sex chromosome
advertisement

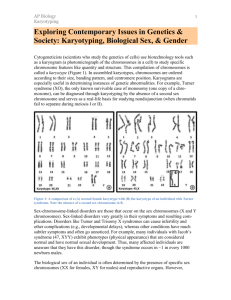
Heredity Chapter 14 Linked Genes • Genes may occur in patterns if two loci are on the same chromosome • During crossing over, these loci are so close they typically will remain together • Ex: blonde hair, blue eyes Chromosome Mapping • The farther apart a gene is on a chromosome, the more likely they will cross over • Mapping a chromosome is a diagram of the loci the chromosome codes for Karyotype • A picture of chromosomes arranged in size order • Used to determine the sex of an individual and to see if there are any chromosomal disorders Karyotype • Trisomy karyotype Karyotype • Monosomy karyotype http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/karyotyping/karyotyping.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/human_bio/activities/karyotyping/karyotyping2.html Sex Chromosomes/Autosomes • Sex chromosomes • • Contain genes that determine the sex of an individual (X & Y chromosomes) Autosomes • Remaining chromosomes that do not determine sex of an individual (chromosomes 1-22) Sex Determination • In mammals, egg cells only contain an X chromosome and sperm can either have an X or Y chromosome • If the new baby cell has XX girl • If the new baby cell has XY boy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMWxuF9YW38 Gene Location • Sex-Linked genes • Characteristics that typically only show up in a certain sex of the organism • • Ex: color blindness in males Traits that are on one sex chromosome and not the other https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Aaivktz8G0 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Iz8xZD9LcI Sex Linked Genes • Colorblindness • Full color vision is dominant over colorblindness • X = color vision, XC = colorblindness Colorblind male, color vision female (homozygous) Color vision male, color vision female (heterozygous) Sex Linked Genes • Eye Color in Drosophila • • Red eyes are dominant over white XR = red eyes , Xr = white eyes Red eyed male, white eyed female White eyed male, red eyed female (heterozygous) X-linked Traits • X-Linked traits are usually recessive • Males inherit X from mom which holds a huge amount of base pairs • If there is no other X to mask the trait, then the individual shows the X-linked trait • Individuals that have one copy of a recessive trait are known as carriers • Carriers do not express trait, but can pass to offspring Sex-Influenced Traits • Males and females can show different phenotypes even if genotype is the same • Ex: pattern baldness • % higher in men due to higher levels of testosterone Pedigrees • Diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over generations • Male = • Female = Pedigrees • Horizontal line between a male and female means they are married or have offspring • Vertical line between a male and female indicates offspring https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wuk0W10EveU Pedigree http://www.ualberta.ca/~pletendr/tm-modules/genetics/70gen-hemophil.html Single-Allele Traits • Some traits are controlled by just one single dominant allele • Ex: Huntington's disease • If individual has one allele for this disease, they have it • There are no carriers Mutations • Change in a sequence of a gene • Germ-cell mutation (gamete/sex cell) • • Change in the individual’s gametes • May be passed onto offspring Somatic-cell mutation • Change in the individual’s body cells and can affect the person • Ex: skin cancer Chromosomal Mutation • Nondisjunction • When a chromosome fails to split during meiosis (anaphase) and sex cell chromosomes are uneven in number Karyotype • Nondisjunction mutations in autosomes Karyotype • Nondisjunction mutations in sex chromosomes Kleinfelter’s syndrome