1 - whitburnscience
advertisement

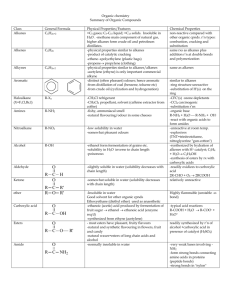
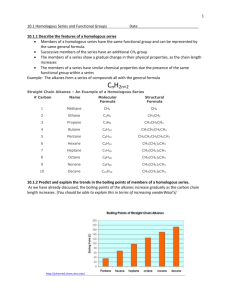
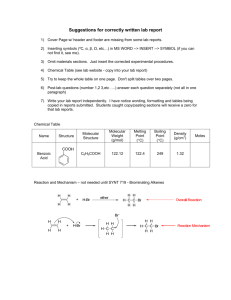
NATIONAL 5 - CHEMISTRY NATURES CHEMISTRY HOMEWORK "Let them who has earned it bear the reward". – Whitburn Academy (est. 1969) –school motto HOMEWORK DEADLINE DATE SCORE TEACHER COMMENTS 1 14 Homologous series (combustion) – 2 32 Homologous series (alkanes) – 3 33 Homologous series (alkenes) – 4 20 Homologous series (cycloalkanes) – 5 26 Homologous series (hydrocarbon reactions) - 6 26 Everyday consumer products (alcohols) - 7 20 Everyday consumer products (carboxylic acids) - 8 23 Everyday consumer products (esters) - 9 10 rating 16 Functional groups - Energy from fuels - HOMEWORK 1 – HOMOLOGOUS SERIES (COMBUSTION) 1) Petrol is an important fuel. The combustion of petrol is a very important reaction that is an exothermic reaction. Explain what is meant by each of the terms underlined. (3) 2) Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), which can be used as a fuel for heating, is a mixture of propane and butane. Propane and butane are members of the homologous series of alkanes. Copy the following table and tick (✓) the two boxes that correctly describe members of the same homologous series. (2) b) Propane is a hydrocarbon, name two products that would be formed when it burns completely in oxygen. (2) c) Copy and complete the word and chemical equation below and try to balance the equation. propane + oxygen ? + ? + O2 ? + ? (3) 3) The viscosity of four types of hydrocarbons was compared by measuring the rate of fall for a ball bearing. The diagram shows the position of the ball bearings 10 seconds after being dropped in each liquid. Below each liquid is the stated length of the hydrocarbon chains found in each substance. a) State the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the effect on the viscosity of the liquid. (1) b) The results after ten seconds were recorded: petrol – 85cm, paraffin – 60cm, diesel – 33cm and Lubricating oil – 16cm. Construct a table to record this information and produce a graph to represent the relationship identified in the previous question (1) (2) HOMEWORK 2 – HOMOLOGOUS SERIES (ALKANES) Q1) Complete the following table for the alkanes. Name of Hydrocarbon Molecular Structure Molecular Formula C2H6 Propane C5H12 (6) 2) Explain what is meant by a homologous series. (1) 3) State the general formula for the alkanes (1) 4) A combustion reaction of a substance occurs in a plentiful supply of air and carbon dioxide and water are produced. Which statement can be made with certainty about the substance? The substance A) is an alkane B) is a hydrocarbon C) contains carbon and hydrogen D) contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (1) 5) a) Draw a diagram to show how all the outer electrons are arranged in a molecule of methane, CH4. (1) b) Draw a diagram to show how all the outer electrons are arranged in a molecule of methanol, CH3OH. (1) Q6) Skeletal structure is a short hand method of drawing hydrocarbon structure and gives some detail about molecular geometry. Complete the skeletal structure below for the alkanes. Methane Ethane Propane Butane Pentane No Skeletal structure (2) Q7) Name the following branched chained alkanes from their full structural formula (4) Q8) (4) Q9) Draw the full structural formula for the following branched alkanes: 2-methyl propane 2,3,4-trimethylpentane 4-ethyl hexane 5-ethyl-3,3-dimethylheptane (4) Q10) A correct name for an isomer of 2,2-dimethyl butane is A) Cyclohexane B) 1,2-dimethyl pentane C) 1,2-dimethyl pentane D) 2,2,3-trimethylpropane (1) *Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula* Q11) Draw the shortened structural formula for the following branched alkanes. (a) 3-ethylhexane (1) (b) 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (1) (c) 3-ethyl, 2-methylpentane (1) Q12) In each of the following lists of hydrocarbons identify which one is in a different homologous series from the others. i) ethane, butene, methane, octane (1) ii) C3H8, CH4, C7H14, C12H26 (1) Q13) Naphtha (long hydrocarbon) can be cracked (broken up) to give a number of useful products. A typical result is shown in the table. Product % by mass methane ethane propene 15 25 16 petrol other 28 16 (a) Draw a pie chart to show this result. (1) HOMEWORK 3 – HOMOLOGOUS SERIES (ALKENES) Q1) Complete the following table for the alkenes. Name of Hydrocarbon Molecular Structure Molecular Formula C2H4 Propene C5H10 (6) Q2) Which structural feature makes the alkenes different from the alkanes? (1) Q3) What is the general formula for the alkenes? (1) Q4) Which two reactions are not commonly undergone by alkenes? A) addition B) neutralisation C) hydration D) displacement E) Combustion (2) Q5) Skeletal structure is a short hand method of drawing hydrocarbon structure and gives some detail about molecular geometry. Complete the skeletal structure below for Q6) The first four members of the amine homologous series are: What is the general formula for this homologous series? (1) Naming Straight/Branched Alkenes Rules 1. Identify the longest carbon chain. Rules 2. Number carbon atoms starting at the end nearest the double bond. 3. Identify the number of the carbon atom where the double bond starts, and insert it into the name. Pent-2-ene 2-methyl propene Q7) Name the following straight and branched chained alkenes. (4) Q8) Name the following alkenes: (4) Q9) Draw the full structural formula for the following branched alkanes: 2-methyl but-1-ene 2,3,4-trimethylpent-2-ene 4-ethyl hex-2-ene 3-ethyl-5,5-dimethylhept-3-ene (4) Q10) Correct names for the two isomers of but-2-ene are: A) Cyclobutane B) pent-2-ene C) 1,2-dimethyl propene D) 2-methyl prop-1-ene (2) *Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula* Q11) Draw the shortened structural formula for the following branched alkanes. (a) 3-ethylhex-2-ene (1) (b) 2,3,4-trimethylpent-1-ene (1) (c) 3-methyl pent-2-ene (1) Q12) a) This table has been extracted from page 9 from the National 5 Data Booklet. State the relationship between number of carbons in the compound and the general trend observed for melting and boiling point. (1) b) Complete the bar graph below for the melting and boiling points of the alkenes (2) HOMEWORK 4 – HOMOLOGOUS SERIES (CYCLOALKANES) Q1) Complete the following table for the alkenes. Name of Hydrocarbon Molecular Structure Molecular Formula C3H6 Cyclobutane C6H12 (6) Q2) What term in chemistry would be used to describe cyclobutane and butane? (1) Q3) What is the general formula for the cycloalkanes? (1) Q4) Skeletal structure is a short hand method of drawing hydrocarbon structure and gives some detail about molecular geometry. Complete the skeletal structure below for the alkenes. Q5) The grid shows some structural formula of hydrocarbons. a) Which two hydrocarbons above are unsaturated? (2) b) Which two are isomers? (1) Q6) a) Which of the following hydrocarbons could not possibly belong to a hydrocarbon with molecular formula C3H6. (1) b) Name the above compounds A) B) C) D) (4) c) When the above compounds undergo complete combustion what products are formed? (1) d) Which of the following is not the first member of a homologous series? (1) HOMEWORK 5 – HYDROCARBON REACTIONS Q1) Complete the following mind map for the addition reactions shown for prop-1-ene. +H2O Addition Reactions +H2 Cl2+ +HBr (8) 2. (a) Explain what is meant by i) a saturated hydrocarbon, ii) an unsaturated hydrocarbon. (2) 3. chloroethane H2 X Y 1,2-dichloroethane (a) Draw the full structural formula for compound X. (1) (b) Name reagent Y. (1) 4. Three different hydrocarbons were treated with bromine solution. Each of the hydrocarbons contained six carbon atoms. The results are shown below. Formula Hydrocarbon Effect on Bromine C6H12 A decolourises quickly C6H14 B no immediate change C6H12 C no immediate change Give the names and possible structures for A, B and C. (6) 5. There are many chemical compounds containing the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The extended structural formula for three such compounds are shown. A class carried out experiments with each of the compounds. Reaction Compound with sodium metal A gas produced Effect on acidified potassium permanganate Flammable or not flammable goes colourless flammable B no reaction goes colourless flammable C no reaction None flammable One pupil’s results are shown. (a) From the results, what general statement can be made about all three compounds? (1) (b) From these results, describe how to distinguish A from B. (1) (c) Predict what will happen when acidified potassium permanganate is added to a compound with the structure shown. (1) 6. Alkanes can be made by the reaction of sodium with iodoalkanes. This is called the Wurtz synthesis. For example, ethane can be made from iodomethane. (a) Name the alkane which forms when sodium reacts with iodoethane. (1) (b) Two different iodoalkanes are used to make propane. Name the two iodoalkanes. (2) (c) The Wurtz synthesis can also be used to make cycloalkanes. Draw the full structural formula of the compound which could be used to make cyclobutane. (2) HOMEWORK 6 – EVERYDAY CONSUMER PRODUCTS (ALCOHOLS) Q1) Complete the following table for the alkanols. Name of Hydrocarbon Molecular Structure Molecular Formula CH3OH Ethanol C4H9OH (6) Q2) Which structural feature is unique to the alkanols different from the alkanes? (1) Q3) What is the general formula for the alkanols? (1) 4) Give the systematic name for each of the following alkanols. 5) Draw a shortened structural formula for each of the following alkanols. Methanol hexan-2-ol pentan-3-ol (3) 6) Give the systematic name for each of the following alkanoic acids. (a) (b) O H C OH O CH3 CH2 CH2 C OH (2) 7) Draw shortened structural formula for each of the following acids. ethanoic acid pentanoic acid butanoic acid hexanoic acid. (4) 8) Which of the following is the alcohol (CH3OH) not used for: A) fuels B) alcoholic drinks D) raw material for industry C) solvent E) making esters (1) Q9) Car manufacturers have developed flexible fuel engines for vehicles. These vehicles can run on ethanol or petrol or a mixture of both. Ethanol can be produced from ethane which comes from cracking crude oil. It can also be made by fermenting glucose which is obtained from crops such as sugar cane and maize. a) The structure of ethanol is shown below. Circle the functional group in this molecule. (1) b) Ethanol is produced from ethane as shown. i) Name the type of chemical reaction taking place. ii) Draw a structural formula for a product of the following reaction. (1) (1) Q10) State a disadvantage of producing ethanol from crops. (1) HOMEWORK 7 – EVERYDAY CONSUMER PRODUCTS (CARBOXYLIC ACIDS) Q1) Complete the following table for the carboxylic acids. Name of Hydrocarbon Molecular Structure Molecular Formula HCOOH Ethanoic acid C3H7COOH (6) Q2) Which structural feature is unique to the alkanoic acids? (1) Q3) What is the general formula for the alkanoic acids? (1) Q4) a) i) Suggest a pH value for hipposudoric acid. (1) ii) Hipposudoric acid contains a hydroxyl group and a carboxyl funstional group. Circle and label each functional group on the structure above. (2) b) Bottles of sun cream display a sun protection factor which gives an indication of how well the sun cream protects against UVB radiation. The table information about sun protection factors. Plot a line graph of the results. (2) Q5) A carbon compound is insoluble in water and cannot decolourise bromine solution. It may be A) Cycloheptene B) propanoic acid C) heptane D) propanol (1) Q6) Some indicators can have different colours when in solutions of different pH values. The table gives information about two indicators, bromothymol blue and methyl orange. The pH of three solutions was investigated using both indicators. The results are shown below. a) Which solution is alkaline? (1) b) Suggest a pH value for solution B. (1) Q7) Synthetic nappies contain hydrogel polymers which attract and absorb water molecules. A section of the polymer is shown. What functional group can you see that is repeating through the polymers structure? (1) Q8) A student tested some compounds. The results are given in the table. Which line in the table below shows the correct results for the following compound? (1) Q9) Sodium ethanoate or sometimes known as sodium acetate is the solution present in click and heat hand warmers. a) Using page 8 of your data booklet write the chemical formula of sodium ethanoate (1) b) Sodium ethanoate can be made in a neutralisation reaction. Write a word equation of a chemical reaction that would produce sodium ethanoate. (1) HOMEWORK 8 - EVERYDAY CONSUMER PRODUCTS (ESTERS) Q1) Complete the table below. Alcohol Carboxylic acid Ester Proponol Propyl ethanoate Hexanol Butanoic acid Butyl butanoate Methyl pentanoate hexanol Methanoic acid (7) Q2) What two substances are reacted together to make an ester? (1) Q3) Which of the following characteristics are not typical of esters? A) fruity smells B) soluble in water C) artificial flavourings D) solvents E) are insoluble in water F) are liquids (2) Q4) State two uses of esters. (2) Q5) Draw the functional group of an ester. (1) Q6) Draw a structural formula for each of the following esters. (2) Making Esters in the lab Q7) A student made an ester in the lab, complete their lab report for them. Aim: To synthesize an ester, ethyl ethanoate and identify some of its properties. The reaction rate was increased by two methods: - Diagram: The function of the ‘wet paper tower’ condenser was … Sodium hydrogencarbonate was added to … Results The two pieces of evidence observed that ethyl ethanoate had been produced was Conclusion Shown below is a complete word and structural equation of the reaction being carried out to produce the ester ethyl ethanoate. (8) HOMEWORK 9 – FUNTIONAL GROUPS Q1) Circle and name all the functional or structural groups in the following compounds as you can. The molecule below is found in the disinfectant Dettol, which we instantly recognise by its distinctive smell. Dettol (chloroxylenol) helps us fight unwanted bacteria. Butanoic acid has a powerful, unpleasant odour. It is found in rancid butter, Parmesan cheese and vomit 4-formamidobenzoic acid is used in pharmaceutical compositions. Cinnamon is a tasty spice used to flavour biscuits, cakes and pies. Cinnamon also has medicinal properties. Methyl anthranilate occurs naturally in grapes and is used as grape flavouring in drinks and chewing gum. Vitamin C is needed in your diet for the growth and repair of tissues in all parts of your body. None identified (Poor) some identified (not bad) most identified (good) almost all identified (Excellent) all identified (Outstanding) HOMEWORK 10 – ENERGY FROM FUELS Q1) Write and define the following terms in the equation to calculate the energy released when fuels burn. (3) Q2) Alkanes burn releasing energy. a) What name is given to any chemical reaction that releases energy? (1) b) A student investigated the amount of energy released when an alkane burns using the following equipment. The student recorded the following data. a) Calculate the energy released in KJ. You may wish to use your data booklet to help you. Show your working. (3) b) Suggest one improvement to the students experiment. c) The table gives information about the amount of energy released when one mole of some alkanes are burned. i) Describe the relationship between the number of carbon atoms and the energy released when alkanes are burned. (1) ii) Predict the amount of heat released, in KJ, when one mole of pentane is burned. (1) Q3) The experiment shown can be carried out to establish how much energy is released when ethanol burns. In the experiment it was found that burning 0.1g of ethanol increased the temperature of the water by 7C. Calculate the energy released in this reaction, in KJ. Show your working. (3) Q4) Cool packs can be used to treat some sports injuries. Cool packs contain solid ammonium nitrate and water in two separate compartments. When the pack is squeezed the ammonium nitrate dissolves in the water forming a solution. This results in a drop in temperature. a) The change in temperature in the cool pack can be calculated using the equation below. Calculate the temperature change using the following information. Energy change (KJ) Mass of water (Kg) 6.72 0.2 (2) b) Write the chemical formula for ammonium nitrate (1) c) What term is used to describe a reaction that takes in heat from the surroundings? (1)