Session Code: OFC402
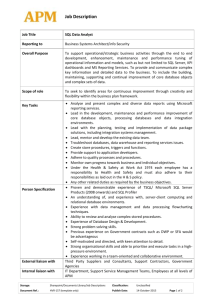
SharePoint Ports, Protocols and
Proxies
An end-to-end overview of SharePoint inter-server
communication
Martin Kearn
Martin.Kearn@Microsoft.com
Senior Consultant
Microsoft UK (Microsoft Consulting Services)
2
Agenda
Why is understanding farm communication
important?
Types of farm communication
Inter-Server communication
Client-Server communication
Extra-Server communication
Tools
References
3
Who is this session for?
SharePoint Architects that are interested in how
servers in the farm communicate
Main target audience since this is in the ‘Office
System’ track
Firewall & network architects that are working
on SharePoint projects
Level 400 (‘Expert’ level content)
I’m going to assume a certain familiarity with
SharePoint terminology and concepts
4
What is a ‘farm’?
A Collection of SharePoint 2007 and SQL
(2005/2008) servers bound together by a single
configuration database
Server Roles
Web Front End (WFE)
Windows SharePoint Services
Web Application Service
Application
Office SharePoint Server Search
Service (Index or Query mode)
Document Conversion Launcher Service
Document Conversion Load Balancer
Service
Excel Calculation Services
5
SQL
Why care about farm communications?
‘Secured’ farms where different parts may be on
different network segments
Firewall guys need to know what traffic they need to
allow/block
Extranet/Internet Farms
Debugging network issues / WAN
Windows Server 2008 is locked by default!
6
Geographically Distributed Farms
Using ‘stretched farms’
Many customers have LAN-like WANs
It is possible to split farms across data centres for DR purposes
Supported in very specific scenarios
WFE has less than 1 millisecond(ms) latency to DB
Typically WFE has less than 10 miles (16 kilometres) to DB, however up to 100
miles has been achieved
All servers on the same network segment
Servers cannot cross time zones
Think long and hard about your network traffic especially to
SQL!
Resources
Plan for availability (Office SharePoint Server):
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc748824.aspx
Optimizing Office SharePoint Server for WAN environments:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc263099.aspx
7
Transport Protocols
3 key transport protocols used for SharePoint
SQL Server Tabular Data Stream (TDS)
Most farm traffic is SharePoint servers talking to
SQL
Default = TCP:443, Named Instances = TCP:0
(random)
Server Message Block (SMB)
Used extensively in SharePoint Index / Query
Servers
TCP:445
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
8
Clients or Web Services
TCP:80 (or whichever port the web application uses)
HTTP Web Services in Web Applications
All web applications have a common set of web
services on all WFEs
Web Services in Web Applications
Dynamic path of
http://<server>:<port>/<sitestructure>/_vti_bin
Always maps to:
C:\Program Files\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web
Server Extensions\12\isapi
This path includes
9
Webs.asmx
Lists.asmx
Search.asmx
etc
HTTP Web Services in SSP
SSP adds several web services to all WFEs
Dedicated IIS Site called ‘Office SharePoint Web
Services’ on all WFE servers
TCP:56737 / TCP:56738 (for SSL)
Use STSADM to change port (for server lock-down)
STSADM.exe –o setsspport
Separate IIS ‘Application’ for each SSP in farm
Always maps to:
C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office
Servers\12.0\WebServices\Shared
This includes web services for Search, Excel ,BDC etc
10
Types of Communication
11
Inter-Server Communication
Traffic between servers in the farm
SharePoint servers talking to other SharePoint
servers or SQL
Main operations
To/from SQL
Search Propagation and Crawling
Web Service Requests
32 Protocols Used
12
Inter
Server
Inter-Server Communication
13
Inter
Server
SharePoint Protocol Documents
Where are they and how are they organised
The resource for planning farm comms
All available online as PDFs
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc339473.aspx
Document types
Front-end
SharePoint only at one end, intended for Interoperability
Extra-Farm
Client-server
Back-end
SharePoint at both ends
Intra-farm
14
Inter
Server
Intra-Server Core Platform
Communication
Protocols used for core platform functionality
Functionality Area
When
SharePoint Protocols
Purpose
[MS-SSPSJ]
SSP Schedule Jobs
Configuration
Used when Scheduled
tasks are executed or
configuration changes
are made to the
SharePoint farm
[MS-SSPSOS]
SQL Configuration
[MS-WSSCFGD]
WSS Configuration
[MS-WSSCADM]
Content DB admin. Recycle bin,
quota etc
[MS-WSSDLIM]
Document and List item
management
[MS-WSSCCSP]
Provisioning of artefacts (features,
schema items such as list schemas,
etc)
[MS-WSSEUX]
User experience (browsing)
[MS-MOSSUAN]
Usage analysis
[MS-WSPROG]
Events, webparts and workflow
[MS-WSSDM]
Data Migration
Lists and Libraries
15
Used in the day-to-day
running of the server
farm, and configuration
changes.
First look at a SharePoint
protocol specification document
[MS-WSSCFGD]
Martin Kearn
Senior Consultant
Microsoft UK
16
Inter
Server
Intra-Server MOSS Extended
Communication (1)
Protocols used by the MOSS-specific features
Functionality Area
When
Excel Calculation
Used for client access
to workbooks, system
access to workbooks
and web-service access
InfoPath Forms
Services
Used in communication
between InfoPath
servers (WFE’s) and
SQL during processing
of Forms
User Profile Services
17
Used when user
profiles are accessed,
modified,
synchronized, changed,
etc
Inter
Server
SharePoint Protocols
Purpose
[MS-EXSPWS]
All Excel Server communication
(Except External Data Access from
workbooks)
[MS-ASPSS]
ASP.net session state
communication
[MS-WSSCFGD]
WSS Configuration
[MS-UPSAUD]
Create, Edit, Delete, maintain
Audiences
[MS-UPSCHNG]
User profile change events
[MS-UPSGRAD]
User profile Service Push
[MS-UPSIMP]
User profile imports
[MS-UPSPROF]
Create, read, update and delete
operations on user information
[MS-UPSSYNC]
Synchronization
Intra-Server MOSS Extended
Communication (2)
Protocols used by the MOSS-specific features
Functionality Area
When
Business Data
Catalog (BDC)
Used when BDC or
Single Sign-on
applications are used,
modified, configured
Content
Management and
Conversion
Used when Content
Migration is set up and
initiated, usually as
Content Deployment
paths and Jobs
Used when File
Conversion services are
set up to convert file
types, eg to HTML.
18
Inter
Server
SharePoint Protocols
Purpose
[MS-SSOSP]
Single Sign On
[MS-BDCSP]
BDC applications (excludes access to
external data)
[MS-DOCTRANS]
File Transformation/Conversion
Services
[MS-CDEPLOY]
Administration and import of
content previously exported using
Content Migration
Search Specifics
Inter
Server
Search Activities
Search Administration
Calls to Office SharePoint Web Services on TCP:56737 & TCP:56738 (SSL)
[MS-GLOADWS], [MS-ADMWS] and [MS-SQLPADM]
Search Crawling
Actual crawling is extra-server, but during crawls there is heavy traffic between
Index and SQL
[MS-SQLPGAT], and [MS-SQLPQ]
Search Index Propagation
Continual copying the index from the Index Server to the Query Server
(C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office Servers\12.0\Data\Office Server\Applications)
Occurs over SMB
[MS-CIPROP]
Search Query Execution
Passing search queries from the WFE Servers to the Query Servers
Occurs over SMB, which is a major design factor for extranet topologies!
[MS-SQP]
19
Search Specifics
Inter
Server
Dedicated WFE for Crawling
It is possible to configure a dedicated WFE for crawling
http://blogs.msdn.com/joelo/archive/2007/02/06/use-adedicated-web-front-end-for-crawling.aspx
This can be on the index server itself or a dedicated server
Advantages
Different network segment, thus reducing firewall holes
Reduced performance impact on real WFEs
If on Index server, no network traffic (reduce overhead on
firewall)
Diss-Advantages
Requires a dedicated server
If on Index server, additional load on Index server
20
Search Specifics
Inter
Server
Index and Query on same Server
The ‘Office SharePoint Server Search Service’ has two
modes of operation: Index & Query
Both roles can run on a single server
Advantages
No propagation traffic
Reduces holes in firewall
Disadvantages
No fault tolerance for query (cannot have additional query
servers in this mode)
Additional load on Index
SMB required to server for querying
21
Search Protocols
22
Inter
Server
Fiddler
HTTP Web Debugging Software
Simple and easy to use
Inserts itself as a local proxy in IE
127.0.0.1:8888
All HTTP traffic goes via Fiddler (Not SQL or SMB)
Clients that do not follow the Winlnet API will
bypass fiddler
This includes .net. To ensure .net goes via Fiddler
set the proxy as follows in web.config
<system.net>
<defaultProxy>
<proxy proxyaddress="http://127.0.0.1:8888"
bypassonlocal="False" autoDetect="False" />
</defaultProxy>
</system.net>
24
Wireshark
Physical-level packet sniffer
Powerful but complex
Physical packet sniffer
Traps all traffic, including HTTP, TDS for SQL and
SMB
Check your
network
policy
25
SQL Profiler
Trace SQL queries
Useful for seeing the queries
coming into SQL
Shows user accounts being used
Can filter on specific events and objects
26
Inter
Server
Using Fiddler and WireShark to
capture Search Communications
Martin Kearn
Senior Consultant
Microsoft UK
27
Extra-Server Communication
Extra
Server
Traffic between servers in the farm and external
servers
Two main types of extra-server traffic
Infrastructure:
DNS: TCP/UDP:53
Active Directory Authentication
LDAP: Used to query AD for list of users
SharePoint
Indexing
BDC
Excel Data Connections
InfoPath Forms Services
28
Extra-Server Communication
29
Extra
Server
Extra
Server
Extra-Server MOSS Extended
Communication
Protocols used for MOSS functionality
Functionality Area
When
Protocols
Purpose
[MS-SMB]
Crawling file shares
Search Index Content
Crawling
Used when Search
Index Crawls are
initiated, and external
Content Sources have
been defined.
[MS-TDS]
Crawling SharePoint sources
HTTP
Crawling web –based sources
Business Data
Catalog (BDC)
When a BDC Catalog
exists that accesses
external data
HTTP
Accessing or crawling Web Service
based business data systems
ODBC
Accessing or crawling SQL based
business data systems
[MS-SQL]
When accessing SQL-based data
External Data Access
When an Excel Services
Workbook or InfoPath
Forms Services form
accesses external
content
ODBC
Accessing or crawling SQL based
data
HTTP
Accessing or crawling Web Service
based data
30
Client-Server Communication
Client
Server
Traffic between servers in the farm and clients
Any integration between the client and servers,
this includes:
General browsing
Synchronisation of lists in Outlook / Groove
Viewing or editing files
Using SharePoint Designer
Almost all client-server traffic occurs over HTTP
Special additions for MS Office
31
Client-Server with MS Office
MS Office gets special consideration
Windows SharePoint Headers Protocol
Authenticating client connections
Communicating error conditions
Sending complex data (Metadata Updates, SPD etc)
Interacting with IRM
Interacting with anti-virus
Interacting with customer crawlers (Protocol Handlers)
MetaWeblog Extensions
Allows retrieval and publishing of blogging content
Slide Library Web Service
Allows PowerPoint to interact with Slide Libraries
RSS Feeds in Outlook
32
Client
Server
Client
Server
Using WireShark to capture
Office to WFE Communication
Martin Kearn
Senior Consultant
Microsoft UK
33
ActiveX Controls
Client
Server
SharePoint makes use of several ActiveX
controls
SharePoint Datasheet Editing Control
Multiple Document Upload Control
Send To Location Control
Document Opener/Launcher Controls
General Documents, Pictures, PowerPoint, InfoPath,
Excel, Access
Presence Control
Personal Sites
List Synchronisation launcher for Outlook
34
Client-Server Communication
35
Client
Server
Client-Server MOSS Extended Communication (1)
Client
Server
Protocols used for MOSS functionality
Functionality Area
When
Excel Services
When custom clients
access Excel Services,
and when Excel
Workbooks are added
to Excel Services
InfoPath Forms
Services
Search Services
36
When a Form is
published to
SharePoint with Web
Access enabled
When Users or custom
applications execute
searches, or legacy or
external systems index
SharePoint
Protocols
Purpose
[MS-ESP]
Access to workbooks stored in Excel
Services
[MS-ESURL]
Resolve the correct URL for
published workbooks
[MS-FSDAP]
Request a list of problems when
publishing a form template
[MS-FSFDP]
Detect if InfoPath Forms Services is
present
[MS-SEARCH]
Clients can issue Search Queries to
the server
[MS-SITED3S]
Site Index creation for Legacy
systems (Support for SharePoint
2003 indexing)
[MS-SITEDATS]
Support site index creation
[MS-SPSCRWL]
Read SSP/Site search items
Client-Server MOSS Extended Communication (2)
Client
Server
Protocols used for MOSS functionality
Functionality Area
When
Protocols
Purpose
[MS-BDCDP]
Retrieve Entity Lists
Business Data
Catalog
Used in ordinary
operation and
administration of the
BDC, and for external
client access
[MS-BDCMP]
Retrieve Catalog Information
[MS-SSP]
Single Sign-on information
[MS-SPLCHK]
Spell Check
[MS-VERSS]
Web service access of file versions
[MS-PUBWS]
Publishing and multilingual
translation
[MS-OFFICIALFILE]
Official File Submission
[MS-COPYS]
Copying of files
Content
Management
37
During Content
Publishing, Editing,
Authoring and
Movement
WFE Server Communication
38
SQL Server Communication
39
Application Server(s) Communication
40
Using Windows & SQL 2008
Additional configuration required
Windows 2008 is locked down by default,
therefore the following changes are required
On the SQL Server set an Inbound Rule to allow
TCP:1433 in Windows Firewall
Server Manager > Configuration > Windows Firewall with
Advanced Security
SQL 2008 does not allow incoming connection
by default
Use ‘SQL Server Configuration Manager’ to enable
TCP/IP
SQL Server Network Configuration > Protocols for
MSSQLSERVER
41
Configuring Windows 2008 &
SQL 2008 for SharePoint
Martin Kearn
Senior Consultant
Microsoft UK
42
Resources
Fiddler: http://www.fiddlertool.com
WireShark: http://www.wireshark.org
Office protocols documents: http://msdn.microsoft.com/enus/library/cc307432.aspx
SharePoint protocol documents:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc339473.aspx
TechNet Articles
Plan security hardening for extranet environments:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc262834.aspx
Plan for secure communication within a server farm:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc263077.aspx
Plan security hardening for server roles within a server farm:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc262849.aspx
Blogs
43
Watch out for an announcement soon around MCS SharePoint Team Blog
http://blogs.msdn.com/martinkearn/default.aspx
Key Takeaways
The documentation is out there, you just have
to find it
Protocol Documents
TechNet / MSDN articles
Blogs
Think about your network when designing farm
architecture
Make use of the tools available when problem
solving
44
45
Resources for IT Professionals
www.microsoft.com/teched
Tech·Talks
Live Simulcasts
Tech·Ed Bloggers
Virtual Labs
http://microsoft.com/technet
Evaluation licenses, pre-released
products, and MORE!
© 2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista and other product names are or may be registered trademarks and/or trademarks in the U.S. and/or other countries.
The information herein is for informational purposes only and represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation as of the date of this presentation. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market conditions, it should
not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information provided after the date of this presentation. MICROSOFT MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS,
IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, AS TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PRESENTATION.
47