Adaptation
advertisement

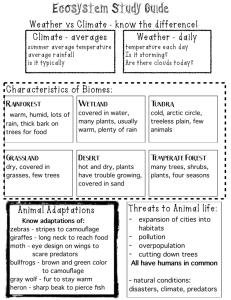
Do-Now Animal Adaptation Miss Scillieri - Take out Science Fair Checkpoint 1: Entry Form and Partner Contract. - Answer the following question as I call you up. - Using page 19 as a source explain one predator adaptation and one prey adaptation. If possible site from documentary. - If you do not have it tomorrow, you will stay in for lunch and will call your parents explaining why it dropped 20 points no exceptions February 18, 2014- Daily Agenda 1. 2. 3. 4. Check Science Fair Checkpoint Discuss Do-Now Finish Documentary Discuss Documentary and power point. Do-Now • Take out Science Fair • As I check science fair answer the following question • Humans interact with their environment on a daily basis. They can have positive and negative effects. Using four vocabulary words from the chapter write a paragraph describe how human interaction affects the environment. • * Underline vocabulary words Response • Humans destroy habitats in a number of different ways. One way is clearing land to build. Pollution may leak into the ecosystem. Oil and gasoline are abiotic factors that can damage the biotic environment like plants and animals. Organisms may have to emigrate to new habitats to survive. One such destroyer was the BP gasoline oil spill where hundreds of marine animals lost more than their homes. Do-Now Directions: Assignment • Take out Science Fair As I check science fair take out notebook paper and pen. Everything else off desk. Read over the writing prompt and outline your ideas. • The Venus flytrap is a booby trap. If the fly touches the two triggers the trap closes and captures the fly. Think of ways you can create a booby trap to capture food. Write and essay explaining your booby traps works, giving instructions, and why you need it. Writing prompt: Today you will practice for the NJ ASK This will count as a lab grade. I am looking for effort not excellence. • What your essay needs • • You have an half an hour to write a 2-3 paragraph essay answering the following - -Intro Paragraph Body explaining how your booby traps work and why it is important Closing relating it to your life or something else you have learned Do-Now Lab Set Up • Set up for lab • 1’s get 4 lab reports on chair • 2’s get 4 pieces of string and two pairs of scissors on radiator • 3’s Get 2 stopwatches and 2 pieces of paper- on table 7. Cut the paper in half • 4’s fill in as sub and manage table make sure everyone has a pen, report, group has all supplies, all other materials on floor and that everyone is behaving. What to do once set up As I am checking science fair read over lab directions! Discuss with group. Answer the question and write your hypothesis Once you finish lab… After lab answer the following question Answer on back page Humans interact with their environment on a daily basis. They can have positive and negative effects. Using four vocabulary words from the chapter write a paragraph describe how human interaction affects the environment. Response • Natural selection is the process of positive adaptations being passed down from generation to generation. For example giraffes with long necks. We see this a lot in the animal kingdom, for example a mouse has brown fur as camouflage. Its predator an eagle has talons to grab the unsuspecting critter. As you can see adaptations are in full affect. Academic Vocabulary Camouflage An adaptation in which an animal protects itself against predators by blending in with the environment. Protective Coloration A type of camouflage in which the color of an animal blends in with its background, protecting the animal against predators. Protective Resemblance A type of camouflage which the color and shape of an animal blends in with its background, protecting it against predators. . Academic Vocabulary Mimicry An adaptation in which an animal is protected against predators by its resemblance to another, unpleasant animal. Adaptation A characteristic that helps an organism to survive in its environment. February 10th, 2015 Learning Target: To discuss adaptations • Come in quietly • Sit in assigned seat • Take out vocabulary HW to be checked • Write tonight's HW into agenda • Complete Do-Now • Do-Now: Complete the T-Chart listing at least 3 adaptations a predator uses to survive and 3 adaptions prey use to survive. Use your schema and vocabulary to guide you • Predators Prey What is an adaptation? Adaptation A characteristic that helps an organism to survive in its environment. Physical Adaptations Physical feature that helps and organism survive Body part that gives an advantage Physical Adaptations Whale and dolphins can hold their breath for long periods of time. Other aquatic animals breathe using gills. Physical Adaptations Reptiles have dry, scaly, waterproof skin. This helps them survive on land and in dry environments. Physical Adaptations THINK OF OTHER BIRDS WHAT ADAPATIONS DO THEY HAVE Birds have hollow, light weight bones to help them fly. Birds that do not fly have other traits to help them adapt. Physical Adaptations Some mammals have thick hair to keep them warm. Physical Adaptations Kangaroos have pouches to carry their young in. When marsupials have babies the offspring is not fully developed and they carry the baby in the pouch until it fully develops. Physical Adaptations The duck billed platypus and the spiny anteater produce milk to feed their young. Behavioral Adaptations Things that organisms DO (voluntary) A Way an Organism purposely acts to survive Behavioral Adaptations Wolves travel in packs to allow them to hunt large prey they may not be able to kill along. Behavioral Adaptations Fish swim in school to protect them from predators. Behavioral Adaptations Aardvarks stay in burrows during the day and only come out at night to hunt for food to avoid the heat. (nocturnal) Behavioral Adaptations Reptiles must “sun” to maintain their body temperature since they are cold blooded. Physical Adaptations Male peacocks have tall feathers to display to attract a mate. Physical Adaptations Crickets chip by rubbing their wings together to attract mates. Physical Adaptations Female alligators carry their young to the water to care for them for several weeks. Instincts An instinct is an inherited behavior that is not learned but done automatically. A newborn puppy can find its way to their mother. They are not taught to do this; it is instinct for them (automatic). What are adaptations to climate? Adaptations differ depending on the environment. Animals that live in frozen areas near the earth’s poles do not have the same adaptations of animals who live in deserts. Animals in colder climates must be able to reduce heat loss. Animals in deserts and hot climates must be able to get rid of excess heat. Camels have humps made of fat to store food and water when they are scarce. Fennec’s, a kind of fox, have big ears to allow the heat to escape. Animals that live in cold have insulation that traps heat like blubber for whales and fur in feathers for birds What are adaptations to climate? Behavioral adaptations also help some animals survive extreme weather. Penguins huddle together for protection for the extreme cold. What are adaptations to climate? Behavioral adaptations also help some animals survive season changes. Some animals such as bats, snakes, turtles, and frogs hibernate in periods of inactivity during the cold. During hibernation, animals live on previously stored energy. Many animals such as birds, butterflies, and fish migrate. Organisms migrate for season change, food availability, and loss of habitat. What adaptations do predators and prey have? Predators Some snakes and lizard have poisons in their jaws The hognose snake will play dead to attack • PREY • Some animals use chemicals when threatened like a skunk. • Gazelles run fast away from predators • Bugs right into a tight ball to avoid prey. What adaptations do predators and prey have? How Predators Catch Prey? Some adaptations help predators catch more prey. Anteaters have long tongues that are covered with tiny spikes and sticky saliva to pick up ants. Woodpecker finches use a twig or cactus spine to remove insects from deep within trees. Camouflage Some animals survive by blending in. Camouflage An adaptation in which an animal protects itself against predators by blending in with the environment. Camouflage predators can sneak up on prey and prey with camouflage can hide from predators. Protective Coloration Protective Coloration A type of camouflage in which the color of an animal blends in with its background, protecting the animal against predators. In the winter, the arctic fox has a white coat to blend in with the snow. In the spring time, they fox’s coat changes colors to blend in with the plants that grow in warm weather. Protective Resemblance A type of camouflage which the color AND shape of an animal blends in with its background, protecting it against predators. The walking stick insect resembles a stick or small branch. Mimicry An adaptation in which an animal is protected against predators by its resemblance to another, unpleasant animal. Coral Snake and King Snake Robber Fly and Bumblebee The viceroy butterfly is protected from predators because it looks like the bad-tasting, poisonous monarch butterfly. Review Physical and behavioral adaptations help animals survive in environments. Adaptations to climate can help animals survive extreme temperatures. Adaptations that allow organisms to avoid predation include camouflage and mimicry. Exit Slip As the movie plays pick an adaption from today’s class or the brain pop and write a “juicy, spicy, Thanksgiving dinner “description. Name: Date: