MATTER
advertisement

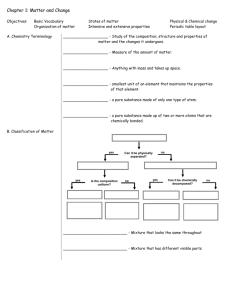
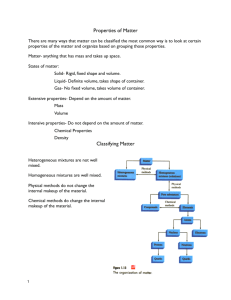
MATTER Chemistry The science of matter and all the changes that it undergoes Matter Anything that has mass and takes up space Is there anything that is not matter?????? Definitions from Matter Tree Mixture – 2 or more materials NOT chemically combined Mixtures Heterogeneous – mixtures made up of substances that are visibly different Ex: oil and water Ex: granite Homogeneous – mixtures consisting of one phase Each piece has the same properties Ex: air, Kool-Aid Another name for a homogeneous mixture is SOLUTION Substance Always has the same composition Element – substance composed of only one kind of atom Ex: S, Ca, O, He, N Compound – Substances composed of 2 or more elements chemically combined ex: Water, salt, hydrochloric acid Physical Properties Properties of a substance that can be observed WITHOUT changing the substance Ex: Length, color, temp. Two types of Physical Properties Intensive – DOES NOT depend on the size of the sample Ex: color, malleability, ductility, conductivity, MP, BP, density Texture – how a substance feels; grainy, smooth, soft State – solid, liquid or gas Luster – how shiny an object is Conductivity – ability to conduct heat or electricity Hardness – ability to scratch another object Density – mass per volume Ductility – can be drawn into a wire Physical Properties Extensive – DOES depend on the size of the sample Ex: mass, length, volume Practice – red heavy 10 ft long shiny soft colorless BP of 100 oC Chemical Properties Describes the behavior of a substance undergoing a chemical change Ex: Cl reacts with Na NaCl Ex: Fe + O2 Fe2O3 (rust) Physical Changes Change that DOES NOT result in a new substance being formed Ex: Cutting, dissolving sugar in H2O, phase changes Chemical Changes Changes that produce a new substance Note: a change in color, change in energy and if a gas is given off are three ways to tell if a chemical change has occurred Ex: Rust, CuCl2 + Al foil