Case Study 2 Powerpoint
advertisement

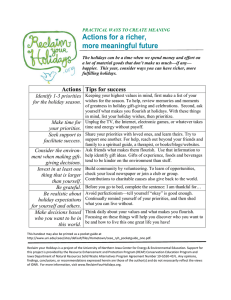
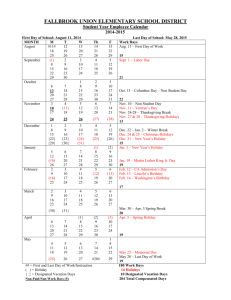
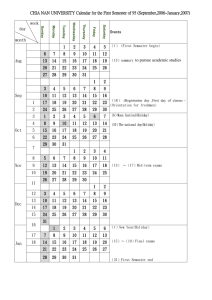
Religion in Schools Case Law Problem 2 David Black, Jim Jennings, Bob Feller, Joe Peters, Mark Goodwin, Connie Snell Religious Holiday break Decision - There was no Impermissible establishment of religion in creating a public holiday at the same time as the Christian holy day of Good Friday . The Board’s argument that these school closings served the secular purpose of saving money and maintaining the school’s effectiveness in the face of high rate absenteeism for those days Koenick V Felton (1999) Religious Holiday break cont. The same reasons the board closed schools for the Jewish holidays of Yon Kippur and Rosh Hashanah. The Court also stated that the holidays did not violate the other two prongs of the Lemon Test. Koenick V Felton (1999) Instruction of Religious Holidays Historical and cultural roots of religious holidays was permitted, but not in a manner which would indicate endorsement or disagreement with that religion or that holiday. School could erect displays with the religious symbols (menorahs, nativity scenes, etc.), but only if they are temporary and part of the general classroom instruction. Public Performance Public performances of religious music, religious dramas, religious poetry, were permitted if they were part of the educational efforts of the school. Results of decision: Public schools are permitted to make extensive use of religious materials during religious holidays of the administrator’s choosing without violating the separation of church and state. So long as the school can claim to be working for the purpose of educating students about the religious and historical heritage of the holiday – even if it is their own holiday which they know well – there is no constitutional problem. Florey V. Sioux Falls S.D. (1980) Proposal to the Student Handbook The school will not acknowledge holiday celebrations. The school will acknowledge seasonal holidays. The content of the curricula will be non-religious in nature. Cammack v. Waihee Pledge Of Allegiance Handbook Revision According to State Law 105:5/27-3, the Pledge of Allegiance will be recited every morning. Anyone whose documented religious beliefs do not allow them to recite the pledge may stand quietly with the class or remain quietly in their seats. West Virginia State Board of Education v. Barnette, 319 U.S. 624, 63 S. Ct. 1178 (1943). Supporting Cases Sherman v. Community Consolidated School District 21, 980 F.2d 437 (7th Cir. 1992). “Under god” is not understood to convey approval of any particular religious belief. Goetz v. Ansell, 477 F.2d 636 (2nd Cir. 1973). Cannot force student to leave the room or stand in silence during the pledge. Wisconsin v. Yoder, 406 U.S. 205, 92 S. Ct. 273 (1972). Due to longstanding and identifiable fundamental beliefs the Amish have demonstrated the sincerity of their religious beliefs that few other religious groups or sects could. We believe the Jehovah's Witnesses also make this case. Elk Grove Unified School District v. Newdow (02-1624) 542 U.S. 1 (2004) 328 F.3d 466, reversed. The Pledge is constitutional and the words “under god” do not violate the Establishment and Free Exercise Clauses. Pre-game Prayers Each student has a right to individually, voluntarily, and silently pray or meditate in school in a manner that does not disrupt instructional or other activities of the school. The school will not require, encourage, or coerce a student to engage in or to refrain from such prayer or meditation during any school activity (including but not limited to assemblies, sporting events, and graduations). School Policy Could Not Allow students to vote on whether a student would present a “brief invocation and/or message” before football games Students could not elect a student from a list of student volunteers to deliver it. Adler v. Duval City School Board, 250 F.3d 1330 (11th Cir. 2001). Court Held: Invocation is not a private speech Remarks were adopted by school officials Prayer took place on government property Game was a school-sponsored event Election System Ensured Minority view were not heard Students forced to decide between attending event or being subjected to offensive religious speech