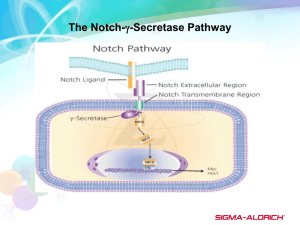
Notch signaling pathway?
advertisement

Notch and Cancer IPO-LISBOA CIPM Angiogenesis group Francisco Caiado Sérgio Dias The Hallmarks of Cancer (Hanahan and Weinberg) Tissue Invasion and Metastasis Cancer Hallmarks and Notch signaling Tissue Invasion and Metastasis Modulation of the Notch Signaling Pathway Notch-Delta signaling pathway • Regulates: • establishment of patterns of gene expression; • cell differentiation; • regulates binary cell fate choice; • maintenance of stem cell populations; • Function: • Embryonic Development; • Adult Self-Renewing Organs; CANCER Roca, C. and Adams, R. Genes & Dev. 2007 21: 2511-2524 Abnormal Notch signaling and cancer Oncogenic activity of Notch Maillard,I. and Pear, W. Cancer Cell 2003 Tumor supressor activity of Notch Abnormal Notch signaling and cancer Targeting Notch signaling: • γ-secretase inhibitors (GSIs) are in early clinical trials; • mAbs targeting the ‘negative regulatory region’ (NRR) of notch; • mAbs that against DLL4 inhibit Notch signaling in endothelial cells and cause non-functional tumor angiogenesis; De la Pompa et al. Endocrine Reviews 28(3):339–363 Cancer Hallmarks and Notch signaling Tissue Invasion and Metastasis Modulation of the Notch Signaling Pathway Tumor Angiogenesis Pro-angiogenic factors: • VEGF, FGF, Neuropillin, Ang-2, MMPs… Vessel factors: stabilizing • Notch-Delta, PDGF1, Ang-1, ECMs… Hashizume, H.l NCR 2000 Notch signaling and tumor angiogenesis Ridgway, J. et al Nature 2006 Thuston, G. et al NCR 2006 Post-natal vasculogenesis Bone marrow (BM) derived progenitor cells: • recruited during physiological “malignant” angiogenesis; and • BM mobilization; homing to angiogenic sites (Integrins); invasion and migration; • Induction of angiogenesis: • Differentiation into endothelial cells; • Activation of pre-existing endothelial cells; Notch signaling pathway? Rafii, S. et al NCR 2002 1. Notch signaling regulates BMprogenitor endothelial differentation? Markers: CD133+CD34+KDR+ Lin- Sca-1+ Flk-1+ Igreja, C. et al Exp. Hematol. 2006 Caiado, F. et al Plos One 2008 Notch signaling inhibition impairs adhesion and integrin expression Caiado, F. et al Plos One 2008 2. BM-progenitor modulate endothelial activation via Notch signaling? Transplant of BMprogenitors control or with reduced Dll4 Subcutaneous injection of human or mouse tumors • Tumor growth; • Tumor apoptosis; • Vessel density; Sub – lethal irrad. NOD-SCID female • Vessel stability; BM progenitors with reduced Dll4 decrease tumor proliferation and increase apoptosis WT-EPC Dll4-EPC 12 Apoptosis index Tumor Volume (mm3) C 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 Real, C Submited 2008 14 1 8 22 Days 26 ** 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 * Control wtEPC Dll4+/-EPC BM progenitors with reduced Dll4 induce increased but non-functional vascularization Vessel Density : Pericyte coverage : Hypoxic index : Real, C Submited 2009 Notch signaling modulates BM-progenitor function during tumor angiogenesis EPC Activated endothelial cell Endothelial cell Apoptotic endothelial cell Pericyte Apoptotic pericyte • Notch signaling regulates BM-progenitor cell endothelial differentiation; • Dll4 expressed on BM-progenitor cells regulates endothelial stabilization during tumor angiogenesis; Acknowledgments: S Dias A. Gomes A. Cachaco Francisco A. Costa Cheila Carla Tânia Cristina Jacinta Cristiana Sara •(2008/2009) Angiogenesis Lab members (Leonor Remédio Missing); • Dr.Antonio Duarte (group members), Dr.Yadgita Hideo (group members); • FCT, GlaxoSmithKline, Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian;