Chapter 3 - Shannon Deets Counseling
advertisement

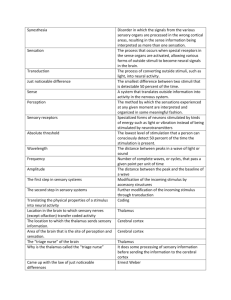
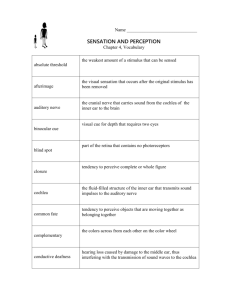
Chapter 3 Powerpoint Questions Q1 Transduction A1 • The process of converting outside stimuli, such as light, into neural activity. Q2 • Frequency A2 • Number of complete waves, or cycles, that pass a given point per unit of time Q3 • Three properties of sound waves A3 • Wavelength, amplitude, purity Q4 • Photons A4 • Tiny particle packets of waves Q5 • Synesthesia A5 • Disorder in which the signals from the various sensory organs are processed in the wrong cortical areas, resulting in the sense information being interpreted as more than one sensation. Q6 • Sound A6 • Vibrations of the air molecules around us Q7 • Who first proposed that light is actually tiny packets of waves A7 • Albert Einstein Q8 • Three psychological principles of light A8 • Brightness; color; saturation Q9 • Somatic pain A9 • Detected by receptors in the skin, muscles, tendons, and joints Q10 • Subliminal perception and advertising A10 • We do perceive sensory information subliminally but it does not influence our voluntary actions such as purchasing objects Q11 • Saccadic movement A11 • The small movements made by the eyes that are generally not consciously noticed by individuals but that keep us from becoming adapted to visual sensory input Q12 • Sensation A12 • The process that occurs when special receptors in the sense organs are activated, allowing various forms of outside stimuli to become neural signals in the brain. Q13 • Opponent-process theory A13 • Theory of color vision that proposes visual neurons are stimulated by light of one color and inhibited by light of another color Q14 • Somatic pain is a signal of A14 • The body being damaged or about to be damaged Q15 • The location to which the thalamus sends sensory information. A15 • Cerebral cortex Q16 • Rods A16 • Visual sensory receptors found at the back of the retina, responsible for non-color sensitivity to low levels of light Q17 • Skin senses A17 • The sensation of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain. Q18 • Visceral pain A18 • Pain detected by receptors in the organs Q19 • Cones A19 • Visual sensory receptors found at the back of the retina, responsible for color vision and sharpness of vision Q20 • Hearing damage caused by a damaged eardrum or damage to the bones of the middle ear A20 • Conduction hearing impairment Q21 • Sensory adaptation A21 • Tendency of sensory receptor cells to become less responsive to a stimulus that is unchanging Q22 • Color blindness A22 • Vision that is color deficient due to having either no cones or cones that do not work properly Q23 • The pathway that visual information takes to the occipital lobe A23 • Lateral geniculate nucleus Q24 • Key point to remember about habituation A24 • In habituation the sensory receptors are still responding to stimulation but the lower centers of the brain (cerebellum) are not sending the signals from those receptors to the cortex. Q25 • Light sensitive area at the back of the eye containing three layers including the ganglion cells, bipolar cells, and photoreceptors A25 • retina Q26 • Just noticeable difference A26 • The smallest difference between two stimuli that is detectable 50 percent of the time. Q27 • Small hole in the Iris A27 • Pupil Q28 • Neurotransmitter that gives umami it’s brothy tastes A28 • Glutamate Q29 • The image on the pupil is focused and manipulated by this A29 • The Iris Q30 • the change in the thickness of the lens as the eye focuses on objects that are far away A30 • Visual accommodation Q31 • The area of the retina that contains the greatest density of photoreceptors A31 • fovea Q32 • A clear structure behind the Iris that is suspended by muscles and changes shape to bring objects into focus A32 • Lens Q33 • Kinesthetic sense A33 • Sense of the location of body parts in relation to the ground and each other Q34 • Depth perception A34 • The ability to perceive the world in three dimensions Q35 • Monocular cues A35 • Cues for perceiving depth based on one eye only Q36 • Contiguity A36 • The tendency to perceive two things that happen close together in time as being related Q37 • Brightness A37 • Determined by amplitude of the wave Q38 • Afterimages A38 • Images that occur when a visual sensation persists for a brief time even after the original stimulus is removed Q39 • Continuity A39 • The tendency to perceive things as simply as possible with a continuous pattern rather than with a complex broken-up pattern Q40 • Color (hue) A40 • Determined by length of wave Q41 • Trichromatic theory A41 • Theory of color vision that proposes three types of cones: red, blue, and green Q42 • Sense A42 • A system that translates outside information into activity in the nervous system. Q43 • What color do you get when you combine blue, red, and green light A43 • White light Q44 • Pacinian corpuscles A44 • Skin receptors that respond to pressure Q45 • Sensory receptors A45 • Specialized forms of neurons stimulated by kinds of energy such as light or vibration instead of being stimulated by neurotransmitters Q46 • Closure A46 • The tendency to complete figures that are incomplete Q47 • Perception A47 • The method by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion. Q48 • Wavelength A48 • The distance between peaks in a wave of light or sound Q49 • The round muscle of the eye A49 • Iris Q50 • Absolute threshold A50 • The lowest level of stimulation that a person can consciously detect 50 percent of the time the stimulation is present. Q51 • Similarity A51 • The tendency to perceive things that look similar to each other as being part of the same group Q52 • What is the visible spectrum A52 • The narrow band of light between 400nm and 700nm that is visible to the human eye Q53 • Five basic tastes A53 • Sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami Q54 • Proximity A54 • The tendency to perceive objects that are close to each other as part of the same grouping Q55 • Saturation A55 • The purity of the color people perceive with light. Light with only one wavelength would be highly saturated in that specific color Q56 • Translating the physical properties of a stimulus into neural activity A56 • Coding Q57 • Dark adaptation A57 • The recovery of the eye’s sensitivity to visual stimuli in darkness after exposure to bright lights Q58 • Location in the brain to which sensory nerves (except olfaction) transfer coded activity A58 • Thalamus Q59 • What kind of stimuli is often perceived of subliminally A59 • Stimuli that produces fear Q60 • A hearing impairment where the problem lies in the inner ear or the auditory pathways and cortical areas of the brain A60 • Nerve hearing impairment Q61 • Reversible figures A61 • Visual illusions in which the figure and ground can be reversed Q62 • Linear perspective A62 • The tendency for parallel lines to appear to converge on each other Q63 • Binocular cues A63 • Cues for perceiving depth based on both eyes Q64 • A type of interneuron that has a single dendrite at one end and a single axon at the other A64 • Bipolar cell Q65 • Overlap A65 • The assumption that an object appears to be blocking part of another object is in front of the second object and closer to the viewer Q66 • Figure-ground A66 • The tendency to perceive objects, or figures, as existing on a background Q67 • Brightness constancy A67 • The tendency to perceive the apparent brightness of an object as the same even when the light conditions change Q68 • Taste buds line the walls of the A68 • Papillae Q69 • The two sources of light are A69 • 1) Directly from the source, 2) indirectly as reflected off of a surface Q70 • Optic chiasm A70 • The crossover point of the visual information from the eyes to the brain Q71 • Somesthetic senses A71 • The body senses consisting of the skin senses, the kinesthetic sense, and the vestibular senses Q72 • Light adaptation A72 • The recovery of the eye’s sensitivity to visual stimuli in light after exposure to darkness Q73 • Shape constancy A73 • The tendency to interpret the shape of an object as being constant, even when its shape changes on the retina Q74 • The axons of the retinal ganglion A74 • Optic nerve Q75 • The second step in sensory systems A75 • Further modification of the incoming stimulus through transduction Q76 • Light from the left visual field falls on the right side of each retina and goes directly to the A76 • Right visual cortex Q77 • Auditory canal A77 • Short tunnel that runs from the pinna to the eardrum Q78 • Light from the right visual filed falls on the left side of each retinal and goes directly to the A78 • Left visual cortex Q79 • Where in the brain is fear based stimuli perceived A79 • Amygdala Q80 • Light from the right visual field falls on the ( ) side of each retina A80 • Left Q81 • Bumps on the tongue A81 • Papillae Q82 • Blind spot A82 • Area in the retina where the axons of three layers of retinal cells exit the eye to form the optic nerve, insensitive to light Q83 • Subliminal perception A83 • Perception of stimuli that are below the level of conscious awareness Q84 • The first step in sensory systems A84 • Modification of the incoming stimulus by accessory structures Q85 • Vestibular sense A85 • The sensations of movement, balance, and body position Q86 • Pinna A86 • The visible part of the ear Q87 • Aqueous Humor A87 • Fluid filled layer behind the cornea that supplies nourishment to the eye Q88 • Light from the left visual field falls on the ( ) side of each retina A88 • Right Q89 • Provides the color to the eye A89 • Iris Q90 • Came up with the law of just noticeable differences A90 • Ernest Weber Q91 • Cornea A91 • A clear membrane that covers the eye. It serves to protect the eye and bends light waves so the image can be focused on the retina. Q92 • Expanded on Ernest Weber’s work by studying absolute threshold A92 • Gustav Fechner Q93 • What area of the brain is responsible for filtering out constant stimuli during habituation A93 • Cerebellum Q94 • The “triage nurse” of the brain A94 • Thalamus Q95 • Why is the thalamus called the “triage nurse” A95 • It does some processing of sensory information before sending the information to the cerebral cortex Q96 • Iris A96 • Round muscle of the eye Q97 • Area of the brain that is the site of perception and sensation. A97 • Cerebral cortex Q98 • Procedure used to remove small portions of the cornea in order to change the curvature of the membrane and thereby improve focus A98 • LASIK Q99 • Habituation A99 • The tendency of the brain to stop attending to constant, unchanging information Q100 • Amplitude A100 • The distance between the peak and the baseline of a wave Q101 • Taste buds A101 • Common name for taste receptor cells Q102 • Congenital analgesia A102 • Pain conditions where individuals cannot feel pain Q103 • Size constancy A103 • The tendency to interpret an object as always being the same actual size, regardless of distance Q104 • Aerial perspective A104 • The haziness that surrounds objects that are farther away from the viewer, causing the distance to be perceived as greater. Q105 • Texture gradient A105 • The tendency for textured surfaces to appear to become smaller and finer as distance from the viewer increases Q106 • Perception A106 • The methods by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion Q107 • Pitch A107 • Psychological experience of sound that corresponds to the frequency of sound waves; higher frequencies are perceived as higher pitches Q108 • Limits of the human auditory spectrum A108 • 20Hz and 20,000 Hz Q109 • Cochlea A109 • Snail-shaped structure of the inner ear that is filled with fluid Q110 • Wavelengths in sound are A110 • Frequency or pitch Q111 • Basilar membrane A111 • Membrane that runs down the middle of the cochlea Q112 • Olfactory bulbs A112 • Areas of the brain located just above the sinus cavity and just below the frontal lobes that receive information from the olfactory receptor cells Q113 • Organ of corti A113 • The receptor cells for the sense of hearing found on the basilar membrane Q114 • Membrane of the inner ear A114 • Oval window Q115 • Place theory A115 • Theory of pitch that states that different pitches are experienced by the stimulation of hair cells in different locations on the organ of Corti Q116 • Olfaction A116 • The sensation of smell Q117 • Sensory conflict theory A117 • An explanation of motion sickness in which the information from the eyes conflicts with the information from the vestibular senses, resulting in dizziness, nausea and other physical discomfort. Q118 • Three bones of the middle ear A118 • Hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), stirrup (stapes) Q119 • Volley principle A119 • Theory of pitch that states that frequencies from about 400 Hz to 4000Hz cause the hair cells (auditory neurons) to fire in a volley pattern, or take turns in firing Q120 • Gustation A120 • The sensation of taste Q121 • Amplitude in sound is A121 • volume Q122 • Auditory nerve A122 • Bundle of axons from the hair cells in the inner ear Q123 • Frequency theory A123 • Theory of pitch that states that pitch is related to the speed of vibrations in the basilar membrane Q124 • Purity of sound is A124 • Timbre or richness of tone Q125 • Hertz (hz) A125 • Cycles or waves per second, a measurement of frequency Q126 • Supertasters A126 • People with greater than average numbers of taste buds Q127 • Relative size A127 • Perception that occurs when objects that a person expects to be of a certain size appear to be small and are, therefore, assumed to be much farther away Q128 • Semicircular canals A128 • Three somewhat circular tubes that coordinate with a specific plane of body movement Q129 • Motion parallax A129 • The perception of motion of objects in which close objects appear to move more quickly than objects that are farther away Q130 • Accommodation A130 • As a monocular cue, the brain’s use of information about the changing thickness of the lens of the eye in response to looking at objects that are close or far away. Q131 • Convergence A131 • The rotation of the two eyes in their sockets to focus on a single object, resulting in greater convergence for closer objects and lesser convergence if objects are distant. Q132 • Otolith organs A132 • Tiny sacs of gelatin fluid and tiny crystals found just above the cochlea that help to tell a person the location of their head in relationship to their body and movement Q133 • Binocular disparity A133 • The difference in images between the two eyes, which is greater for objects that are close and smaller for distant objects Q134 • Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis A134 • Disorder where individuals do not feel pain and also cannot sweat Q135 • The two chemical senses A135 • Gustation and olfaction Q136 • Treatment for conduction hearing impairments A136 • Hearing aids Q137 • A hearing impairment where sound vibrations cannot be passed from the eardrum to the cochlea A137 • Conduction hearing impairment Q138 • Perceptual set A138 • The tendency to perceive things a certain way because of previous experiences or expectations influence those perceptions Q139 • Decreases pain A139 • Laughter, distraction, sense of control, competing signals from other senses Q140 • Top-down processing A140 • The use of preexisting knowledge to organize individual features into a unified whole Q141 • Food preference is impacted by A141 • Individual, cultural, genetic influences, weight. Q142 • Increase pain A142 • Anxiety, fear, helplessness Q143 • Bottom-up processing A143 • The analysis of the smaller features to build up to a complete perception Q144 • Synesthesia A144 • Disorder in which the signals from various sensory organs are processed in the wrong cortical areas, resulting in the sense information being interpreted as more than one sensation Q145 • Gate-control theory A145 • Theory of pain where a chemical substance for pain is released into the spinal cord and passes through a gate on the way to the brain. The brain then sends a reverse message either further opening the gate or closing the gate. Q146 • Phantom limb A146 • Condition where a person can still feel pain in a limb that has been amputated Q147 • Hearing damage caused by exposure to loud noises A147 • Nerve hearing impairment Q148 • True/false taste sensations are processed all over the tongue A148 • True Q149 • Treatment for nerve hearing impairment A149 • Cochlear implants Q150 • Two types of hearing impairments A150 • Conduction hearing impairment and nerve hearing impairment