Economics of Food Markets
advertisement

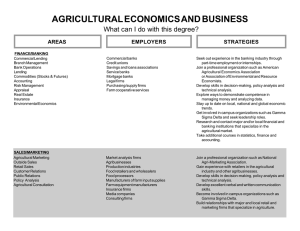
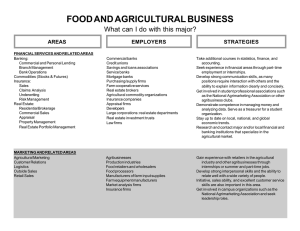
Economics of Food Markets Course revision Resources • • • • • • • • Course outline (revised Jan 2007) Course website Lecture summaries on the web Powerpoint slides Lecture – key questions Tutorial class questions Essay and project titles Readings Motivation 1. Agricultural policy objectives 2. EU agricultural policy 3. Agriculture and environment 4. Economics of price support policies 5. World market effects of ag policies 6. Doha Round negotiations on ag liberalisation 7. Market power in the food chain 8. Economics of food safety 1. Agricultural policy objectives • The farm problem – Definition/measurement of farm incomes – Explanations for the farm problem • Multifunctionality – Redefinition of EU farm policy objectives – Conditions for multifunctionality • Jointness, public goods – Is it a justification for supporting agriculture? • Measurement of agricultural support – Producer Support Estimate 2. EU agricultural policy • Features of the CAP – Pillar 1, Pillar 2 • The milestones of reform – MacSharry, Agenda 2000, Mid Term Review – ‘health check’ • Pressures for reform – budget, objectives, external • Decoupling – single farm payment • Rural development policy reform 3. Agriculture and environment • The market failure arguments for intervention • Economic approaches to controlling negative externalities (pollution) – Market-based approaches vs regulation – Nitrates, greenhouse gas emissions • Economic approaches to promoting positive externalities – Operation of the REPS scheme 4. Economics of price control policies • Graphical analysis – Closed, small open and large open economy situations – Price and quantity effects, welfare effects • Instruments – Subsidies, tariffs, quotas, export subsidies etc. • Measurement of transfer efficiency • Assessing cost of EU agricultural policy 5. World market effects of ag support • Graphical analysis – Impacts on level and stability of world market prices • Uruguay Round Agreement – Disciplines imposed (the three pillars) – Impact on protection and trade 6. Doha Round and agricultural trade liberalisation • Progress and issues in the Doha Round – Market access, domestic support, export competition – Positions of the main players • Measuring trade liberalisation effects – Review findings of major studies, account for differences • Developing country perspectives – Heterogeneous impacts due to differences in trade status, access to preferences, competitiveness – Special and differential treatment in WTO rules 7. Market power in the food chain • Evidence on structural change • Measurement and existence of market power – Marketing margins, SCP studies, NIEO studies, price transmission studies • Abuse and control of market power – Supermarkets, suppliers and customers • UK investigations, Groceries Order – Processing plants and farmers (Sheehy) 8. Economics of food safety • The market failure rationale for intervention • Efficient regulation – Public and private regulatory approaches – Measuring costs and benefits • SPS measures as a non-tariff barrier to trade – Structure of the SPS Agreement – Operation of the SPS Agreement – Developing country concerns Structure of examination • Eight multi-part questions, with marks allocated. • Answer four • Answers marked on understanding, breadth, depth, analysis