Transformational Leadership
advertisement

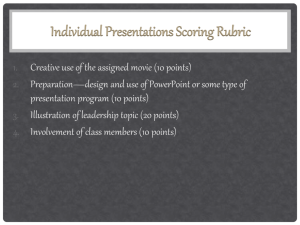
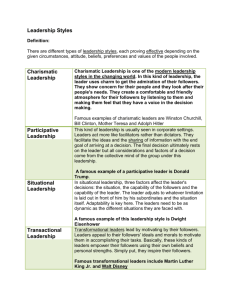
Leadership Definitions 1. The act of leading a group of people or an organization 2. A process of social influence in which one can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common task 3. The art of leading others to deliberately create a result that wouldn’t have happened otherwise 4 Different types of leaderships: 1. Authoritarian: An authoritarian leader is one who keeps strict, close control over his followers. He possesses total authority over his followers and no one is allowed to challenge his authority. Countries that operate under authoritarian leadership include Cuba and North Korea. 2. Democratic: A democratic leader gets his followers to participate in decision making and values the opinions of his followers. This can get the followers to feel more involved and their morale can be boosted, which often leads to higher productivity. In a democratic leadership system, the leader acts as a person who gets to make the final decision. 3. Laissez-faire: Laissez-faire(French phrase for “leave it be”) leadership is described as a hands-off leadership style where the leaders give their followers the right to make their own decisions regarding the completion of their work. The leader’s role is to assign tasks to his followers for them to complete, and the leader will not directly participate in the decision making unless his followers request it. 4. Transactional: A transactional leadership system is a meritocratic system, where workers receive certain tasks to perform and are rewarded or punished based on their performance. This allows the leader to promote the compliance of his followers and leaders who use this form of leadership pay attention to followers’ work in order to find faults and correct them. It focuses on supervision and group performance as this form of leadership makes the assumption that followers need to be carefully monitored to ensure that expectations are met. 5. Transformational: A transformational leader enhances the morale and efficiency of the followers through a variety of mechanisms, such as being an inspiring role model, This often leads to positive changes for the followers which improves their performance results. 6. Educational: The vision, skills, and capabilities that principals need to possess to build and maintain their schools. These same qualities are also used to attract talented teachers, and create educational programmes that can provide children with a conducive academic environment. 7. Entrepreneurial: An entrepreneurial leader is one who organises a group of people in order to achieve a common goal, using proactive entrepreneurial behavior by optimising risk, innovating to take advantage of opportunities, taking personal responsibility and managing change within a dynamic environment for the benefit of the organisation. 8. Servant Leadership: A servant leader is one who always puts the need of others before him and aims to help others whenever possible. It is often associated with the democratic style as his priority is to encourage subordinates to unfold their full potential. By being a “servant” to one’s subordinates, a leader can gain the support of his subordinates easily which can improve efficiency and productivity. List of quotes “Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower” Steve Jobs “Leadership and learning are indispensable to each other” John F. Kennedy “The single biggest way to impact an organization is to focus on leadership development. There is almost no limit to the potential of an organization that recruits good people, raises them up as leaders and continually develops them.” John Maxwell “A leader is one who knows the way, goes the way, and shows the way” John Maxwell “The pessimist complains about the wind. The optimist expects it to change. The leader adjusts the sails.” John Maxwell “The key to successful leadership today is influence, not authority.” Kenneth Blanchard “As we look ahead into the next century, leaders will be those who empower others.” Bill Gates “Do not follow where the path may lead. Go instead where there is no path and leave a trail.” Harold R. McAlindon “Leadership: The art of getting someone else to do something you want done because he wants to do it.” Dwight D. Eisenhower “I cannot give you the formula for success, but I can give you the formula for failure: Try to please everybody.” Herbert B. Swope “A leader takes people where they want to go. A great leader takes people where they don’t necessarily want to go, but ought to be.” Rosalynn Carter “A ruler should be slow to punish and swift to reward” Ovid “A man who wants to lead the orchestra must turn his back on the crowd” Max Lucado “Education is the mother to leadership” Wendell Willkie “If your actions inspire others to dream more, learn more, do more and become more, you are a leader” John Quincy Adams “Leaders aren’t born, they are made” Vince Lombardi “Example is not the main thing in influencing others, it is the only thing” Albert Schweitzer “A leader is best when people barely know he exists, when his work is done, his aim fulfilled, they will say:we did it ourselves” Lao Tzu Examples of Leaders (Asia) 1. Lee Kuan Yew a. Transformational and Charismatic Style Lee Kuan Yew demonstrated both transformational and charismatic leadership styles, explaining why he is such a great all-rounded leader. He is able to inspire and motivate people, at the same time able to bring about huge changes. He has managed to transform Singapore drastically by appealing to his followers’ values and sense of higher purpose to execute his vision for a new and improved Singapore, also being able to align his vision with his followers b. Servant Leadership Lee Kuan Yew has always been concerned with developing his people’s welfare and socioeconomic status, health and education standards. He did not ignore the needs of the country and solved many of Singapore’s problems, which was one of the factors that kept him in power for such a long time. For example, there was a shortage of housing so he organised housing to be built on government owned land. He always ensured that his people’s interests were placed first and his three main concerns were national security, the economy, and social issues. c. Democratic Leadership Lee Kuan Yew consistently consulted his cabinet and party members as well as other experts and the people of Singapore when it came to decision making. This can be shown by how during Lee Kuan Yew’s political reign he started the “Meet-The-People” campaign where the political leaders would meet the ordinary Singaporeans and ask them about what they think could be improved. Examples of accomplishments: He increased Singapore’s GDP per capita increased from $516.26 in 1965 to $11,645.41 in 1990 before he stepped down. 2. Aung San Suu Kyi a. Background Aung San Suu Kyi is a Burmese opposition politician and chairman of the National League for Democracy (NLD) in Burma. She was under house arrest for 21 years from 1989 to 2010, but is now running for the next presidential elections in 2015 while pushing for constitutional reforms and fighting for the freedom of her country b. Fighting for democracy Aung San Suu Kyi returned to Burma in 1988, after years living and studying abroad, only to find widespread slaughter of protesters rallying against the brutal rule of dictator U Ne Win. She spoke out against him and initiated a nonviolent movement toward achieving democracy and human rights. In 1989, the government placed Suu Kyi under house arrest, and she spent 15 of the next 21 years in custody. In 1991, her ongoing efforts won her the Nobel Prize for Peace, 3. Sim Wong Hoo a. Background Mr Sim Wong Hoo is the founder, CEO and chairman of Creative Technology, a designer and manufacturer of products for personal computers and personal digital entertainment devices. Creative is notable for products such as the SoundBlaster audio card and the Creative ZEN range of audio and media products. b. Transformational Leadership Sim Wong Hoo had a vision of selling 100 million units of something back when Creative was only a tiny little company. He knew that people would make fun of him for his ridiculous vision, but that did not stop him from being creative. He shared his vision with his team of about 10, including himself, working day and night to develop a new motherboard, the BIOS, a sound card, a new graphics board and a Chinese OS. Everyone strived to achieve this goal and together they build the vision for Creative. However, things did not turn out as planned, but he still strived to achieve his vision. His dream eventually came true when Creative had sold over 100 million units of Sound Blasters. Examples of accomplishments: His foresight has led him to become the youngest billionaire in Singapore at the age of 45 Examples of Leaders (Global) Martin Luther King Jr. Martin Luther King Jr. is vividly remembered as an inspirational leader. His famous speeches such as his “I have a dream” speech at the civil rights march in Washington of August 1963 inspired people of all races, and created an unprecedented coalition for anti-racist legislation. He spearheaded the nonviolent civil rights movement in america and used his charisma to gain the support of many other African-Americans as well as american whites. Example of his accomplishments as a leader: He brought bus segregation in 1920s to an end by organizing a mass boycott where a large number of African-Americans refused to board buses which practiced racial segregation. Mahatma Gandhi Gandhi is widely recognized as one of the 20th’s Century’s greatest political and spiritual leaders. Honored in India as the father of the nation, he pioneered and practiced the principle of Satyagraha-resistance to tyranny through mass nonviolent civil disobedience. Through this, Gandhi led India to independence and inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. Examples of accomplishments: Freed India from the British through nonviolent protests Winston Churchill Churchill was a charismatic and transformational political leader. His leadership skills were called upon during the time of crisis in World War II. His inspiring speeches encouraged the British to be courageous and hopeful in a time of despair, one of his famous quotes being “Never,never,never give up”. Examples of accomplishments as leader: Prime Minister of UK during World War II, maintained a strong stand against Hitler and would not cooperate with him Steve Jobs Steve Jobs, ex-CEO of Apple Inc, is widely recognized as a charismatic pioneer of the personal computer revolution and his influential career. Besides being charismatic, he also had vision of what he wants to do and was detail-oriented, ensuring that his goals were accomplished. All of this made him one of the greatest entrepreneurial leaders in history. Examples of accomplishments: He increased the value of 100 Apple shares, from $1369 in 1997 to 150,590 in 2011. Apple cash reserves also increased from 1.2 billion in 1997 to 75.9billion in 2011. Arguments For and Against Authoritarian leadership Arguments for: 1. If a decision needs to be made quickly, an authoritarian leadership style is the most efficient as it tells the subordinates exactly what they are supposed to do 2. For subordinates who are less capable, a good leader who utilizes an authoritarian style can take charge of the group and assign tasks to different subordinates 3. It allows group members to focus on performing specific tasks without having to worry about making complex decisions, which allows group members to become highly skilled at performing certain duties. Arguments against: 1. Subordinates may view the leader as bossy and controlling, causing them to have a poor relationship with their leader. This creates an unhappy work environment which could potentially lead to poor quality of work. 2. Creativity is severely limited as since one person gets to make all the decisions, people in the group do not get to contribute their ideas Democratic leadership Arguments For: 1. It leads to a creative work environment as all members are encouraged to share ideas and opinions 2. Group members feel more involved and committed, making them more likely to care about the end result. 3. There is stronger team bonding within the group as they can share their ideas with one another and discuss about it, in addition to the leader being more popular with his subordinates. A positive work environment like this can increase the productivity of the group. Arguments against: 1. It is time-consuming as leaders have to take into account everybody’s opinion before making a decision. 2. Group members may lack the necessary knowledge of expertise to make quality contributions to the decision-making process. 3. Even though it encourages communication between group member, communication errors may occur which leads to further complications 4. People may see their leader as easy-going and lose their respect for their leader, causing the leader to be unable to establish a professional relationship with his followers Laissez-faire leadership Arguments For: 1. It is effective if group members are highly skilled, motivated and capable of working on their own. 2. It gives group members freedom to do whatever they see fit without having a leader to tell them what to do, which could lead to increased productivity Arguments against: 1. It is ineffective if group members are incapable of doing things without the guidance of a leader, and if left to their own devices they will fail to produce satisfactory work. 2. Group members can lose their motivation to do work without having a leader. Transactional leadership Arguments For 1. Followers that are motivated by a system of rewards and punishments will work well under a transactional leader 2. It clarifies everyone’s roles and responsibilities 3. It is effective in areas where it is clear what the goals and objectives are and there is little room for creativity or innovations Arguments against 1. It limits creativity and is almost only effective for simple tasks where no creativity is needed 2. It is a very basic form of motivation which would not be effective for workers who wish to engage in a professional environment at a higher level as they are motivated by other things. 3. It does not improve job satisfaction Transformational leadership Arguments For 1. Transformational leaders inspire their followers by being a role model and expecting the best out of everyone and themselves, leading to higher productivity and engagement 2. It can lead to improvements in the followers as a result of the influence by the leader Arguments Against 1. It depends entirely on the leader 2. It lacks necessary details required to get things done as the leaders imply provide a vision or an objective everyone should be headed towards 3. It assumes that everyone wants to work together as a group towards a goal with little or no merit. Some workers would not want to work for something with no immediate reward Controversies . Does a good leader have to be a moral one/bring benefits to his followers? One of the biggest controversies of all time regarding leadership is whether or not people like Adolf Hitler can be considered a good leader. They managed to influence the people into believing in their goals and following them willingly, but they manipulate the people to do things that are immoral and unjust. This depends on one’s definition of leadership. If leadership refers to the ability to influence others to support a common cause, Hitler would be one of the best leaders as no other person in history has influenced as many people willingly into supporting one common cause. However, others make the argument that Hitler was a horrible leader as he did not lead his citizens to a good cause. In the end, he led Germany to its downfall so he cannot be considered a good leader as he did not bring about good for his followers. There is also the argument that he rose to power not because of his charisma, but because of his manipulative abilities through deceiving the people and eliminating any political enemies. Does a good leader really need the popularity of the people? Another controversy is whether a leader can be considered good as long as he can get things done. This mostly applies to authoritative leaders who are usually not well-liked by his followers or subordinates but he can still get things completed. Some leaders get work done by using force of using a disincentive in the form of harsh punishments to force their subordinates into getting things done. This has proven to be an effective form of leadership, despite being unpopular. Thus, the controversial question would be whether a good leader have to get his followers to willingly et a task completed.