投影片 1
advertisement

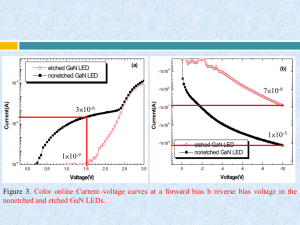
Improved Leakage Current, Output Power, and Electrostatic Discharge Characteristics of GaN LEDs by Chemical Etching Tae-Young Park, Chang-Hee Cho, Il-Kyu Park, and Seong-Ju Park Outline Introduction Experiment Results and Discussions Conclusions References Introduction Investigated the effect of chemical etching of the pGaN surface on the leakage current, light output power, and ESD characteristics of GaN LEDs. Experiment Ni/Au(30/80nm) Ni/Au(5/5nm) current spreading layer P MQW Mg(2×1020cm-3)-doped p-GaN(0.13 μ m) 5- period-InGaN(3nm)/GaN(7nm) N Si(9×10-18cm-3)-doped n-GaN(2 μ m) sapphire substratrs LED size 300 ×300 μ m Ti/Al(30/80nm) Results and Discussions CFB = 1/1/Cox + LD/εs Cox :氧化物電容3.5 10−11 F LD :德拜(Debye)長度 1.02 10−8 m εs : GaN介電常數8.9 德拜長度: 一方面是靜電作用的屏蔽半徑 一方面是區域性電荷分離的空 間尺度。 量測電容Sample: Al(100nm)/SiO2(15nm)/p-GaN(1μm)/u-GaN(2μm) Figure 1. Color online C-V curves for nonetched and etched p-GaN MOS capacitor devices at 100 kHz. DDAP :施子與淺層受子對,波峰是決定於摻雜的鎂濃度大小。 鎂摻雜濃度較高時,只能觀察到2.8eV 的波峰。 Mg GaN Figure 2. Color online Room-temperature PL spectra for the etched and nonetched p-GaN layer. 7×10-8 3×10-6 1×10-5 1×10-9 Figure 3. Color online Current–voltage curves at a forward bias b reverse bias voltage in the nonetched and etched GaN LEDs. Figure 5. Color online ESD characteristics of the nonetched and etched GaN LEDs: a forward voltage measured at 20 mA after application of positive-voltage ESD stress and b forward voltage measured 20 mA after application of negative-voltage ESD stress. 58% at 20mA Figure 4. Color online Light output power of etched and nonetched GaN LEDs as a function of injection current. Conclusions Defects were densely concentrated near the surface region ~18 nm of the p-GaN layer and were effectively removed by using a molten KOH and NaOH solution. The defect-assisted leakage currents at the forward and reverse bias voltage were remarkably decreased due to a reduction of DDAP defect, and the light output power of etched GaN LEDs was significantly improved by 58% at an injection current of 20 mA due to enhanced injection efficiency. The negative-voltage ESD characteristics of GaN LEDs were also improved from −0.3 to − 0.9 kV. References 1. S. Nakamura, M. Senoh, N. Iwasa, and S. Nagahama, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., Part 2, 34, L797 1995. 2. S. Nakamura and G. Fasol, The Blue Laser Diode, Springer, New York 1997. 3. X. Cao and S. D. Authur, Appl. Phys. Lett., 85, 3971 2004. 4. G.-Y. Ha, T.-Y. Park, J.-Y. Kim, and S.-J. Park, IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett., 19, 813 2007. 5. S. J. Chang, C. H. Chen, Y. K. Su, J. K. Sheu, W. C. Lai, J. M. Tsai, C. H. Liu, and S. C. Chen, IEEE Electron Device Lett., 24, 129 2003. 6. S.-C. Shei, J.-K. Sheu, and C.-F. Shen, IEEE Electron Device Lett., 28, 346 2007. 7. T. Inoue, Jpn. Pat. H11-040848 1999. 8. J. J. Horng, Y. K. Su, S. J. Chang, W. S. Chen, and S. C. Shei, IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab., 7, 340 2007. 9. T. C. Wen, S. J. Chang, C. T. Lee, W. C. Lai, and J. K. Sheu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 51, 1743 2004. 10. Y. K. Su, S. J. Chang, S. C. Wei, R. W. Chuang, S. M. Chen, and W. L. Li, IEEE Electron Device Lett., 26, 891 2005. 11. J. I. Pankove and T. D. Moustakas, Gallium Nitride (GaN) II, Vol. 57, Academic Press, New York 1999. 12. J. Sun, K. A. Rickert, J. M. Redwing, A. B. Ellis, F. J. Himpsel, and T. F. Kuech, Appl. Phys. Lett., 76, 415 2000. 13. D. Li, M. Sumiya, S. Fuke, D. Yang, D. Que, Y. Suzuki, and Y. Fukuda, J. Appl. Phys., 90, 4219 2001. 14. C. M. Tsai, J. K. Sheu, P. T. Wang, W. C. Lai, S. C. Shei, S. J. Chang, C. H. Kuo, C. W. Kuo, and Y. K. Su, IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett., 18, 1213 2006. 15. J. B. Fedison, T. P. Chow, H. Lu, and I. B. Bhat, Appl. Phys. Lett., 72, 2841 1998. 16. P. Visconti, K. M. Jones, M. A. Reshchikov, R. Cingolani, H. Morkoç, and R. J. Molnar, Appl. Phys. Lett., 77, 3532 2000. 17. J. L. Weyher, P. D. Brown, J. L. Rouviére, T. Wosinski, A. R. A. Zauner, and I. Grzegory, J. Cryst. Growth, 210, 151 2000. 18. T. Kozawa, T. Kachi, T. Ohwaki, Y. Taga, N. Koide, and M. Koike, J. Electrochem. Soc., 143, L17 1996. 19. P. J. Hartlieb, A. Roskowski, R. F. Davis, W. Platow, and R. J. Nemanich, J. Appl. Phys., 91, 732 2002. 20. R. S. Muller, T. I. Kamins, and M. Chan, Device Electronics for Integrated Circuits, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York 2003. 21. S. M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York 2002. 22. S. J. Pearton, C. R. Abernathy, B. P. Gila, A. H. Onstine, M. E. Overberg, G. T. Thaler, J. Kim, B. Luo, R. Mehandru, F. Ren, et al., Opto-Electron. Rev., 10, 231 2002. 23. Y. Nakano, T. Kachi, and T. Jimbo, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B, 21, 2220 2003. 24. S.-W. Kim, J.-M. Lee, C. Huh, N.-M. Park, H.-S. Kim, I.-H. Lee, and S.-J. Park, Appl. Phys. Lett., 76, 3079 2000. 25. Y. J. Lin, Z. L. Wang, and H. C. Chang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 81, 5183 2002. 26. W. Götz, N. M. Johnson, and D. P. Bour, Appl. Phys. Lett., 68, 3470 1996. 27. A. Y. Polyakov, A. V. Govorkov, N. B. Smirnov, A. E. Nikolaev, I. P. Nikitina, and V. A. Dmitriev, Solid-State Electron., 45, 261 2001. 28. M. Smith, G. D. Chen, J. Z. Li, J. Y. Lin, H. X. Jiang, A. Salvador, W. K. Kim, O. Aktas, A. Botchkarev, and H. Morkoc, Appl. Phys. Lett., 67, 3387 1995. 29. U. Kaufmann, M. Kunzer, H. Obloh, M. Maier, C. Manz, A. Ramakrishnan, and B. Santic, Phys. Rev. B, 59, 5561 1999. 30. X. A. Cao, J. M. Teetsov, M. P. D’Evelyn, D. W. Merfeld, and C. H. Yan, Appl. Phys. Lett., 85, 7 2004. 31. X. A. Cao, E. B. Stokes, P. M. Sandvik, S. F. LeBoeuf, J. Kretchmer, and D. Walker, IEEE Electron Device Lett., 23, 535 2002. 32. L. S. Yu, L. Jia, D. Qiao, S. S. Lau, J. Li, J. Y. Lin, and H. X. Jiang, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, 50, 292 2003. 33. X. A. Cao, P. M. Sandvik, S. F. LeBoeuf, and S. D. Arthur, Microelectron. Reliab., 43, 1987 2003.