Alert: Waste Spill
advertisement

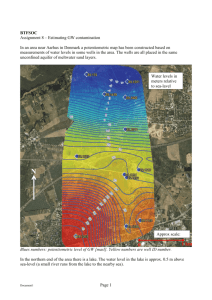
Alert: Waste Spill Environmental Science Artesian well Artesian Well There are two broad classes of drilled-well types, based on the type of aquifer the well is in: Shallow or unconfined wells are completed in the uppermost saturated aquifer at that location (the upper unconfined aquifer). Deep or confined wells are sunk through an impermeable layer into an aquifer that is sandwiched between two impermeable strata The majority of deep aquifers are classified as artesian wells. Ground water well Artesian wells are … where the water is confined under pressure below layers of relatively impermeable rock. Artesian Well Situation… You are a geologist for the Clear Hydro Environmental Geology Company. You receive this urgent email message from a Lake County Illinois Conservation officer: Geologist…studies land formations, rocks and soil Complaints from residents near Round Lake re: unusual odors coming from their well water. Residents informed that a tanker was carrying liquid chemical waste had an accident and overturned a month ago. URGENT MESSAGE FROM LAKE COUNT CONSERVATION BOARD!! Concern: Waste spill has infiltrated into the groundwater and has contaminated wells of the 15 residents. Wells sites #1 and #2 complaints of odors and funny-tasting well water. Residents were told not to drink the water from their wells. Possible health risk. URGENT WATER WARNING!! Geologists Action Required: Part A: Identify soil layers & properties 1. Label Maps #2 with the soil properties. 2. Review Map 3 and understand well layouts and the direction of water flow. 3. Color in Map 3 with data from Table 3 on the different layers of soil within the groundwater topographical profile. URGENT-WATER WARNING! 4. Conduct well-water analysis where you determine the extent of the groundwater pollution plume. 5. Record your findings and make a recommendation to the Lake County Conservation Board on which wells are contaminated. URGENT- WATER WARNING! How a well is dug Urban and suburban toxic waste sites usually arise from: industrial operations leaking underground storage tanks and pipes (such as from gas stations) c. municipal dump sites d. leaking hazardous waste storage sites, and perhaps e. contamination left over from closed military bases. a. b. The severity of groundwater contamination depends on characteristics of the waste or leachate (e.g., volume, composition, solubility, concentration of various constituents, time rate of release of contaminants, the size of the area from which the contaminants emanate, groundwater pumping and recharge, and other factors). Major concerns at a polluted site is: 1. The migration of contaminants offsite to the underground aquifer, where they can pollute the groundwater. 2. Many communities pump groundwater for their drinking water and these contaminants can severely compromise its quality. Vocabulary: Plume: A featherlike structure, form, or object, generally narrow at its origin and spreading out as it progresses. Dispersion: process of leachate moving out from original source. Theoretically, plumes will be conically shaped - the exact shape depending on contaminant and soil properties Infiltration: Flowing into the ground or aquifer. Surface water will usually infiltrate if the soil is permeable. Rainfall helps contaminants infiltrate the soil and possibly move into the aquifer and groundwater. Hydraulic gradient: The slope of the water table. The groundwater flows downhill and the gradient determines the rate of flow. Maximum Contaminant Level (MCL): The maximum level of certain contaminants permitted in drinking water supplied by a public water system as set by EPA under the federal Safe Drinking Water Act. Plume A Plume B How are they different? Plume C Plume D Different types of plumes What types of conditions affect a plume? 1. Porosity and permeability of the soil 2. Rate of groundwater infiltrating the soil Location: Round Lake Illinois Topography