Weir Flow Lab Manual
advertisement
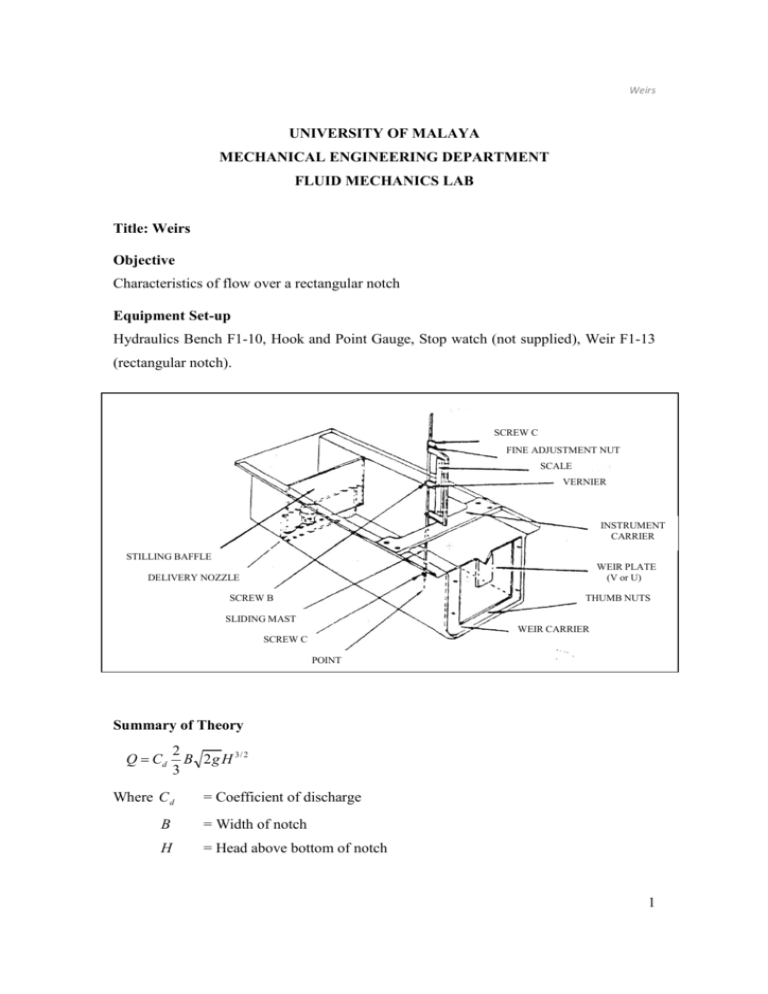
Weirs UNIVERSITY OF MALAYA MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT FLUID MECHANICS LAB Title: Weirs Objective Characteristics of flow over a rectangular notch Equipment Set-up Hydraulics Bench F1-10, Hook and Point Gauge, Stop watch (not supplied), Weir F1-13 (rectangular notch). SCREW C FINE ADJUSTMENT NUT SCALE VERNIER INSTRUMENT CARRIER STILLING BAFFLE WEIR PLATE (V or U) DELIVERY NOZZLE SCREW B THUMB NUTS SLIDING MAST WEIR CARRIER SCREW C POINT Summary of Theory Q = Cd 2 B 2 g H 3/ 2 3 Where C d = Coefficient of discharge B = Width of notch H = Head above bottom of notch 1 Weirs Procedure Ensure that the hydraulics bench is located on a level floor as the accuracy of the results will be affected if the bench top is not leveled. Set up the equipment as shown in the diagram. Set Vernier Height Gauge to a datum reading, by placing the point on the crest of the weir. Take extreme care not to damage the weir plate with the point gauge. Position the gauge about half way between the notch plate and stilling baffle. Admit water to the channel, adjust flow control valve to obtain heads, H, increasing in steps of about 1cm. For each flow rate, stabilized conditions, measure and record H. take readings of volume and time using the volumetric tank to determine the flow rate. Results and Calculations Tabulate volumes, time and heads. Compute and tabulate: QH 3 / 2 C d = Plot 3Q 2B 2 g H 3/ 2 Q 2 / 3 , log Q, log H Q2/3 against H log Q against log H Cd against H Conclusions 1. Is C d constant for this notch? 2. Estimate an average value of C d for the range of the test. 3. Can the Q-H relationship be described by and empirical formula Q = kH n ? If so, find values of k and n. 4. If Cd varies, suggest a functional relationship between C d and H . B 2