Breeds Of Chickens
advertisement

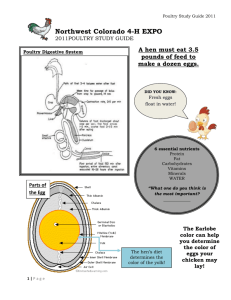
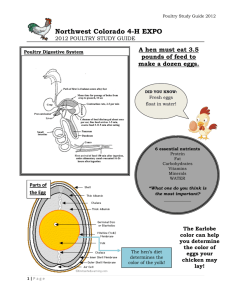
Know 10 things you KNOW about poultry/chicken s Want 10 thing you WANT to learn about poultry Learn -We will complete this once finished WHAT ARE YOU LEARNING? ID breeds of economically important animals Husbandry and Mangement practices for Industrial animals Know Poultry Types Basic Anatomy Management Practices • • • Understand Poultry desired Characteristics Internal and External Anatomy Vertical Integration Do • ID Breeds • Outline egg production • Outline Integration model Unit EQ: Why is the poultry industry a successful industrial model? Concept Breeds and Types Lesson EQ: What are purposes of poultry? Vocab Egg Laying, Meat, Dual Purpose, Ratites Concept : Anatomy Lesson EQ: How are poultry manipulated for production? Vocab Spur, Cloaca Concept : Management Lesson EQ: What is vertical intergration? Vocab Vertical Integration, Beak Trimming Students will: Identify major breeds of chicken and minor breeds of poultry Describe characteristics of each breed Identify breed purpose What are purposes of poultry? (think terminology) Breed (Specific) Type (General) 3 Facts Purpose (with definition) Leghorn Chicken Lays white eggs, Loud, Always all white Table Egg Laying: lays eggs for human consumption. Fowl (birds) raised on farms and used as food “Chicken is the number one most consumed meat in American” Discuss: Do you feel this is true why or why not? High protein Low fat Economical to eat 2nd in consumption only to beef Meat- Plymouth Rock Feathers- Peafowl Eggs- Leghorn Showing- Polish White Crested Black Fancy/Ornamental Dual Purpose Meat Purpose Table Egg Laying Weighs: 4 lbs. to 6 lbs. Egg Shell Color: White. Use: An egg-type chicken. Origin: city of Leghorn, Italy. Characteristics: A small, noisy bird, known for being all white in color The most numerous breed. Standard Weight: 5 ½ lbs to 8 ½ lbs. Egg Shell Color: Brown Use: Egg production, and meat (Dual Purpose) Origin: Massachusetts and Rhode Island. Recognized for its long wattle and head plumage Originated Poland in Can only see forwards and downwards Considered ornamental/fa ncy Famous for its fighting skills during the revolutionary war. Delaware’s regiment was nicknamed “The Blue Hen Chickens” Not a “TRUE” breed University of Delaware’s mascot UD has one of the only remaining pure bred flocks Any breed of chicken raised specifically for meat. (Typically Plymouth Rocks) Grown to specific weight and age. Between 5-12 weeks in age. Average is 7 wks from egg to processing Selected to gain lean (no fat) weight quickly Most common widespread goose in America is the Canadian Goose A group of geese is called a gaggle Hunted for sport. Meat and feathers are used Large waterfowl in between a swan and ducks. Very heavy birds (40-60 lbs) Wild Turkeys hunted for sport. Meat is more “gamey”, weigh less than industry birds Selectively bred for large size All industry produced turkeys bred for meat must be artificially inseminated because they are so large! Produce eggs, meat, and feathers (down feathers) All duck breeds are descendants of wild mallard China is top duck market Used for meat, eggs Normally eaten meat and bones Wild Quail that has fed on hemlock, can be toxic to consume causing kidney failure Flightless !!! Birds in this group include; ostrich, emu and kiwi Ostrich and emus used for eggs and medicinal purposes Emu oil provides health benefits for painful joints and bruises Emu’s cannot walk backwards Put your name and the date on your worksheet packet Define the following words: Poultry Dual Purpose (give breed example) Table Egg Laying (give breed example) Fancy/ Ornamental (give breed example) Meat Purpose (give breed example) Broiler Gaggle Ratites Person A Person B Give the word and the definition Use the vocab word in a sentence Library Project (Optional) Directions: Choose a poultry breed not discussed in class. Provide a picture to the teacher (chosen from the internet) to be posted on the screen while you present. Library Project Compile a profile of your bird. Include: Origin Color characteristics Average Size Purpose Product from or by the animal Fun Fact Answer the Following Where did Mike go? What is his job? What part of the job is dangerous? 5 facts about ostriches How do you catch or steer an ostrich and why? Discuss the video with your partner Why are ostriches considered poultry? What products do we use and why? What was one interesting thing you learned ? Please Follow along with your worksheet provided Label the major parts of poultry anatomy Explain the purpose of specific anatomical differences in digestion anatomy. Discuss the general reproductive anatomy of a hen. How are poultry manipulated for production? I think it means…. Because of… (clues) We have selectively bred chickens to have large breast meat because this is the cut of meat that brings the most profit. It is actually defined as… Ways to help me remember this/Examples are Breeding for desired characteristics We have selective bred chickens to have enlarged breasts and grow quickly (7 weeks) to increase profits What do you call a mature male? Rooster What do you call a mature female? Hen What do you call a young female? Pullet What do you call a castrated male? Capon Chickens [Hatch] (they are not “born”) Crop- food storage Birds are prey animals. Need to “eat and run” Gizzard- grinds food Birds don’t have teeth. Gizzard is muscular organ that contains grit (stones) to help grind food Proventriculus Secretes digestive enzymes to break down food Cloaca Vent when poop and eggs are expelled How are chicken’s (and bird’s in general) digestive systems specialized and different from our own? Give 3 examples Hens only lay legs NOT ROOSTERS Male reproductive organs are located inside the bird Temperature regulation EXTRA important to prevent infertility Spaying a chicken = difficult ▪ Therefore: Capons are mainly for religious purposes How have birds adapted ? Hollow bones = light weight Keeled sternum= lower center of gravity and large bone provide extra large pectoral muscle attachments ▪ WE EAT THE PECTORAL (breast) muscle in chickens! Fused wrists and bones ▪ Give wings their shape ▪ We EAT the wings. Two types Drumstick and double bone wing Add these to your list and Define the following words: Spurs Primary Feathers Crop Gizzard Cloaca Person A Person B Give the word and the definition Use the vocab word in a sentence Egg hatching Video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PY Lm3SK_vRE Label the basic anatomical parts of the egg, and reproductive system of the hen Explain the process of gestation within the egg. Discuss the process of fertilization and egg development. Understand the importance and purpose of gestation. Define the process of incubation and its importance. What is an egg? What parts of an egg do you know? What do they “do”? What parts do we eat? Egg- the female germ cell. The egg becomes the embryo. Avian egg- bird eggs. It includes the following: ▪Shell ▪Shell membranes ▪Albumen ▪Yolk Together they protect and nourish. 1.Ovulation- release of mature yolk from the ovary. 2.Infundibulumreceives the yolk, about 15 minutes spent. 3.Yolk moves into magnum 50% of albumen is added. Takes 3 hours. 4.Spends 1.5 hours in the Isthmus. Shell membranes added. 5. Total process takes about 24 hours Draw how an egg is formed inside of a hen should be 6 boxes Step One Step Two Step Three Step Four Step Five Egg is LAID! What will the chicken do now? The yellow part of the egg is called the… The white part of the egg is called the … What do these do?!? 1. Shell- hard outer surface; calcium 1.Shell has pores to allow loss of CO2, moisture. 2. Shell membranesthere are two one next to the shell, and surrounding albumen, yolk. a. Known as Inner and Outer Membrane 3. Air Cell- air space between two shell membranes. 4. Albumen- egg white. 5. Yolk- true egg, if fertilized become embryo. Germinal DISC Mammals: Young developing within the mother Mother provides nourishment (milk) Avian: Young develop outside the mother (hen) Mother does not provide nourishment What do you see in this picture? What is happening? How do you know? How does the yolk sac change throughout gestation? Artificially keeping an egg warm until hatching= incubation Completed in an incubatorartificially heated container. Gestation period: approximately 3 weeks The incubator must be kept at a certain temperature range 99 to 103 F. Eggs must be turned while incubating -Why do we turn eggs during incubation?? -Temperature = 92-95 degrees under light, 70-75 deg in house -Decrease temp. 5 degrees / week until 60 degrees MUST REGULATE TEMP! -If chicks are huddled together under light = too cold -If none are under light = too hot -Should be scattered -Teach how to drink right away Eggs are great examples of a self sufficient way to raise a young animal. This statement is true because………… The most interesting part/ adaptation of the egg is the ……. Define the following words: Ovum Albumen Gestation Yolk Sac Incubation Person A Person B Give the word and the definition Use the vocab word in a sentence Describe required management practices and their purpose in poultry health. Evaluate basic parts of poultry nutrition. Define vaccinations and their purpose within the poultry industry. -Do not over crowd young or adult birds ALL Birds have a minimum space requirement as highlighted by the USDA EXAMPLE:CHICK-Space requirements: 10 square inches / chick under light 25 square inches / chick house space Chicks shouldn’t be allowed to get more than 3 ft away from light I think it means…. Because of… (clues) Vertical Integration has allowed for the poultry industry to become the most successful food model that has led to other industries attempting to duplicate the business model. It is actually defined as… Ways to help me remember this/Examples are Chicken Management Strategies Housing and Feeding (Methods) Nutrition Biosecurity /Disease Prevention Definition: Several steps in production, from raw materials to final product, are controlled by company or owner. Debeaking: remove 1/3 of the top beak and a small part of the bottom (prevent cannibalism) at 6-8 days old Controversial practice. 15-20 birds per minute. This fast pace sometimes results in inappropriate cuts causing excessive bleeding Vaccinate (hatchery can do this) Sprays, shots, eye drops Lighting: birds naturally reproduce in spring, simulate spring, chickens molt (shed feathers) production increases Requirements: Heaters Radiant =heat the litter and items in the house. Not the air. More efficient Feeding system Thermometers Electronically hooked to Always filled, but no wasteful spilling emergency back up Litter systems. Regular Low dust, absorbent mercury thermometer for back up Requirements Continued: Humidity Prevents dusty conditions, heat regulation more effective, decreases stress (too dry = stress) Watering system No spilling, sanitary!, monitored with meter Alarm systems Prevent unhealthy and stressful conditions Standby equipment Ready for power or other emergency, prevents losses (deaths) Water: MOST IMPORTANT nutrient Birds need this to aide in digestion and temperature regulation Protein Build muscle quickly Carbohydrates and fats Energy Minerals and Vitamins proper growth and development Feed Additives: Marigold petals: provide yellow tint to chicken skin. Marketed by Perdue chicken as “healthier”. NO health benefits for yellow skinned chicken but public bought in •Marek’s Disease: vaccine given in ovo Symptoms include : paralysis , blindness, gasping •Infectious bronchitis: caused by a virus. Prevented through vaccination Symptoms include gasping, decreased feed intake, soft egg shells Security measures taken to prevent the spread of disease Define the following words: Litter Marek’s disease Vaccination Biosecurity Infectious Bronchitis What type of management practices do you think are used in this photo? Define vertical integration. Label major parts of the poultry industry. Summarize the main processes in poultry product production. How does vertical integration help chicken producers? Over 90% of eggs produced are by layers in cages. The most common grouping is four hens per cage. Controversial practice because many birds become over crowded, never spread their wings, and are injured by cage or other birds -Most eggs sold in the U.S. are white. Produced by what type of bird? -In large scale commercial operations, lighting is used to stimulate the hormonal activity of the hens to increase their production of eggs. They produce eggs naturally when the days are longer than the nights. Most operations allow 14 - 15 hours of light per day Collect eggs 2-3 times per day (if hot) Wash eggs immediately in warm water Sprayed with protective coding to maintain freshness Refrigerate Production Goal: 4 lbs feed / dozen eggs Hens produce 7 eggs / 10 days -Eggs are coated with a thin coat of mineral oil to prevent carbon dioxide from escaping from within the egg. -Eggs are graded according to size and checked for cracks and interior spots by candling. Market at 4 1/2 lbs for males, 3 1/2 lbs for females (about 8 weeks) 2.1 lbs feed / lb of gain This rate of gain can cause health issues like “flopping” Down birds fall under their own weight. Bone structure cannot keep up with weight gain of meat Most are white Colored birds have pigmentation spots in their skin which is undesirable to the consumer Kept to certain age, based on weight ALL IN ALL OUT 1. All birds are hatched at same time 2. 3. Grow together at same general rate All sent to slaughter at same time Entire house disinfected and cleaned 5. New “generation” brought in 4. Define the following words: Vertical Integration Draw on a poster with your group a representation on vertical integration. Label each segment (grain mill, slaughter house etc) Agronomy Sales Shift supervisor Seed Production Grain Operations Farm Marketer Feed Mill Manager Plant Manager Waste Water Supervisor Barn Supervisor www.mrpoultry.com/opport unities.html Modern Livestock & Poultry Production 5th Edition. By James Gillespie. Oklahoma State University- Animal Science department. http://www.ca.uky.edu/agripedia Outline the steps in chicken processing from egg to plate. Include the major processes in slaughter What is the trend in the Australian food industry? How does this mirror America? How are producers catering their products to meet consumer demand? What are consumers demanding? What is value added chicken? What are common cuts of birds? How do they guard against contamination in the slaughter house? Why is chicken good nutritionally? Is your vocabulary sheet completed? (First page of your packet) Use each vocabulary word in a sentence. Answer the following: List the purposes of chickens and give a breed example of each. Define each purpose. Explain vertical integration. Give an example of a company. What is the current trend in the American food industry? How is the poultry industry meeting these demands? What are common items found in an adult broiler house? What are the purposes behind these items? What are common care practices for poultry and what are the reasons for these practices?