Structure & Function
advertisement

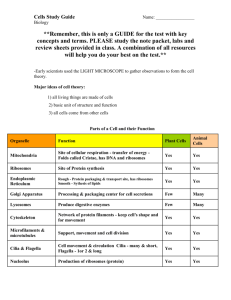
The Cell Structure & Function Dr. Childs Science Computer Lab Spring, 2004 Types of Cells Two major groups of cells: • Prokaryotes • Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Prokaryotes are simple cells: - Lack a membrane-bound nucleus - Lack membrane-bound organelles - Reproduce by binary fission - Includes bacteria Eukaryotes Eukaryotes: - Membrane-bound nucleus - Membrane-bound organelles - Reproduce by mitosis - Includes fungi, plants, animals Organelles Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound structures called “organelles” Structure and Function • Cells look like what they do!! Nerve cells – transmit electrical nerve impulses Muscle cells – contractile fibers Red blood cells – carry oxygen in tiny blood vessels White blood cells Ingest & destroy bacteria Protozoa – cilia for swimming Eukaryotic Cell Structure • Cell membrane • Cytoplasm • Nucleus • Membrane-bound organelles mitochondria chloroplasts • Endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes Think of the cell as a factory! Eukaryotic Cell Structure nuclear membrane nucleolus mitochondria nucleus cell membrane Nucleus Chromatin Nuclear pores Nucleolus Nuclear membrane • Surrounded by a double nuclear membrane with pore. • Chromatin is site of DNA – forms chromosomes. • Prominent nucleolus – site of ribosome synthesis. Factory – Nucleus is the control center. Blueprints in DNA. Nucleus chromatin – site of DNA nuclear pore – allows passage of molecule nuclear membrane - double membrane nucleolus – produces ribosomes rough endoplasmic reticulum Note: during mitosis chromatin condenses to form chromosomes In a factory, the nucleus would be the control center and contains blueprint in the form of DNA Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum rough endoplasmic reticulum “rough ER” Rough endoplasmic reticulum (or “rough ER”) is the site of protein synthesis. These are membranes lined with ribosomes. The ribosomes look like “dots”. In a factory, the rough ER would be the assembly line. Ribosomes Ribosomes The “dots” on the rough ER are ribosomes. Ribosomes are composed of a “large subunit” and a “small subunit”. Proteins are assembled on the ribosomes. In a factory, the ribosomes are the machines on the assembly line. Golgi Complex Golgi complex • The Golgi complex is a series of flattened membrane sacs. These complete final protein assembly. Secretory vesicles • Proteins are “shipped” from the cell in secretory vesicles (membrane-bound sacs). In a factory, the Golgi complexes are the site of final assembly and shipping. Protein Synthesis Proteins are synthesized on the ribosomes on the rough ER. Final synthesis is in the Golgi complex. Secretory vesicles carry proteins to membrane, then out of the cell. Lysosomes lysosomes Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes. Small spherical organelles with single membranes with a dense interior. Site of intracellular digestion. Digests food or foreign bodies as bacteria. In a factory, the lysomes are the “vacuum cleaners” and recycling centers of the cells. Mitochondria Mitochondria are the site of energy production. Energy is used for almost all cellular functions. Respiratory enzymes break down sugars into high energy molecules. Mitochondria have double membranes. The inner membrane has finger-like “cristae”. In a factory, the mitochondria are the “powerhouses” of the cell. Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis and are unique to plant cells. Chloroplasts are green because of the presence of chlorophyll, the pigment that captures energy from the sun chloroplast grana The chlorophyll is located in the membranes of “stacked coins” or grana Vacuoles Plant cells have a large central vacuole. This serves to store water and nutrients as well as to have maintain the rigid shape of the cell. central vacuole Vacuoles Contractile vacuoles occur in singlecelled protozoa. contractile vacuole These help pump out excess water. Cell Membranes & Cell Walls Both plant and animal cells have a cell membrane that is bilaminate – it has two layer. In addition, plant cells have a rigid cell wall composed of cellulose. This helps the plant cell maintain their shape. cell membrane cell wall Microtubules Centrioles Centrioles are usually located near one of the poles of the cells. They are composed of short sections of microtubules. Centrioles are only found in animal cells; not in plant cells. These have a role in mitosis (cell division) Microtubules Flagella & Cilia Flagella and cilia are commonly found in protozoa. Flagella are long and few; cilia are short and many. Cilia are also found in some animal cells; for example, cells lining the respiratory tract ciliated. cilia flagella Flagella and cilia are composed of microtubules. microtubules cross-section of flagellum