Lecture 1: Introduction into data communication
advertisement

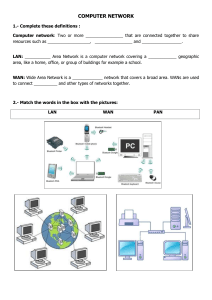
Chapter 1. Introduction 1. DATA COMMUNICATIONS • Telecommunication: communication at a distance • Data: information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the parties creating and using the data • Data communications: exchange of data between two users / devices via some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable – – – – Delivery Accuracy Timeliness Jitter Five components of data communication • • • • • Message Sender Receiver Medium for transmission Protocol: set of (explicit and implicit) rules Data Representation • • • • • Text: ASCII, Unicode, … Numbers Images Audio Video Data flow (simplex, half- and full-duplex) • Communication can be two-way by nature 2. NETWORKS • Network: a set of devices (often referred to as users or nodes) connected by communication links – A node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network • Performance of network – – – – Throughput Delay Reliability (Accuracy and freq. of failures) Security Physical Structure of Network • Types of connections – Point-to-point, multi-point • Types of topologies – Mesh, star, bus, ring • Covering areas – LAN, MAN, WAN Types of connections Categories of Topology Ring Mesh Star Bus Hybrid Topology • Star + Bus Covering Area LAN: Local Area Network WAN: Wide Area Network MAN: Metropolitan Area Network – between LAN and WAN, e.g., Campus networks Inter-network • A heterogeneous network made of four WANs and two LANs 3. THE INTERNET • Impact of “the Internet” – Revolutionized many aspects of our daily lives: business, leisure, communications, … • History – ARPANET Project (1960s) led by Advanced Research Project Agency (ARPA) in the Dept. of Defense (DoD) to establish reliable networks – Evolves in 1970s and 1980s – TCP/IP Hierarchical organization of the Internet 4. PROTOCOLS AND STANDARDS • Protocols: a set of rules for communications – Syntax – format – Semantics – meaning / interpretation – Timing – when data should be sent, and how fast they can be sent • Standards – Essential in guaranteeing interoperability, and in creating and maintaining an open and competitive market Standards • Two types – De facto: not formally approved, but everyone accepts • MS Word (except Korea), MS Excel – De jure: formally approved • WIPI (middleware platform in Korea) • Standards Organizations – ISO, ITU-T, CCITT, ANSI, IEEE, EIA, … • Internet Standards – Internet Draft, Request for Comment (RFC) Homework • Exercise in Chap. 1 – 16 – 17 – 22 – 25