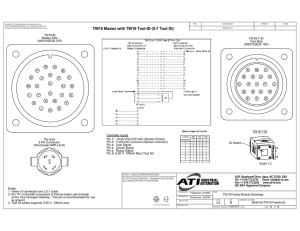
PIC - WikiService.at
advertisement

Microcontroller µC (PIC) • What`s the meaning of PIC ? • Programmable Integrated Circuit = Microcontroller • A PIC is a one-chip-microcontroller. • A normal computer with a “normal” microprocessor is build with some chips (IC). • PIC`s are integrated in one single chip. But why not all the computers are build in this way. The answer is very simple. The performance of PIC`s is compared with a normal computer very low. • One-chip-microcontroller are used to solve small tasks in a simple and cheap way. A solution build in a discrete analog or digital way would be more expensive. • µController are small, cheap and easy to use. The development of the circuit is very simple and we can concentrate our intelligence in the development of the program for the PIC. Microcontrollers make small embedded applications with minimal external circuits possible The 2. meaning of PIC • PIC is a family of Harvard architecture microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1650 originally developed by General Instrument`s Microelectronics Division. • PICs are very popular for developers and hobbyists because of their low cost, wide availability, large user base, extensive collection of application notes, availability of low cost or free development tools, and serial programming (and re-programming with flash memory) capability. • PICs were also commonly used to defend the security systems of popular consumer products (pay-TV, PlayStation), which attracted the attention of crackers. • Microchip recently announced the shipment of its 5 billionth PIC processor. Why to use PIC processors • There are different families of microcontrollers and what`s the main difference. <= ROM <= RAM CPU = central-processing-unit ALU = arithmetic-logic-unit RAM = random-access-memory ROM = read-only-memory <= RAM Von Neumann Computer • In a “von Neumann Computer” program-code and data are in the same memory. A normal personal-computer has exactly this architecture. • Programs are loaded from the hard-disk in the RAM (random-access-memory) and executed. In the same memory are also the data and even the information of the BIOS-Chips (Basic-Input-Output-System) (from mainboard, grafic-card or network-card, etc. are loaded in this memory. • This design has problems with viruses as everybody knows from his own PC. A virus or a trojan can come as data in the PC and can change in executable programcode and do a lot of damages. Harvard-architecture • A PIC is build in Harvard-design. Program-memory and Datamemory (RAM) are totally separated. This is very useful specially for microcontrollers. • With a PC we want to do all the time different tasks but a microcontroller is normally used only for one specialized task. • Program-memories for PIC`s are another type of memory. It`s called ROM (Read-Only-Memory) • The main differences between RAM and ROM : • RAM => Read and Write Memory – Data are lost when the computer is switched off • ROM => Read Only Memory – Data are stored when the computer is switched off • ROM`s are ideal for PIC`s They don’t loose the information and they cannot be disturbed from viruses and trojans. The program for PICs is all the time available. Different types of ROM`s • PROM = Programmable Read Only Memory only programmable not erasable • EPROM = Erasable Programmable Read-Only-Memory erasable by UV-light (100-200 times) • EEPROM = Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (1.000.000 times) • Flash-EEPROM like EEPROM fast and compact but only datablocks are erasable Memory- and bus-sizes • Low price PICs have only a data-bus and a datamemory with 8 bits. But for a program-command 8 bits are not enough. • Harvard-design permits the use of different sizes of dataand program-bus. Data-bus and –memory have for example 8 bit and and program-bus and -memory 12-, 14-, or 16- bit. • For more sophisticated applications are also 16-, 24-, 32- bit Microcontroller available • PICs from Microchip Technologie are available with 16bit Data- and 24-bit program-bus and -memory RISC and CISC • In the processor-technology are two different designs in use : • CISC = Complex Instruction Set Computer and • RISC = Reduced Instruction Set Computer • A CISC processor has a great and complex set of instructions and the programming is comfortable one command needs between • 4 – 10 clock-cycles • A RISC processor is faster because only a reduced set of instructions is used and one command needs normally only one clock-cycle • PICs have a RISC processor and PIC16F84 has 35 instructions PIC16F84 PIN # NAME DESCRIPTION 1 RA2 Second pin on port A. Has no additional function. 2 RA3 Third pin on port A. Has no additional function. 3 RA4 Fourth pin on port A. TOCK1 which functions as a timer is also found on this pin 4 MCLR 5 VSS Ground of power supply. 6 RB0 Zero pin on port B. Interrupt input is an additional function. 7 RB1 First pin on port B. No additional function. 8 RB2 Second pin on port B. No additional function. 9 RB3 Third pin on port B. No additional function. 10 RB4 Fourth pin on port B. No additional function. 11 RB5 Fifth pin on port B. No additional function. 12 RB6 Sixth pin on port B. 'Clock' line in program mode. 13 RB7 Seventh pin on port B. 'Data' line in program mode. 14 VDD Positive power supply pole. 15 OSC2 Pin assigned for connecting with an oscillator 16 OSC1 Pin assigned for connecting with an oscillator 17 RA0 Zero pin on port A. No additional function. 18 RA1 First pin on port A. No additional function. Reset input and Vpp programming voltage of a microcontroller PIC16F84 Test-Board Stückliste für 16F84-Testplatine1a • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 2 Buchsenleiste 36-polig 73 63 68-xx 2 Stiftleiste 8-polig 73 94 48-xx 1 Packung Brücken/Jumper 74 29 02-xx 2 LED-Zeile 8-fach, rot ZAQS 0807 18 57 60-xx 2 8-fach-Widerstand 8x1 kOhm Reichelt: SIL9-8 1,00k 1 IC-Fassung 14polig 18 96 18-xx 1 0-KraftSockel 20-polig --- 3 Klemmleisten, 8-polig Reichelt: WAGO 233508 2 DIL-Schalter, 8-polig BS-8 70 47 84-xx 2 Schaltkreis 74LS245 17 21 62-xx 1 Umschalter 70 15 05-22 1 Buchse f. Netzteil 73 39 80-xx oder ähnlich 2 ELKO 47uF / 35V 47 25 06-xx 1 Schaltkreis 7805 17 92 05-xx 1 Mini-Kühlkörper FK231 SA-220 18 82 71-xx 1 Gleichrichter B80C800 50 13 87-xx 3 Kondensator 100 nF 45 33 58-xx 1 HC18-Sockel für Quarze 16 87 77-xx 2 Kondensator 22 pF 45 16 73-xx 1 Taster 70 04 79-xx 1 Widerstand 220k 41 85 36-xx Components of a Microcontroller • CPU (Control Processing Unit): • It is the most important part of a µC, and it's in charge of: • Addressing the instruction's memory. • Receiving code from the instruction that is running. • Decode the operation sent by the instruction • Search the operands • Store the result. • Its memory locations are called registers