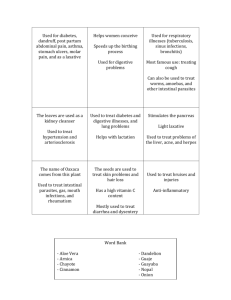
There are six main types of disease causing agents or pathogens
advertisement
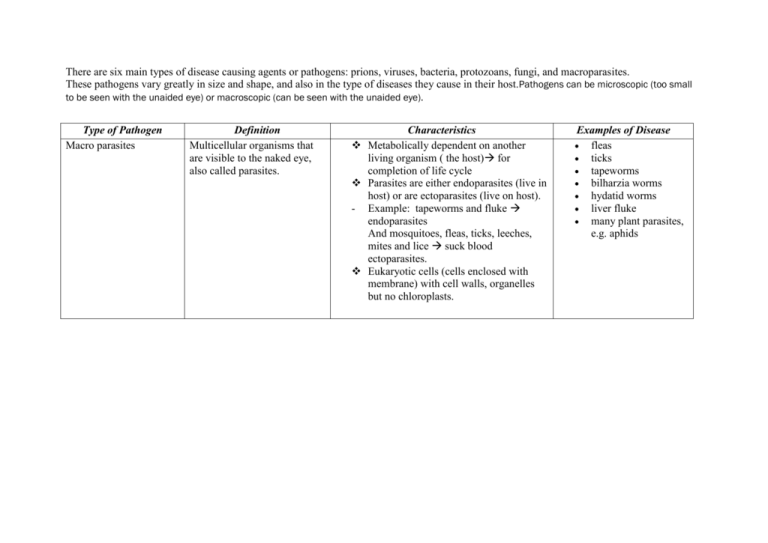
There are six main types of disease causing agents or pathogens: prions, viruses, bacteria, protozoans, fungi, and macroparasites. These pathogens vary greatly in size and shape, and also in the type of diseases they cause in their host.Pathogens can be microscopic (too small to be seen with the unaided eye) or macroscopic (can be seen with the unaided eye). Type of Pathogen Macro parasites Definition Multicellular organisms that are visible to the naked eye, also called parasites. Characteristics Metabolically dependent on another living organism ( the host) for completion of life cycle Parasites are either endoparasites (live in host) or are ectoparasites (live on host). - Example: tapeworms and fluke endoparasites And mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, leeches, mites and lice suck blood ectoparasites. Eukaryotic cells (cells enclosed with membrane) with cell walls, organelles but no chloroplasts. Examples of Disease fleas ticks tapeworms bilharzia worms hydatid worms liver fluke many plant parasites, e.g. aphids Virus: Protozoa: Fungi: