Growth Stimulants, Retardants, and Rooting Hormones
advertisement

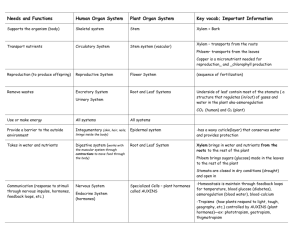
Growth Stimulants, Retardants, and Rooting Hormones Unit 5 Objectives • List 1 example of a substance used to stimulate plant growth • Explain why chemical retardants are applied to floral crops and name 2 commonly used retardants • Explain the use of rooting hormones on cuttings and list several rooting hormones • Describe orally the source of 1 plant growth stimulant • Demonstrate the proper application of a rooting hormone to cuttings • Explain how rootstock is used in dwarfing fruit trees • Define biostimulants Hormones • Growth regulating substances in plants • Hormones are organic chemicals that act and interact to affect growth rate • Auxins – (to increase) – accelerate growth by stimulating cell enlargement • Gibberellins – stimulate growth in stem and leaf by cell elongation – Also stimulate premature flowering, growth of young fruits, and breaking of dormancy Hormones (cont’) • Cytokinins – stimulate cell division – Work along w/ auxins – Will not work w/o auxins present • Inhibitors (abscisic acid) – inhibit seed germination, stem elongation, and hasten ripening of fruit • Chemicals react w/ one another in complex systems in the plant Apical Dominance • Terminal Bud secretes chemicals that inhibit or prevent growth of auxiliary buds – Causes the plant to grow tall rather than send out side branches (p. 51 fig. 5-1) – Helps in competition with other plants • Methods other than pruning have been researched to control plant growth rate, size and shape Stimulants • • • • Enable plants to grow taller (p. 52 fig. 5-2) Causes the stems to stretch out Nodes are further apart Example: – Gibberellic Acid – may be natural or artificial Chemical retardants • Cause plants to be shorter and more compact (p. 53 fig. 5-4) • Used on lawn grasses (Limit) • Interrupts cell division, stem elongation, and seed head formation • Roots continue to grow • May reduce the natural Gibberellic acid Rooting Hormones • Used when propagating plants from cuttings – Large percent of plants root and root quickly • Usually mixed w/ talc and used as powders or dissolved in liquid and used as a wet dip • All rooting hormones should contain a fungicide to prevent fungi from rotting of the cutting – (p. 54 fig. 5-7) Dwarfing Rootstocks • Developed to decrease labor costs in orchards • Rootstock – Root or piece of root used for grafting • Malling Rootstock – made it possible to control the size and rate of growth of apple trees by selecting the proper rooting stock Plant Biostimulants • Natural and Organic Product (from living organisms) • Work to stimulate soil microbial activity, stimulate plant growth and promote disease resistance • Humic acid (byproduct of Humus) is an example • Methanol – blocks photorespiration so plants use water for growth rather than transpiring it into the air Allelopathy • The production of a chemical compound by 1 plant that slows down or stops the growth of another plant • Naturally used to stop competition from other plants • Some green manure or cover crops have this effect on weeds Objectives • List 1 example of a substance used to stimulate plant growth • Explain why chemical retardants are applied to floral crops and name 2 commonly used retardants • Explain the use of rooting hormones on cuttings and list several rooting hormones • Describe orally the source of 1 plant growth stimulant • Demonstrate the proper application of a rooting hormone to cuttings • Explain how rootstock is used in dwarfing fruit trees • Define biostimulants