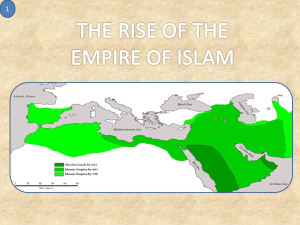
Islam - MrsStriegleswikispace
advertisement

Islam -The word Islam means “submission” signifying obedience to the will of Allah (God). -One who submits is a Muslim. -When Islam started, it quickly attracted followers. -During the first century of this new faith’s existence, it reached far beyond it original homeland of Arabia. -By the eighth century the world of Islam was matched only by Christianity as the greatest religion in the world. The Early Life of Muhammad -Muhammad was born in Arabia around 570 AD. -He was orphaned before he was 6, and he was raised by his uncle who was a successful merchant. -He was employed by a wealthy woman – a widow named Khadija, whom he married in 595 AD. -By age 30, he was a successful merchant living in Mecca, where people recognized many gods and where there were many Jewish and Christian communities. The Quran (Koran) -Muhammad was meditating in a cave one day when he received revelations from Allah stating that there was only one God (Allah) and that Muhammad was God’s prophet. -As Muhammad taught, his followers compiled written versions of his teachings and they became the Quran (Koran), the holy book of Islam. Muhammad’s Migration to Medina -The growing popularity of Muhammad’s preaching brought him into religious conflict with the rulers of Mecca. Monotheism offended the polytheistic Arabs. -Muhammad attacked idolatry and greed. This was seen as dangerous to many merchants, and many of his followers were forced to flee to Ethiopia. -Eventually the pressure mounted until in 622 AD Muhammad fled to the rival trading city of Medina. -This event was known as the hejira (migration) and serves as the official starting date for the Islamic calendar. Muhammad riding into Medina Muhammad in Medina -In Medina, Muhammad found himself at the head of a growing society and organized his followers into a community called the umma (community of the faithful). -Muhammad personally led the umma in daily prayers and in various battles with enemies. -Muhammad organized successful commercial ventures and used the profits to provide relief for widows, orphans and the poor. -Muhammad referred to himself as the final prophet of Allah and accepted earlier prophets such as Abraham, Moses, and Jesus, and held the Torah and Muhammad preaching in Medina the Christian Bible in very high esteem. Establishment of Islam in Mecca -By 630 AD, Muhammad and his followers were so strong that they attacked and conquered Mecca. -Muhammad forced the leaders of Mecca to accept Allah. He destroyed pagan shrines and built mosques (Islamic places of worship). -Muslims kept only one pagan shrine, the Kaaba (cube), and transformed it into a shrine to Allah. The Kaaba contains Abraham’s stone, now called the Black Stone. -Muhammad himself led the first pilgrimage to the Kaaba (Ka’ba), establishing the hajj as an example for all devout Muslims. The Kaaba in Mecca Spiritual Transformation -About 610 AD, Muhammad, age 40, underwent a profound spiritual transformation. -Muhmmad became convinced that there was only one true god (Allah – God), and that recognition of other gods was wicked. -Muhammad experienced visions (revelations) delivered through the archangel Gabriel, a messenger from God. -Without meaning to found a new religion, he told his family and friends of these revelations, and by 620 AD, a minority of Meccans had joined Muhammad’s circle. Spread of Islam Throughout Asia & Africa Spread of Islam -Muhammad and his followers launched a series of military campaigns against other towns and Bedouin clans in Arabia and by the time of his death in 632 AD, much of Arabia was under Muslim control. -After Muhammad’s death his advisors selected one of his closest disciples to serve as caliph (one who comes after), Abu Bakr, to become head of the Islamic state, as well as chief judge and religious and military leader. -Under Abu Bakr’s leadership, Islamic armies then began to carry their message into the worlds beyond Arabia such as Palestine and Mesopotamia. -In the 640s AD, Arab forces conquered Egypt and North Africa. -By 661 AD, they had reached Persia. By 711 AD, they were in Afghanistan and Northern India and by 718 AD, they crossed the Strait of Gibraltar and conquered most of Spain. Spread of Islam Throughout Asia & Africa Disagreements Over Succession -Disagreements over succession led to the emergence of the Shia sect, which offered an alternative to the standard Sunni version of Islam. -The Shia had favored the appointment of Ali (Muhammad’s son-in-law) as successor instead of Abu Bakr. -Eventually Ali was assassinated, and his supporters organized their own Shia (sect). The Five Pillars of Islam -Muhammad’s faith was based on five obligations: 1. Shahadah: Muslims must acknowledge Allah as the only god, and Muhammad as the last prophet. Second Pillar 2. Salat: Muslims must pray to Allah daily while facing Mecca. -Five times a day (dawn, noon, midafternoon, dusk, sunset) -Kneeling in a prone position. -Speaking in Arabic. Third Pillar 3. Muslims must fast during the daylight hours of the month of Ramadan. -Fasting from dawn to sunset. -Eat only after sunset. Fourth Pillar 4. Zakat: Muslims must contribute alms for the relief of the poor. -Generous giving to the poor is expected (2.5%). That is beyond giving to the mosque (place of worship). Fifth Pillar 5. Muslims must try and undertake the hajj (pilgrimage) at least once in their lives. -To Mecca -March seven times around the Kaaba and kiss the Black Stone for forgiveness of sins. Changing Status of Women -Pre-Islamic society was patriarchal, but women enjoyed unusual rights (to inherit property, divorce their husbands, & engage in business). -The Koran enhanced the security of women by outlawing female infanticide and ensuring dowries went directly to brides, not to their husbands. -Women are portrayed not as possessions but honorable individuals equal to men before Allah. -Muhammad’s own kindness and respect to his wives served as an example of this. Male Dominance -However, for the most part the Quran ( and later Sharia law) reinforced male dominance. -Succession was through the male line, and a premium was placed on genealogical purity. To ensure the legitimacy of heirs, the social and sexual lives of women were subject to strict control by men. -To reinforce patriarchy, men could also have up to four wives, women only one husband. Veiling of Women -When Islam moved into Central Asia, it adopted longstanding traditions such as the veiling of women. -Women were forced to veil in public, and could only leave home in the company of servants or family chaperones. -Women were expected to not only cover their faces, but their whole bodies with a burqa to exhibit modesty. -Women were not allowed to pursue traditional men’s occupations, work alongside men, or even (in modern day) to drive cars! Islamic Law: The Sharia -Islamic holy law (the sharia) emerged in the centuries after Muhammad’s death, offering guidance on all aspects of daily life. -It was worked out by legal experts, and was inspired by the Quran. -It offered guidance on marriage and family life, inheritance, slavery, business dealings, politics and crime. -The Sharia has become a way of life with a complete set of social and ethical values. Taboos (Things Forbidden) 1. Alcohol 2. Pork 3. Gambling 4. Graven Images 5. Hunting for Sport Arabesque Art -Since Muhammad insisted that the mosques could use images to decorate with, the Muslims developed beautiful art to decorate their mosques. It has become called Arabesque Art. -Since graven images could be used when printing their Quran, Muslims developed fancy writing called calligraphy. Islamic Vocabulary -Caliph: “one who comes after” Muslim leaders who followed Muhammad. -Arabic: official language of Islam. -Mosque: Islamic place of worship. -Minaret: prayer tower. -Muezzin: Leader of Prayer. -Sultan: Political Ruler. Mosque More Islamic Vocabulary Dome of the Rock: Holy Shrine of Muslims in Jerusalem Imam, Mullah, Ayatollah: All names given to religious leaders depending on what country or sect they are from. Jihad: Religious War; Fighting for Allah. Contributions of the Arabs (Muslims) Grapefruit Foods: Pepper Apricots Lemons Asparagus Limes Bananas Melons Barley Rice Cherries Spinach Dates Strawberries Figs And Even……… A Cup o’ Joe! Coffee Cultural Contributions of the Arabs (Muslims) Guitar Numerals Pajamas Coins Pottery More Cultural Contributions Medicine Astronomy Clock Alphabet Ink Cosmetics More Cultural Contributions Dice Tulips Bowling Chess Windmills Soap More Contributions Compass Carpet Macrame Vocabulary List for Teacher Alms Muezzin Islam Umma Shia Infanticide Sultan Allah Mosque Sunni Sharia Dome of the Rock Muslim Kaaba Ali Genealogy Imam Mecca Black Stone Shahadah Veil Mullah Quran Hajj Salat Burqa Ayatollah Revelation Pilgrimage Ramadan Taboos Jihad Prophet Gabriel Sawm Arabesque Medina Caliph Fast Calligraphy Hejira Abu Bakr Zakat Minaret