May 4, 2012 - LAN Standards Update (Gary Eifert, TE)
advertisement

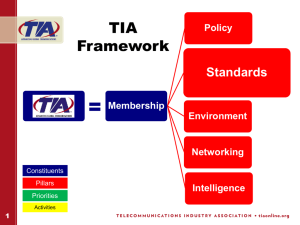
LAN Standards News and Trends Report BICSI Breakfast Meeting Hawaii Chapter May 4, 2012 Sponsors TE Connectivity CSC TR-42 Suite • Common Standards – End-users – Broadly Applicable Common Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.0 (Generic) • Premises Standards – End-users – Narrow Focus – Exceptions/Allowances to Common Standards • Component Standards – Manufacturers TIA-569 (Pathways and spaces) ANSI/TIA-606 (Administration) ANSI/TIA-607 (Bonding and grounding [earthing]) ANSI/TIA-758 (Outside plant) ANSI/TIA-862 (Building automation systems) Premises Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.1 (Commercial) ANSI/TIA-570 (Residential) ANSI/TIA-942 (Data centers) ANSI/TIA-1005 (Industrial) ANSI/TIA-1179 (Healthcare) Component Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 (Balanced twistedpair cabling and components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.3 (Optical fiber cabling components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.4 (Coaxial cabling and components) TR-42 Projects Common Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.0 (Generic) New Standard TIA-569 (Pathways and spaces) ANSI/TIA-606 (Administration) Premises Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.1 (Commercial) ANSI/TIA-570 (Residential) ANSI/TIA-942 (Data centers) New Revision ANSI/TIA-607 (Bonding and grounding [earthing]) Revision In Progress New Project ANSI/TIA-758 (Outside plant) ANSI/TIA-862 (Building automation systems) ANSI/TIA-1005 (Industrial) ANSI/TIA-1179 (Healthcare) Component Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 (Balanced twistedpair cabling and components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.3 (Optical fiber cabling components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.4 (Coaxial cabling and components) TR-42 Projects Common Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.0 (Generic) New Standard TIA-569 (Pathways and spaces) ANSI/TIA-606 (Administration) Premises Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.1 (Commercial) ANSI/TIA-570 (Residential) ANSI/TIA-942 (Data centers) New Revision ANSI/TIA-607 (Bonding and grounding [earthing]) Revision In Progress New Project ANSI/TIA-758 (Outside plant) ANSI/TIA-862 (Building automation systems) ANSI/TIA-1005 (Industrial) ANSI/TIA-1179 (Healthcare) Component Standards ANSI/TIA-568-C.2 (Balanced twistedpair cabling and components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.3 (Optical fiber cabling components) ANSI/TIA-568-C.4 (Coaxial cabling and components) TIA-FAQ • Can I use 568-C.0 for office-oriented building networks? • NO! – 568-C.0 is the foundation for 568-C.1, but the exceptions and allowances in 568-C.1 apply to office-oriented networks – Using 568-C.0 as the stand-alone standard when a type of premise has a standard is not appropriate TR-42 TR-42 Subcommittee Updates TR-42.1 Document Summary – 568-C.0 (Generic) • 568-C.0 – Generic Structured Cabling – Addendum 1 - (PUBLISHED) • Updated References for Balanced Twisted-Pair – Was 568-B.2 when publised – Now refers to » 568-C.2 » ANSI/TIA-1152-2009, Requirements for Field Test Instruments and Measurements for Balanced TwistedPair Cabling Document Summary – 568-C.0 (Generic) • 568-C.0 – Generic Structured Cabling – Addendum 2 – Default Ballot • General Updates – Fiber polarity » Method C illustration for parallel and 24-fiber – Field-testing updates for new OFSTPs » OFSTP-14B for multimode (adoption of IEC) – Revision to the MICE table – Revisions to application tables » OM4 fiber and 10GBASE-ER » OM3/4 lengths in table are “lowest common denominator” Document Summary – 568-C.1 (Comm’l/Offices) • 568-C.1 – Commercial Building Cabling •Addendum 1 – Pathways and Spaces (default ballot – will be held until 569-C publishes) •Work is taking place in TR-42.3 •Addendum 2 – General Updates (project approved) Document Summary – 568-C.1 (Comm’l/Offices) • 568-C.1 – Commercial Building Cabling – Addendum 1 – Tabled until 569-C publishes • Pathways and Spaces content from 569-B – Addendum 2 – Approved for Publication • General Updates – Entrance facility includes P&S – Reference to 568-C.0 for centralized cabling – Updated References for Balanced Twisted-Pair » Was 568-B.2 when published » Now refers to 568-C.2 and TIA-1152 Document Summary – 942-A (Data Centers) • 942-A – Data Centers – 2nd Industry Ballot – Removed the 100 meter length limitation for optical fiber horizontal cabling – Category 3 and category 5e are longer recognized for horizontal cabling – OM1 and OM2 are no longer recognized – Adds the IDA – intermediate distribution area – LC (1- or 2-fiber) and MPO (array) are recommended connectors for new fiber installations – Allowance for active components in the ZDA anve been removed – Recommendations for energy effciency have been added – OM4 recommended in the horizontal and backbone for all data centers – Comments to remove recommendation for Cat 6A in backbone not approved – Comments to include building information modeling (BIM) not approved Document Summary – 570-C (Residential • 570-C – Industry Ballot – Modification to text now include category 6A – Optical fiber drop cable added – Comments to allow violations of minimum bend radius for BIF not accepted – Comments recommending replacement of category 5e with category 6A were not accepted – Comments to add fiber to Grade 1 were not accepted Document Summary – 569-C (Pathways/Spaces) • 569-C Default Ballot (5 items) – Power separation and EMI/RFI debates continue • Contributions Still coming in showing evidence of problems • Language in documents – NOTE – The diversity of services currently available, coupled with the continual addition of new services, means that there may be cases where limitation to desired performance occur. When applying specific application to the infrastructure described in this Standard, the user is cautioned to consult application standards, regulations, equipment vendors, and system and service suppliers for applicability, limitations, and ancillary requirements. Document Summary – 569-C (Pathways/Spaces) • 569-C – Default Ballot (5 items) – Table for power separation edited to more closely align with ISO – Agreed to add a note • NOTE – These guidelines should be considered for all applications. Newer and , particularly, higher data rate applications (e.g., 10Gb/s) may be more susceptible to EMI. Accordingly, extra precautions or more conservative minimum separation distances should be considered. • Not without controversy – Other comments adding 230 VAC power strips, commentary on cable management and BAS accepted Document Summary – 606-B (Admin) • 606-B – Industry Ballot – Adopts identification scheme specified in 606-A Addendum 1 for racks, cabinets, frames – Creates new identification format for horizontal links, backbone cables, campus backbone cables, but allows old identifiers to continue being used. – Creates new identifiers for telecommunications outlets, equipment outlets, splices, etc. Document Summary – 606-B (Admin) • 606-B – Industry Ballot – Adopts graphic symbol for identifying powered ports – Introduces “Automated Infrastructure Management” • The automated infrastructure management systems should be capable of automatically documenting the infrastructure elements as described in this standard, providing a comprehensive record of all the connected equipment, facilitating easy trouble shooting, providing and automated method of discovering and documenting configuration of LAN and SAN switches and automatically discovering and documenting end devices that connect to the network. – Adding Symbols Document Summary – 1183 (1GHz) • New Standard to be TIA-1183 – 3rd Industry Ballot – Test Methods & Fixtures to 1000MHz – Comments to increase the frequency range from 1 GHz to 2GHz were rejected • A task group was set up to work on the 2GHz extension – Addition of an informative annex on test fixture de-embedding TR-42.7 Projects and Task Groups • Project approved to develop “next generation cabling for data transmission higher than 10GBps” – Not necessarily Category 7A • Recognized in ISO 11801 and IEEE 802.3an (10GBASE-T) • Project to Add Category 7A Cabling to the 568-2 Standard – Previous proposals “failed” in June and in February » One vote short of “greater than 2/3rd majority” • Task Group created to look at category 6A patch cord testing – Differences in ISO and TIA 568-C.0 Document Summary – 1005-A (Industrial) • TIA-1105-A – Default Ballot – Most changes result from making this a premise standaard based on 568-C.0 (not 568-B.1) – Separation content removed in favor of references to 569-C 568-C.1 Document Summary 568-C.3 (Fiber Components) • 568-C.3 New Addendum Published • 1st Addendum – Approved for Publication – Add OM4 to Table 1 • OM4 already allowed, just not previously called out – More on array connectors (40G and 100G support) – No new proposed color (aqua applies) – Comments that would have resulted in the introduction of fiber “categories” were not approved TR-42.1 Projects and Task Groupd • Looking at connector loss limits, loss budgets, and design guidance – Design to worst case model • 0.75dB maximum connector loss per mated pair – Design to a more realistic, satistical model • Provide a more accurate expectation for link loss • Connection performance – Connector performance based on max, 97%ils and mean loss – Proposals for four connector grades • 1.0, 0.75, 0.5 and 0.25 dB • Targets for max loss, 97%ile upper limits, mean loss upper limits 942 Document Summary – 598 (Color Codes) • TIA-598-C – Industry Ballot – Routine revision to the fiber cable color code standard – Adding testing and OM4 issues – This document establishes aqua for the OM4 color (as well as OM3) 942 LAN Standards News and Trends Report LAN Application Update IEEE 802.3 Projects • 802.3az – Energy Efficient Ethernet – Released for publication at February meeting – Reduced power consumption during idle periods • 802.3bg – 40GBASE-LR (serial 40G) – No disapprove votes on first ballot – Document will “fast-track” to publication – Lower cost option than current 40GBASE-LR4 IEEE 802.3 Calls for Intrest • Next Generation 100Gb/s Ethernet Interfaces for Optical Fiber – To explore the market need and solutions to reduce the cost, power and panel size of 100Gb/s optical interfaces that can be implemented with the interfaces currently defined by IEEE Std 802.3ba-2010 • Extended EPON PMDs – To explore the market demand, available technologies and definition of optical interface parameters for higher power EPON PMDs, building on top of IEEE Std 802.3ah and IEEE Std 802.3av, to address demand for high power budget classes to address requirements for longer reach and/or increased split ratio. 802.3ba IEEE 802.3 Other Subjects • Power Over Ethernet – There is a collective effort to pursue a “POE++” standard, but debates about the true demand need to be addressed. IEEE 802.3 LAN Standards News and Trends Report Thank You