Erik Erikson's Stages of Psychosocial Development in my
advertisement

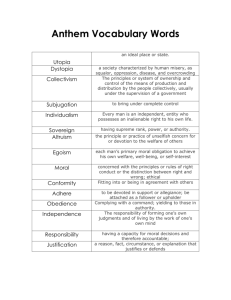
Shandrea Foster Chapter 9- Human Development Notes Issues in Developmental Psychology from the book Lifespan Development Developmental Psychology The study of how humans grow, develop, and change throughout the lifespan Nature and Nurture Heredity imposes some limits on what a person can become. Home, education, nutrition, etc. can evoke positive and negative influences. Resilience: the ability to bounce back Risk factors Difficult temperament, genetic disorders Protective factors High intelligence, good coordination, easy-going personality Theories of Development Stages or No Stages Quantitative changes — height Qualitative changes — advancements in logical thinking Approaches to Studying Development Longitudinal study Same group of participants is followed at different ages Cross-sectional study Groups of participants of different ages are compared on various characteristics to determine age-related differences Cross-Sequential Combines both types into one study Infancy Perceptual and Motor Development Neonate: newborn up to 1 month old Reflexes: inborn, unlearned responses http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rjnQhno3LA4 Maturation: genetically determined biological pattern of individual development Shandrea Foster Cephalocaudal - head to toe Proximodistal - inside to outside Results of Fantz Study(1961) Preferential looking – research technique that gives infant a choice of what to look at Newborns have preferences for odors, tastes, sounds, and visual configurations Fantz (1961): an infant’s interest can be gauged by length of time fixated on it Human face preferred Demonstrated infants have clear preferences and power of discrimination Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development Important Concepts: Changes in schemes underlie four stages of cognitive development Each stage reflects a qualitatively different way of reasoning and understanding the world Stages occur in fixed sequence Accomplishments of one stage provide the foundation for the next stage Children throughout the world seem to progress through the stages in the same order, but they show individual differences in the rate they pass through them Each child’s rate is influenced by the level of maturation and experience Transition from one stage to another is gradual, not abrupt Children often show aspects of two stages while going through transitions Organization Mental process that uses specific experiences to make inferences that are generalized to new experiences Schemes A cognitive structure or concept used to identify and interpret information Assimilation The process by which new objects, events, or experiences, or information is incorporated into existing schemes A child who calls any male stranger “Daddy” Goal to incorporate new experineces Accommodation The process by which existing schemes are modified and new schemes are created Incorporates new objects, events, experiences, or information Goal is to change or make new schemes Sensorimotor Stage (0-2 years) Infants gain an understanding of the world through their senses and their motor activities Actions and body movements Infant’s behavior gradually moves from mostly reflexive to complex and intelligent Infant learns to respond to and manipulate objects and use them in goal-directed activity Object Permanence Realization that objects continue to exist, even when they can no longer be perceived http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKZ9IPRKkkU Preoperational Stage (2-7 years) Symbolic Function The understanding that one thing can stand for another An object, a word, a drawing The use of words to present object Orange - both a color and a fruit Shandrea Foster Pretend Play Imagining a block is a car Imagining a doll is a real baby Egocentricism Child’s belief that everyone sees what he/she sees, thinks as he/she thinks, and feels as he/she feels Results in illogical thinking “A cookie is only good if it is unbroken.” Concrete Stage (7-11 or 12 years) Reversibility Realization that any change in the shape, position, or order of matter can be reversed mentally Conservation Concept that a given quantity of matter remains the same despite being rearranged or changed in appearance, as long as nothing is added or taken away Formal Operations (11 or 12 years and beyond) Preadolescents and adolescents can apply logical thought to abstract, verbal, and hypothetical situations and to problems in the past, present, or future Hypothetic-Deductive Thinking Ability to base logical reasoning on a hypothetical premise Comprehend abstract subjects like philosophy and politics and become interested in the world of ideas Begin to formulate their own theories and think of what might be Conceive of “perfect” solutions to the world’s and their own problems Formal Operations (continued) Naïve Idealism A type of thought in which adolescents construct ideal solutions for problems Teens with divorced parents may idealize the non-custodial parent Imaginary Audience Adolescents believe that they are or will be the focus of attention in social situations and that others will be as critical or approving as they are of themselves Teens spend many hours in front of the mirror trying to please this audience Personal Fable An exaggerated sense of personal uniqueness and indestructibility May be the basis for adolescent risk taking Many believe they are somehow indestructible and protected from misfortunes that befall others Piaget’s Contribution Piaget’s Methods Relied on observation and interview Newer techniques require nonverbal responses Infant’s knowledge of hidden knowledge of hidden objects may be more advanced Critique of Stages Few believe cognitive development occurs in stagelike fashion Cross-cultural research Studies have verified sequence of cognitive development but have revealed differences in the rate of development Formal operational thought Formal operational thought is not universal Shandrea Foster Many people fail to show formal operational thinking Piaget’s greatest contribution was to found the field of cognitive development Attachment Freud saw importance of oral stage babies developed bonds to mothers who satisfied their physical need to eat Harlow saw importance of contact comfort rather than food. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hsA5Sec6dAI Erikson emphasized feelings developed in the stages of Trust vs. mistrust Autonomy vs. shame and doubt Ethical Aproach Bowlby infants are biologically driven to maintain closeness to their mothers, in order to survive Ainsworth infants need parents to survive and that they also need to venture into the environment to learn and develop Attachment theorists believe a secure attachment forecasts favorable adjustment later in life. Ainsworth’s Attachment Classications As a result of the strange situation experiments, Ainsworth developed these classifications: Secure Insecure avoidant Insecure ambivalent (or resistant) Disorganized (added later) Four Main Attachment Ideas 1. Infants become attached to one or more caregivers across cultures 2. Secure attachment is typical and desirable 3. Maternal sensitivity is major cause of secure attachment 4. Attachment security predicts emotional and social competence throughout life Evaluating Attachment Theory Kagan – Strange Situation behavior reflects variations in child rearing practices and temperamental differences, not attachment Limited support for premises that: sensitive parenting promotes secure attachment attachment security relates to later social competence The Lifespan Perspective Developmental changes happen throughout the lifespan and that interdisciplinary research is required to fully understand human development Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development Individuals progress through eight psychosocial stages Each one is defined by a conflict involving the individual’s relationship with the social environment Each must be satisfactorily for health development to occur The stages are named for a series of “alternative basic attitudes” Adult personality foundations are laid in the four childhood stages Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development Trust vs. Mistrust (Birth-1 year) Depends on the degree and regularity of care, love, and affection they receive from the mother or primary caregiver Basic trust is the cornerstone of a healthy personality Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (1-3 years) Children demonstrate independence by saying “No!” Shandrea Foster Physical and mental abilities develop Initiative vs. Guilt (3-6) Initiate activities, plan tasks, develop motor skills Industry vs. Inferiority (6-11) Children begin to enjoy and take pride in accomplishments Sense of inferiority develops if child rebuffed by parents and teachers Identity vs. Role Confusion (11-22) Identity crisis should lead teens to an idea of how they fit into the adult world A healthy identity leads to next stage Intimacy vs. Isolation (22-40) Leads to finding a life partner or acceptance of single life Generativity vs. Stagnation (40-65) Desire to guide the next generation via parenting, teaching, or mentoring Ego Integrity vs. Despair (65+) Acceptance of one’s life in preparation for facing death Kohlberg Levels of Moral Reasoning Preconventional Moral reasoning is based on the physical consequences of an act: Reasoning and actions governed by standards of others and not internalized standards Stage 1 “Right” is whatever avoids punishment Stage 2 Right is whatever is rewarded, benefits the individual, or results in a favor being returned Conventional Individual has internalized standards of others Right and wrong are based on the internalized standards of others Right is whatever helps or is approved of by others Right is whatever is consistent with the laws of society Stage 3 Called the “good boy-nice girl” orientation Good behavior is that which: Pleases others Helps others Is approved of by others Stage 4 Orientation towards authority Right is: Doing one’s duty Respecting authority Maintaining the social order Postconventional Individuals weigh moral alternatives Realize the law may conflict with basic human rights “Right” is whatever furthers basic human rights Requires ability to think at Piaget’s stage of formal operations Stage 5 Believes the laws are formulated to protect both society and the individual Laws should be changed if they fail to do so Stage 6 Shandrea Foster Ethical decisions based on universal principles Respect for human life, justice, equality, and dignity Believe following conscience may require violation of laws Development of Moral Reasoning Discussion of moral dilemmas does not reliably improve behavior Direct teaching of moral values is necessary General cognitive development strongly influences how children respond to moral teaching Young children’s ability to infer moral messages is strongly linked with reading comprehension skills Parents who read moral stories to children (Little Red Hen) should provide explicit information about the moral message and how it relates to the characters in the story Kohlberg’s stages of development occur in all cultures Gilligan asserts sexual bias Research did not include women, nor did it include mercy, compassion, love, or concern for others Content of moral reasoning differs between sexes but does not differ in the complexity of moral reasoning Others assert that moral reasoning is not the same as moral behavior People can be capable of making mature moral judgments yet fail to live morally Parenting Styles (Baumrind,1967) Authoritarian-parents set high standards and expect unquestioned obedience; use power assertion. Permissive-parents demand little from children and do little to teach independence. Democratic-indulgent Rejecting-neglecting Authoritative-parents set high standards and are supportive, nurturant, and firm; use induction. Different types of parents tended to have different types of preschoolers: Those of authoritarian parents were obedient but unhappy. Power assertion Those of permissive parents tended to be unhappy and lack self-control and self-reliance. Those of authoritative were adjusted, well-behaved, and independent. Induction What works best? Some cross-cultural studies have found benefits from authoritative parenting, and yet Asian parents successfully use authoritarian style. Many parents have characteristics from more than one style. Effective parenting practices include parenting that: Is culturally-consistent. Is warm and responsive. Sets consistent limits. Includes inductive parenting.