Poetry
advertisement

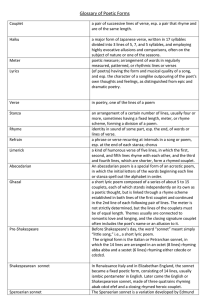
Structures, Forms, Genres and Rhyme Scheme The structure used in poems varies with different types of poetry. The structural elements include the line, couplet, and stanza. visual effect of a finished poem. The structure of many different types of poetry result in groups of lines on the page which enhance the poem's composition. Poetry is often separated into lines, may be based on the number of metrical feet, or may emphasize a rhyming pattern at the ends of lines Lines can separate, compare or contrast thoughts expressed in different units, or can highlight a change in tone COUPLET (TWO) QUATRAIN(FOUR) TRIPLET(THREE) SONNET HAIKU ODE FREE VERSE Sonnet, which by the 13th century was a poem of fourteen lines following a set rhyme scheme and logical structure. The sonnet's conventions have changed over its history, and so there are several different sonnet forms. Sonnets are particularly associated with love poetry, and often use a poetic diction heavily based on vivid imagery Shakespeare's sonnets are among the most famous in English poetry. Haiku is a popular form of unrhymed Japanese poetry, Generally written in a single vertical line, the haiku contains three sections, structured in a 5-7-5 pattern. Odes were first developed by poets writing in ancient Greek The ode generally has three parts: a strophe, an antistrophe, and an epode. Odes are often intended to be recited or sung Form of poetry that does not use consistent meter patterns, rhyme, or any other musical pattern. It thus tends to follow the rhythm of natural speech. a poet can still use them to create some sense of structure. Because of a lack of predetermined form, free verse poems have the potential to take truly unique shapes. Narrative Elegy Epic Verse Dramatic Prose Satirical Speculative Lyric Fable Narrative- tells a story, appeals to human interest, may be the oldest genre. Epic- lengthy poems concerning events of a heroic or important nature to the culture of the time. It recounts, in a continuous narrative, the life and works of a heroic or mythological person or group of persons. Dramatic- drama written in verse to be spoken or sung Satirical- vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, ideally with the intent of shaming individuals, and society itself, into improvement Lyric- does not attempt to tell a story but instead is of a more personal nature. Rather than depicting characters and actions, it portrays the poet's own feelings, states of mind, and perceptions Elegy- A mournful, melancholy or plaintive poem, especially a lament for the dead or a funeral song, may also reflect something that seems to the author to be strange or mysterious Verse Fable- The fable is an ancient literary genre. It is a succinct story that features anthropomorphized animals, plants, inanimate objects, or forces of nature that illustrate a moral lesson Prose- looks in form more like a short story than a poem but preserving poetic qualities such as heightened imagery and emotional effects Speculative- deals thematically with subjects which are 'beyond reality‘ as in science fiction pattern of rhyme between lines of a poem or song. It is usually referred to by using letters to indicate which lines rhyme; lines designated with the same letter all rhyme with each other. In other words, it is the pattern of end rhymes or lines. Bid me to weep, and I will weep A While I have eyes to see; B And having none, and yet I will keep A A heart to weep for thee. B Your quiz Friday will include questions on everything covered today as well as annotation (covered last week). I will be checking your interactive notebooks tomorrow. Your table of contents must be complete and all notes present. If you were absent on a day we had notes it is your responsibility to make sure they are completed.