CCNA4E_CH1_STUDY_GUIDE
advertisement
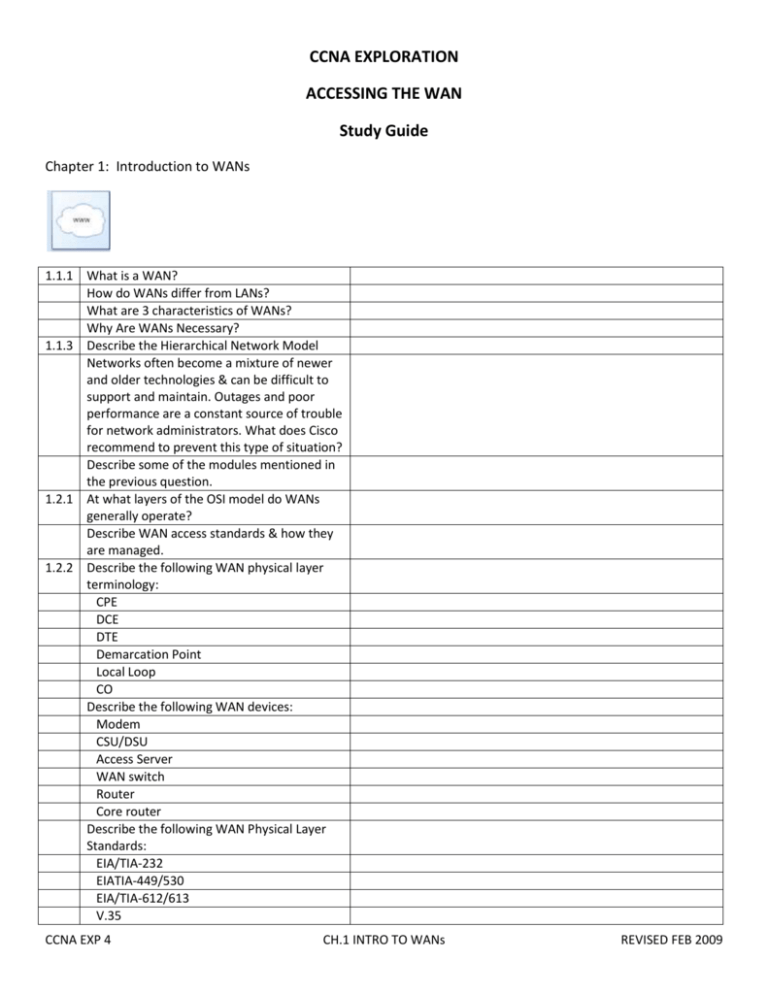
CCNA EXPLORATION ACCESSING THE WAN Study Guide Chapter 1: Introduction to WANs 1.1.1 What is a WAN? How do WANs differ from LANs? What are 3 characteristics of WANs? Why Are WANs Necessary? 1.1.3 Describe the Hierarchical Network Model Networks often become a mixture of newer and older technologies & can be difficult to support and maintain. Outages and poor performance are a constant source of trouble for network administrators. What does Cisco recommend to prevent this type of situation? Describe some of the modules mentioned in the previous question. 1.2.1 At what layers of the OSI model do WANs generally operate? Describe WAN access standards & how they are managed. 1.2.2 Describe the following WAN physical layer terminology: CPE DCE DTE Demarcation Point Local Loop CO Describe the following WAN devices: Modem CSU/DSU Access Server WAN switch Router Core router Describe the following WAN Physical Layer Standards: EIA/TIA-232 EIATIA-449/530 EIA/TIA-612/613 V.35 CCNA EXP 4 CH.1 INTRO TO WANs REVISED FEB 2009 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.3 X.21 What is the purpose of the WAN Physical Layer Standards? What is the purpose of the WAN Data Link Protocols? What are the most common WAN data-link protocols? Describe WAN encapsulation. Describe the basic HDLC frame fields. What is Circuit Switching? What are some examples of Circuit Switching? What is TDM? What is Packet Switching? The switches in a packet-switched network determine which link the packet must be sent on next from the addressing information in each packet. There are two approaches to this link determination. Describe them. What are Virtual Circuits? Describe the 2 types of VCs. What is the main difference between the 2 types of VCs? What is needed to connect to a PacketSwitched Network? What are some examples of packet- or cellswitched connections? WAN connections can be either over a _________or over a _________, such as the Internet. Describe Dedicated communication links. Describe Switched communication links. Describe Public WAN Connection Options. What is meant by leased lines? Are latency or jitter a concern with leased lines? Why or why not? What types of applications require constant availability in a line? What type of additional equipment is needed for leased lines? What is the standard connection link option in the US? What is the standard connection link option in the Europe? In today’s technology when is analog dialup a viable option? What are the advantages & disadvantages of analog dialup? Describe ISDN. Describe ISDN’s channels. Describe the 2 types of ISDN interfaces. CCNA EXP 4 CH.1 INTRO TO WANs REVISED FEB 2009 Describe the differences between ISDN PRI in the US & Europe. What is call setup time? 1.3.4 Describe x.25 & its applications. Describe Frame Relay & its applications. Describe ATM & its applications. 1.3.5 Describe the typical Broadband connection options are used to connect telecommuting employees to a corporate site over the Internet. Describe Municipal WiFi. Describe WiMAX. Describe Satellite InternetDescribe VPN Technology. What are Benefits of VPN? Describe the 2 types of VPN access. What is Metro Ethernet? What are the benefits of Metro Ethernet What are some considerations Network Admins. need to take into account when choosing a Wan link connection? CCNA EXP 4 CH.1 INTRO TO WANs REVISED FEB 2009