Impact of parenting according to the psychological perspectives
advertisement

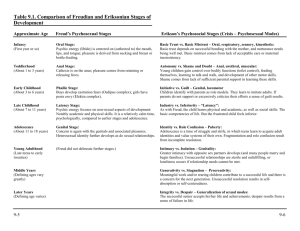
There Are Four Different Parenting Styles • Authoritarian~ Low Love and High Limits • Permissive ~ High Love and Low Limits • Authoritative ~ Democratic or Balanced: High Love and High Limits • Uninvolved ~ Rejecting/Neglecting: Low Love and Low Limits Impact of parenting according to the psychological perspectives Behaviorism • “Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I’ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select—doctor, lawyer, artist, merchant-chief and, yes, even beggar-man and thief, regardless of his talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors.” (1930) — John B. Watson Behaviorism • The environment a child grows up in has the most significant impact on shaping a child’s personality and skills • Children learn behaviors through rewards and punishments • Children learn through modeling and imitation • Activity: Outline a set of dos and don’ts for parents who wish to raise a child with high self esteem and to be socially acceptable Parenting Tips • Parenting Dos • Parenting Don’ts Humanism • positive regard - children seek for love, approval and acceptance from others especially their parents • unconditional positive regard - parents love and approval are freely granted not conditional on the child’s behavior • conditional positive regard - we receive love and approval for our positive behavior • conditions of worth - we see ourselves as worthy only under the conditions that are acceptable to our parents. We avoid behaviors or conditions that are not acceptable to our parents Activity: Create a “family sculpture” showing a parenting style and it’s impact on the function of the family. Psychoanalytic • emphasized the recognition of childhood events that could potentially influence the mental functioning of adults • Emphasizes importance of parents in guiding children to overcome certain “crises” that occur in development • Focus on unconscious conflicts that need to be overcome for normal development Psychoanalytic Psychosexual Development Pleasure-seeking energies become focused on certain erogenous areas. This psychosexual energy, or libido, was described as the driving force behind behavior. • If certain issues are not resolved at the appropriate stage, fixation can occur. A fixation is a persistent focus on an earlier psychosexual stage. • Psychosexual Development Oral Stage (birth-1year) • Erogenous Zone: Mouth- Pleasure from sucking and swallowing • Crisis: Weaning • Fixation: Oral receptive personality Oral aggressive personality Psychosexual Development Anal Stage (1 to 3 years) • Erogenous Zone: bowel and bladder control • Crisis: Potty training • Fixation: Anal retentive Anal expulsive Psychosexual Development Phallic Stage (3 to 6 years) Erogenous Zone: genitals Crisis: Oedipus complex or Electra complex castration anxiety and penis envy Identification with same sex parent Fixation: Failure to resolve complex explains many behaviors Psychosexual Development Latency Stage (6 to 11 years) Erogenous Zone: Sexual desire is repressed Crisis: Sexual energy is converted to socially valued activities Fixation: the child must develop a certain degree of competence in socially acceptable behaviors Psychosexual Development Genital Stage (11 years on) Erogenous Zone: genitals Crisis: sexual and romantic interest is directed toward’s one’s peers Fixation: If the other stages have been completed successfully, the individual should now be wellbalanced, warm and caring.