The Regional System of Fisheries Refugia: Multiple Stakeholder
advertisement

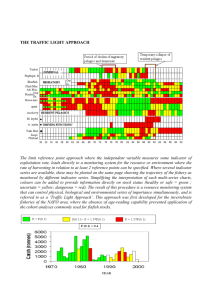
REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG THE REGIONAL SYSTEM OF FISHERIES REFUGIA: MULTIPLE STAKEHOLDER INVOLVEMENT IN FISHERIES AND HABITAT MANAGEMENT UNEP/GEF RWG-Fisheries REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Fisheries of the South China Sea Fish stocks critically important for food security, income, and foreign exchange Fish production from SCS ≈ 10% of global production Most fish stocks fully-fished or over-fished Future landings will decline unless total effort reduced Difficult to reduce effort – high community dependence REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Role of Fisheries Habitats in Sustaining Fisheries SCS habitats play a critical role in sustaining fish stocks, food supply, and incomes Mangroves Coral Reefs Seagrass Wetlands Habitats are refuges for fish during critical stages of their life-cycles - e.g., as larvae, when spawning, and feeding REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Loss of Fisheries Habitats of the South China Sea Continued decline in the total area of habitats has raised serious concerns for sustainability of fisheries Estimated Decadal Rates of Habitat Loss: Seagrass – 30% Mangroves – 16% Coral Reefs – 16% Fishing is a key factor in the continued loss of marine habitats and biodiversity in the South China Sea REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Fishing and the Loss of Marine Habitats and Biodiversity Key characteristics of marine fisheries in Southeast Asia contributing to habitat loss: Over-capitalisation and over-fishing, particularly in the small-scale sector High level community dependence on fish for food and income Excessively high fishing effort in most inshore areas Use of destructive fishing gear and practices REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Need for Multiple Stakeholder Involvement: Need for improved management of links between fish stocks and habitats Several global initiatives have been promoted (e.g., MPAs/LMEs) A wide gulf exists between fisheries and environment sectors Many environment initiatives have not delivered purported benefits to fishing communities Fisheries ministries and departments busy trying to maintain stocks in face of high community dependence and participation Need for partnerships and enhanced communication between fisheries and environment sectors REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Emerging Challenge for Fisheries and Environment How to effectively integrate fisheries and habitat management? Role of multi-lateral, inter-governmental projects The UNEP/GEF South China Sea Projects is working to develop regional capacity to meet this challenge by: improving the understanding amongst fishing communities, managers, and policy makers of habitat and fish stock linkages, and building the capacity of both fisheries and environment ministries and departments to ensure effective integration of fish stock and habitat management REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Developing a Mechanism to Improve the Management of Links Between Fish Stocks and Habitats The RWG-F recommended that any mechanism developed should: Focus on maximising the benefit-cost ratio of management interventions for fishing communities; Promote sustainable use rather than prohibition of fishing; Focus on links fish life-cycle and critical habitat linkages; and be Relevant at the fishery level, i.e., should be easily understood by fishing communities, local government officials, and provincial level fisheries managers REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Development of the Fisheries Refugia Concept Fisheries Refugia: Specific areas of significance to the life-cycle of fish species Should be defined in space and time Should NOT be no-take zones Serve to safeguard spawning aggregations, nursery grounds, and migration routes Fisheries Refugia are “Spatially and geographically defined, marine or coastal areas in which specific management measures are applied to sustain important species [fisheries resources] during critical phases of their life-cycle, for their sustainable use.” REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Stakeholder Consultations on Refugia Concept Review of Fish Egg and Larvae Data for Refugia Identification Intergovernmental Guidelines on Refugia Technical Workshops on Mapping Known Refugia Development of a Fisheries Refugia Information Portal Conduct of Regional Training Events on Refugia Science and Management REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Conduct of Country Consultations on the Identification and Establishment of Fisheries Refugia Sites REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Review of Information Collated by the South China Sea Project on Links Between Fish Life-Cycle and Critical Habitats National Reports on Fisheries National Reports on Coral Reefs, Seagrass, Wetlands, Mangroves 142 Habitat Site Characterisations Habitat Demonstration Site Documents The South China Sea MetaDatabase REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Review of Information Collected by SEAFDEC on Larval Fish Distribution and Abundance REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Review of Information Collected by SEAFDEC on Larval Fish Distribution and Abundance Sardinella spp. REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Review of Information Collected by SEAFDEC on Larval Fish Distribution and Abundance Scomberomorous spp. REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Candidate Fisheries Refugia Sites - Cambodia REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Candidate Fisheries Refugia Sites - Indonesia REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Candidate Fisheries Refugia Sites - Philippines REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Candidate Fisheries Refugia Sites - Thailand REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Candidate Fisheries Refugia Sites – Vietnam REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Development of a Regional System of Fisheries Refugia Regional Actions • Policy guidance • Capacity development • Data & Information Management • Support establishment of national fisheries management systems • Promote regional fisheries management frameworks National Actions • Establish programme for refugia identification and mapping • Develop national fisheries management systems Local Actions • Establish local management board • Delineate refugia boundaries with fishers • Implement awareness programmes • Identify fisheries management problems/solutions for refugia sites • Support regional data sharing • Establish regulations and monitoring REVERSING ENVIRONMENTAL DEGRADATION TRENDS IN THE SOUTH CHINA SEA AND GULF OF THAILAND WWW.UNEPSCS.ORG Importance of Stakeholder Involvement at the Local Level Success of Regional Fisheries Refugia Depends on Actions at the Local Level Level of Community Support Depends on Involvement of Stakeholders in Actions Harnessing Local Knowledge Critical for Good Site Selection and Establishment of Management Measures