COMPUTER SYSTEM
advertisement

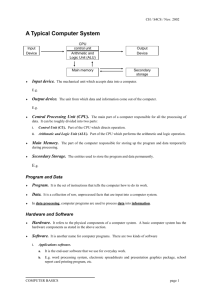
Overview of a computer system Introduction This Unit explores the purpose of computer systems, their structure and provides a technical description of the components. Overview of a computer system Learning Objectives After studying this Unit, you will be able to: 1. Describe the major functions of a general-purpose computer system 2. Explain the functions of the major hardware components of a computer system Overview of a computer system After studying this Session, you will be able: 1. Explain the difference between a computer and a computer system 2. Describe the various components of a computer 3. List the different devices that are typically attached to a computer to allow the user to input data and view output 4. Illustrate the components of the Central Processing Unit (CPU) 5. Explain the function of the components of the Central Processing Unit Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer When you look at a desktop computer, it comprises: A monitor, Keyboard, Mouse, and A vertical or horizontal box called a system unit. It is acceptable to refer to all of these components as a computer. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer Technically however, the system unit houses the actual ‘computer’ Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer Computer: An electronic programmable machine which executes (carries out) or responds to a sequence of program instructions Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer A computer system is a collective term for a computer (housed within the system unit), as well as these other components that are attached to it to allow the user to input data and view output using different devices. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer Some of these components include a monitor, keyboard, mouse, printer, disk drives, scanners, microphones, and speakers, which are also referred to as peripherals. The peripherals work together to help the user accomplish a given task effectively. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer The peripheral devices mentioned above are collectively called hardware devices, since they can be physically attached to the computer. Hardware: The physical components that can be seen and touched. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer computer systems also include software, or programs that are integral in the functioning of some of these peripheral devices and are necessary to make the computer operate. Software: A set of instruction (programs) which tells the computer what to do. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer Every computer system requires an operating system. An operating system is a program that establishes communications with the various peripherals and acts as a bridge to other application (specific) software programs. Overview of a computer system Components of a Computer An operating system is like the command centre of the ship. It makes all of the decisions about how the computer will function and work with others. Overview of a computer system Functions of the major hardware components of a computer system The major components of a computer system include input and output devices as well the important processor or Central Processing Unit (CPU). Overview of a computer system Functions of the major hardware components of a computer system The CPU is the brain of a computer system and is responsible for processing the data that is input from a peripheral device and output to another peripheral device. Overview of a computer system Functions of the major hardware components of a computer system The major components of a computer system include input and output devices as well the important processor or central processing unit (CPU) Overview of a computer system The CPU comprises a set of electronic circuits kept within the system unit. The CPU is the brain of a computer system and is responsible for processing the data that is input from a peripheral device and output to another peripheral device Overview of a computer system The sketch above illustrates the major components of a computer system. Overview of a computer system The Figure illustrates the components of the CPU along with the other components of a system unit attached to an input and output device. Overview of a computer system The Central Processing Unit (CPU), also known as the processor or microprocessor has components that control the operating system and other software installed on the computer. The CPU also sends commands and data to the peripherals attached to the computer, such as the monitor or printer. Overview of a computer system Overview of a computer system Now let’s look into the operation of the CPU. All computer systems have a CPU which comprises: 1. a Control Unit (CU) and 2. an Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU). Overview of a computer system The Control Unit (CU) The control unit is similar to an efficient manager or traffic cop. It is responsible for directing other parts of the computer system in order to carry out the instructions for the task required. The control unit (CU) must interact with the arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) and memory to complete its tasks. Overview of a computer system The Control Unit (CU) The CU interprets the instruction. The CU then sends commands to other components to gather data that may be needed to complete the instruction, even if it involves a transfer of data from other components and devices. The CU than determines where to send the result. This may include activating the printer, showing the result on the monitor or playing a sound on the speakers. Overview of a computer system Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) is the part of the CPU which performs all arithmetic and logic operations, this involves arithmetic calculations including addition, subtraction and multiplication. Overview of a computer system Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) As calculations are required, the Control Unit sends them to be performed in the ALU which sends the result back to the Control Unit. It also performs logic operations such as comparisons of numbers or letters to test for, such as equal-to (=), less-than (<), greater- than (>) and other combinations, such as less-than or equal-to (<=).