Generalist Practice
advertisement

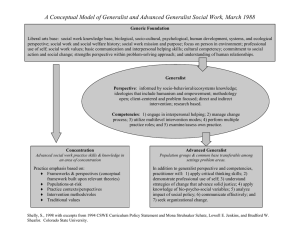
Generalist Practice Social Work What is Social Work? • ?? Why do you want to be a social worker? • !! Baby-snatcher! 5 agreed upon dimensions: 1. Importance of multiple level interventions – Individuals ---- micro – Families ---- micro/mezzo – Groups --mezzo – Organizations --mezzo/macro – Communities --macro *Each is viewed as a system within its environment macro micro mezzo 5 agreed upon dimensions: 2. Practitioners use a problem-solving, plannedchange approach to resolve issues encountered by any of these systems. Engagement • Generalist Intervention Model (GIM) Assessment Planning Implementation Evaluation Termination Follow-up 5 agreed upon dimensions: 3. Ethical principles and social work values. *Include a focus on private issues of human wellbeing, social and economic justice, and appreciation of human diversity. 5 agreed upon dimensions: 4. Practitioners assume a wide range of roles: • • • • • • • • Counselor Broker Mobilizer Facilitator Manager Negotiator Organizer Advocate Educator Case Manager Mediator Integrator/Coordinator Initiator Spokesperson Consultant 5 agreed upon dimensions: Generalist social workers must have infinite flexibility, a solid knowledge-base about many things, and a wide range of skills at their disposal: 5. - Select effective strategies - Evaluate results of practice - Professional competence Knowledge base chosen from a range of theories: - Systems - Ecological - Structural functionalism - Role theory - Psycho-dynamic - Learning Theory - Erickson’s Psychosocial Development - many more Generalist Practice Definition • Generalist Practice is the application of an eclectic knowledge-base, professional values, and a wide range of skills to target systems of any size for planned change within the context of three primary principles, a context, and four major processes Organizational structure Supervision YOU AS GP Cultural competency 1.Knowledge 2. Values 3. Skills Processes Assuming a wide range of roles Using critical thinking Following a planned-change process Application Principles/Values Emphasizing client empowerment Human Diversity Advocacy/Social and Economic Justice TARGET SYSTEM Macro System Mezzo System Micro System MSUM School of Social Work’s Definition of Generalist Practice Social Work • Generalist practice is the critical application of an eclectic knowledge base, professional values, and a wide range of culturally competent skills to a planned-changed process at any system level. Generalist Intervention Model Engagement • • • Substantively and effectively prepare for action with IFGOC Use empathy and other interpersonal skills Develop a mutually agreed-on focus of work and desired outcomes Engagement Assessment Assessment • • • • Collect, organize, and interpret client data Assess client strengths and limitations Develop mutually agreed-on intervention goals and objectives Select appropriate intervention strategies Planning Implementation Intervention • • • • • Initiate actions to achieve organizational goals Implement prevention interventions that enhance client capacities Help clients resolve problems Negotiate, mediate, and advocate for clients Facilitate transitions and endings Evaluation • Critically analyze, monitor, and evaluate interventions Evaluation Termination Follow-up Systems Theory Definition of Systems Theory • System – a set of elements that are orderly and interrelated to make a functional whole. • Systems theory: – Targets multiple systems of different size – Focus on boundaries WITHIN a system System Dynamic Interact Homeostasis (equilibrium) Input Output Equifinality Ecological Theory • Refers only to living dynamic interactions • Focuses on transactions BETWEEN the individual and environment at the interface point. Social Environment Energy (input/output) Adaptation Interdepedence Person in Environment Interface Coping Ecological Theory School Individual Friends/ Peers Family Spiritual orientation Dance Team