The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE
advertisement

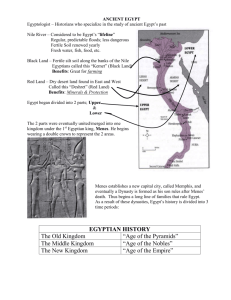
The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE: _________________ OBJECTIVES: Excellent mathematical knowledge helped build pyramids and palaces. Great medical knowledge!!! Old Kingdom Declines Around 2180 BC o Middle Kingdom restores or and trade from (2040-1640 BC)Control the Nile for farming and improved trade. Nomadic Invaders Rule Egypt 1. We will be able to identify key characteristics of Egypt’s civilization. 2. We will be able to analyze the rise of the Kingdoms in Egypt, the Assyrian Empire, Nubian Empires and their declines. 3. We will be able to assess the military might of the Assyrian Empire. Looking at Ancient Egypt (OLD KINGDOM EGYPT2660 to 2180 BC) o The NILE RIVER was vital to Egypt King Menes united Upper and Lower Egypt in 3100 BC o Egypt’s Rulers, Pharaohs were equal to Gods Pharaohs were the center of Egypt's religion, government, and army. This is a theocracy (A government o Weak Pharaohs emerged after the Middle Kingdom o Asiatic invaders Hyksos ruled 1640 to 1570 BC During this time, Hebrews settled in Egypt Some say the Hyksos encouraged 1600 BC-Changes are Coming o Warlike rulers began to restore Egypt's power Hyksos driven out of Egypt to Palestine controlled by religious leader). Hieroglyphics A form of Egyptian writing based on pictorial characters for words and sounds (part of a civilization) Egyptian Life o Menes' family passed the double crown of upper and lower Egypt from father to son (Dynasty) The pharaoh ruled even after his death Tombs were left valuables and heavily decorated for the Pharaoh to live comfortably (PYRAMIDS) o Pharaohs expected to reign for eternity. o Tombs were more important than their palaces. Polytheistic like Mesopotamia o Egyptian Advances Invented a better writing surface papyrus. Egyptians developed a calendar to keep track of floods. o Hebrews remain and are enslaved Would not leave Egypt until The Exodus (1500-1200 BC) The New Kingdom of Egypt New Kingdom (1570-1075 BC) look to strengthen by building an empire. o Did so by increasing military Bronze weapons, chariots, archers, charioteers, infantry But not just war! o Hatshepsut (1472 BC) encourages trade The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE: _________________ o o Carried out trading expeditions to land near present-day Somalia Thutmose III changes this and becomes much more warlike Took lands to the east (Palestine and Syria) and Pushed farther in Nubia Egyptians and Hittites clash but Ramses II gets an alliance (1285 BC) Great BuildersOld Kingdom=Pyramids New Kingdom=Temples The Decline By Land and Sea o Began to slip after Ramses II around (1200 BC) Sea and desert could no longer protect Libyans take control but change little (950 to 730 BC) o Nubians come north and seize power, but change little too United the entire Nile Valley However, it was short lived. Assyrians conquered Egypt in 671 BC o Even with loss, Kushites experienced a golden age The Golden Age of Meroe o Moved further south and toward Red Sea Major supply of iron and good for trade o Fell as Aksum took trade o The Mighty Assyrian Empire….Which Takes Place In Mesopotamia after Sumer, Babylon, and the Hittites 850 BC Assyria acquired large empire Conquered Babylon and others with well-equipped soldiers Showed no mercy (killed or enslaved victims) o Forced the conquered to move Large Land Ruled-Great System Local government reported to central government o Do we still have this? Kushites Conquer the Nile Region Assyrian Culture Kingdom of Kush between 2000-1000 BC dominated by Egypt o Emerged as power before rise of New Kingdom Consistently influenced by Egyptian culture Kushite princes: learned languages, dress, customs o Wanted to guard Egyptian values as it declined in 1200 BC to the Libyans Piankhi Captures the Egyptian Throne 751 BC Painkhi, Kushite king, overthrew Libyan ruled Egypt A Great Library o 20,000+ clay tablets Organized by subject matter Cataloged collection Conquered by Medes and Chaldeans o Chaldeans reestablished Babylon in 600BC 1000 years after Hammurabi King Nebuchadnezzar rebuilt city and established Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Fell shortly after Nebuchadnezzar's death However, great ziggurat allowed for astronomy and astrology to grow. The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE: _________________ CHARACTERISTICS OF ANCIENT EGYPTIAN SOCIETY ARCHITECTURE TECHNOLOGY GOVERNANCE ECONOMY SOCIETY Pyramids of Giza Temples and Statues in the Valley of the Kings High levels of mathematics to build great buildings MedicineStitching wounds, bandaging, Irrigation Improved Produced first government to rule entire nations Highly centralized with the Pharaoh (Army, Religion, and Government Under His Control) o Civil Service (officials and scribes to help governBureaucracy) Nile provided large surplus for crops Nile provided great trade route to get goods: Ivory, Gold, and Slaves o Would trade internationally Small nobility class Extremely hierarchal Women hold higher status Polytheistic CRASH COURSE QUESTIONS: Mesopotamia 1. Who held a lot of power in early ancient Mesopotamia and why? 2. What form of writing did ancient Mesopotamia create and what did it lead to in this area? 3. What did Hammurabi create and why was it so important? The Egyptian, Nubian, and Assyrian Empires (2.2, 4.1, 4.2) DATE: _________________ 4. What political organization did the Assyrians bring and what does this mean? In addition, why was it good to have meritocracy?