2.4 - SBI3URHKing
advertisement

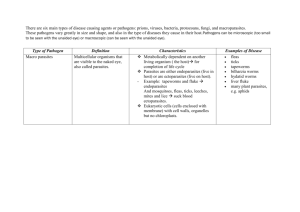
Most are unicellular There are 3 groups Animal like Fungus like Plant like A protist is an eukaryote that is NOT a plant, animal or fungus Aka protozoans They are heterotrophs – they eat prokaryotes and other protozoans Many are parasites (living off other organisms i.e. where they live – at the expense of that organism) Ex. Amoeba No cell walls, only cell membrane Changes shape using cytoskeleton to move and create different forms Creates pseudopod (refer to page 73 figure 2.18) Lives in salt/fresh water, mud, inside animal hosts They have short hair like projections called cilia They help in cell movement Many speices are large and complex Some are are free living, some are parasite Have one or more flagellum Have hard protective covering Some are free living, some are parasites, some exist in mutualistic relationships Ex. Flagellates in intestines that help hosts digests plants These are parasites of animals They alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction (Refer to pg 74 Figure 2.21) Heterotrophs They have spores like fungi Ex. Slime mould Visible to the naked eye Slug like organism near damp, decaying plant materials Contains many nuclei Engulfs materials like an amoeba Exist as individual amoebid cells Feeds by ingesting bacteria/ yeast cells Filamentous organisms Live on dead organic material Some are parasites \Releases threads into hosts, then digestive enzymes, then absorbs nutrients Contain pigments in their chloroplast that allows for photosynthesis to occur Phytoplankton, single celled free floating aquatic oragnism Rigid cell walls made of silica Asexual, reproduce via mitosis most of the time Sexually, if unfavourable conditions Most are phytoplankton 2 flagella perpendicular to each other Reproduce very quickly Sometimes , so quickly that it produces a “red tide” Some dinoflagellates live in other organisms Most exhibit mutualism Most are found in shallow fresh water Conduct photosynthesis AND can absorb nutrients Autotrophs in sunlight Heterotrophs in absence of sunlight Has light detectors called eyespots that allows the flagella to orient the euglenoid towards the light