Principles of Business, Finance and Marketing
advertisement

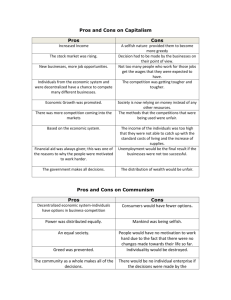
PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS, FINANCE AND MARKETING Units 1 & 2 Economic Decisions and Systems UNIT 1.01 Satisfying Wants & Needs Economic Choices Economic Systems Supply and Demand SATISFYING WANTS AND NEEDS Wants Not necessary for survival, but add comfort and pleasure to our lives i.e. video games, designer clothes, Needs Things that are necessary for survival i.e. food, clothing, shelter Question: Is a car a want or a need? BASIC ECONOMIC PROBLEM Unlimited wants and needs, limited economic resources Scarcity Not having enough resources to satisfy every need Limited supplies of goods and services Someone’s going to go without ECONOMIC CHOICES Opportunity Cost Value of the next best alternative that you were not able to chose Trade Off – what you make when you give something up to have something else Job College College vs. Work Annual Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 15 20 25 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ Income/ Expense 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 Cumulative $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 40,000 60,000 80,000 100,000 120,000 140,000 200,000 300,000 400,000 500,000 Annual Income/ Expense $ (20,000) $ (20,000) $ (20,000) $ (20,000) $ (20,000) $ 50,000 $ 50,000 $ 50,000 $ 50,000 $ 50,000 $ 50,000 Cumulative $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ (40,000) (60,000) (80,000) (100,000) (50,000) 150,000 400,000 650,000 900,000 DECISION MAKING PROCESS 6 Steps Define the problem Identify the alternatives List all pros and cons Choose among alternatives Act on your choice Evaluate your decision Example Can’t get to work Walk, bike, car, mooch ride Lazy, embarrassing, cool CAR! Spend $20K on used car Can’t afford gas FACTORS THAT AFFECT DECISION-MAKING Values Things that are important to you in life Goals Things a person wants to accomplish i.e. college degree, starting a business Freedom of Choice – the freedom to make decisions independently while accepting the consequences of those decisions ECONOMIC RESOURCES Factors of Production Natural Resources: raw materials (water, oil, trees) Renewable resources can be replaced Non-renewable resources cannot be replaced Human Resources : people who contribute physical or mental energy Capital Resources : tools, equipment, buildings, money, etc. used to produce goods and services ENTREPRENEURIAL RESOURCES Initiative to combine natural, human and capital resources to produce goods or services The 3 economic questions 1. What to produce? 2. How to produce? 3. What needs and wants to satisfy? Who decides this determines a countries economic system ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Traditionalism or Traditional Economy Do things the way they’ve always been done Pros: everyone has a role in the economy; economic life is stable Cons: discourages new ideas; growth is limited Examples: parts of Africa, Latin American rain forest ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Communism or Command Economy Government owns/controls all resources Pros: everyone has a job and benefits; can make a dramatic change in a short time on production of goods Cons: consumer goods rank low on priority list, few consumer wants are met; lack of incentive to work hard Examples: North Korea, China, Cuba ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Capitalism or Market Economy People owns/controls all resources Pros: produce goods & services people want and need; freedom of choice; income: input ratio; competition keeps prices lower Cons: wealth of economy not equally distributed Examples: US, Japan, Canada, Great Britian ECONOMIC SYSTEMS Socialism or Mixed Economy Government owns major industries; allows for private ownership of other businesses Pros: gov’t and private business work together; insurance/social security benefits provided Cons: high tax rates; smaller spendable income; discourages private business Examples: Sweden, France THE US ECONOMIC SYSTEM Private Property Business or individual owns their own property, not the government Freedom of Choice Freedom to make decisions independently while accepting the consequences of those decisions Profit Amount of money available to a business after all costs and expenses have been paid Competition Rivalry among businesses to sell their goods and services ECONOMIC DECISION-MAKING The process of choosing which needs and wants will be satisfied Consumer – person who buys and uses goods & services Producer – business that makes the goods & services Demand – the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing to buy The cheaper an item is, the more people will want/be able to afford it (and visa versa) Supply – the quantity of a good or service that businesses are willing and able to provide The more expensive it is to produce, fewer businesses are willing to make it (and visa versa) Consumers set demand, producers establish supply SUPPLY AND DEMAND ACL 1200 1000 Price of 3-day Pass 800 600 400 Demand 200 0 100000 150000 200000 250000 300000 350000 Number of Passes Sold 400000 450000 500000 550000 SUPPLY AND DEMAND ACL 1200 1000 Price of 3-day Pass Supply 800 600 400 200 0 100000 150000 200000 250000 300000 350000 Number of Passes Sold 400000 450000 500000 550000 SUPPLY AND DEMAND ACL 1200 1000 Price of 3-day Pass Supply 800 Market Price 600 400 200 0 100000 Demand 150000 200000 250000 300000 350000 Number of Passes Sold 400000 450000 500000 550000