needed. Investment in Natural Resources- Raw materials are used to make goods. (land, water, forest, minerals, soil, and climate) There is a direct correlation between investment capital (factories, machinery, and technology) and the GDP of a country. There is a relationship between education levels and human capital in terms of their ability to produce income. Goods- A good is something that you can use or consume, like food or CDs or books or a car or clothes. You buy a good with the idea that you will use it, either just once or over and over again. Services- A service is something that someone does for you, like give you a haircut or fix you dinner or even teach you social studies. You don't really get something solid, like a book or a CD, but you do get something that you need.