The Road to Revolution
advertisement

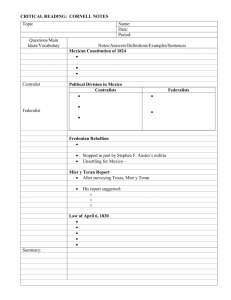
The Road to Revolution Chapter 9 Differences Arise • Some settlers established their own : – Newspapers – schools • Some settlers: – Kept their own customs – Did not become Catholic States Rights • Mexico’s Constitution of 1824 – Established states rights – Placed the province of Texas in the Mexican state of Coahuila y Tejas • Nationalist concerns increased hostilities Edwards Brothers • In 1825 Haden Edwards received a very large land grant in eastern Texas-near Nacogodoches. • Required to honor previous land grants-but many did not have proof. • After a bogus election the Governor reversed the election decision and took away the land grant. • Edwards negotiated a treaty with the Cherokees. Fredonian Rebellion • Occured near Nacogdoches in 1826. • Edwards and followers formed the Fredonian Republic. • Stephen Austin’s milita joined the Mexican government’s troops to defeat the Fredonians. An Attempt to Purchase Texas • Mexican officials feared that the settlers had secret ties with the U.S. • In 1826 U.S. president John Quincy Adams sent Joel Poinsett to Mexico with an offer buy all or part of Texas. The Mier y Teran Report • An increasing number of settlers from the U.S. the Fredonian Rebellion, and the offer to buy Texas fueled concerns of the Mexican nationalists. • Mexico sent Manuel Meir y Teran, a commander in the Mexican army, to investigate the conditions in Texas. Mier y Teran Report • Teran reported that the Anglo settlers outnumbered the Mexican settlers 10 to 1. • Noted that the United States influence was growing in Texas. • Mexican President Vicente Guerrero responded by attempting to make Texas less attractive for future colonists. The Law of April 6, 1830 • Purpose was to control Texas colonists. • Outlawed immigration from the U.S. to Texas and canceled all empresarial grants that had not been fulfilled. • The United State could no longer colonize any Mexican border state • This law also included other provisions designed to slow Anglo American immigration: – Slaves could no longer be brought in work the fields – New forts and presidios were built to stop illegal immigration – A customs duty was placed on all goods entering Texas from the U.S. The Law of April 6, 1830 • The government encouraged Mexican and European settlers to relocate to Texas-the law of April 6, 1830 even provided land and money for these settlers. • This law upset and alarmed Anglo Texans. • The law also raised questions within the Mexican government. • Increased the tensions between Texas and the Mexican government. Bitter Division • The Law of April 6, 1830 marked a turning point in the relationship between the Texas colonists and the Mexican Government. • Mexican troops were sent to Texas to collect customs duties. – Texans were upset at the presence of military force and the new taxes! Santa Anna • President Bustamante was ignoring the Constitution of 1824. – This upset many Anglo-Americans and Mexicans living in Texas. • Santa Anna claimed he was not a centralist. • He staged a revolution to oust President Bustamante. • Stephen F. Austin helped to convince the Mexican government that the Texans were in favor of Santa Anna. • Santa Anna lied and was actually a centralist. – He wanted all power centralized in himself, not in states’ rights. Turtle Bayou Resolutions • Settlers sent John Austin to Brazoria to bring back a cannon. • Turtle Bayou Resolutions – Colonists pledged their loyalty to Mexico and Santa Anna. – Remember: Santa Anna was a centralist posing as a nationalist! Battle of Velasco • John Austin has the cannon and he’s on his way back to Brazoria. – He and his men sail down the Brazos River toward the Gulf of Mexico. • They arrive in Velasco. – Colonel Urgartechea refuses to let the men pass through Velasco with the cannon. – Fighting breaks out! – First time Mexican and Texan troops fire at one another. Convention of 1832 • Texans met in San Felipe de Austin and drafted a set of resolutions. • Texans pledge their support for the Constitution of 1824. • Called for a repeal of the Law of April 6, 1830 and the customs duty. – Repeal: to take away • Wanted to allow U.S. immigration to Texas. • Wanted the Mexican government to divide the state of Coahuila y Tejas and grant Texas statehood. • Established a plan to create a militia. • Donate government lands for public schools. Convention of 1833 • Same proposals at the Convention of 1832 EXCEPT they drafted a new Constitution. – Mexican state of Texas! • To the Mexican government, this looked like an act of defiance! SFA is in Mexico • SFA leaves for Mexico to take the new resolutions to the Mexican government. • 1833 – impatient SFA wrote a letter to his fellow Texans. – The letter suggested the Texans establish a new state government. – New state government would make Texas separate from Coahuila but still a part of Mexico. • SFA meets with Santa Anna – Santa Anna repealed the immigration law prohibiting immigrants from the U.S. – Promised fair taxes on goods imported from the U.S. – Rejected separate statehood for Texas. SFA Arrested! • Austin’s letter to the Texans was intercepted. • He was accused of treason. • He was imprisoned in Mexico City for a year and never received a trial. Conflict Escalates • Texans soon found out that Santa Anna was a centralist and not a nationalist. • He had a new constitution written that placed all the power in his hands! • To squash any rebellion that might take place in Texas, Santa Anna sent General Cos to watch over Texas. Battle of Gonzales • General Urgartechea hears there is a 6 pound cannon in the town of Gonzales. • Texans refused to return the cannon. • When the Mexican army arrived, the Texans fired on the Mexicans forcing them to retreat to San Antonio. • This battle showed that the Texans were willing to use military force if necessary. • The Battle of Gonzales is the battle that began the revolution! Siege of Bexar (San Antonio) • Texans capture the city of San Antonio from General Cos. • Texans believed the crisis was over. • Santa Anna had other ideas!