Bullet Point 1 - Wired and Wireless Technology, transfering data
advertisement

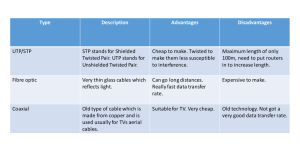
CAMBRIDGE NATIONALS The use of wired and wireless technology to transfer information to portable devices and the benefits and drawbacks of doing so. Networks: LANs (Local Area Network) What hardware do you need for a LAN network? •File Server : Runs software, stores files. •Terminals : Workstations that give network access. •Print Server : Queues up all print jobs from users in network. •Cables (wire/fibre optic) : Sends data •Switch/Router – direct data packets around the network •Modem – Connects a LAN to the internet LAN – LOCAL AREA NETWORK File server stores data and allows the sharing of files. File Server WorkStation 3 Printer Peripheral WorkStation 1 WorkStation 2 Scanner Peripheral ADVANTAGES OF NETWORKS Programs can be shared - software packages can be installed onto the file server and accessed by all individual workstations at the same time. This reduces cost, maintenance and makes upgrades easier. You can access your work from any workstation on the network. Very handy if you have to change computer every time you go to a different classroom. Data can be shared by all users at the same time. Many people can access or update the information held on a database at the same time. Thus information is up to date and accurate. Users can communicate with others on the network by sending messages and sharing files. MORE ADVANTAGES… Individual workstations do not need a printer, one high quality printer can now be shared by everyone, thus cutting costs. Networks provide security. A user must have the correct Password and User ID in order to be able to access the information on the network. Private areas on the network can be set up that allows each user to store their personal files. The only other person who can access these files is the 'system administrator' who looks after the network. WAN – WIDE AREA NETWORK When pcs or LANs connect together over the internet, these create Wide Area Networks WAN – WIDE AREA NETWORK Many modern companies have offices, shops or factories in various locations around the country, and for large corporations, across the world. Even though staff work in different places, they often need to be able to access the same information no matter where they are. It would not be possible to connect computers in different buildings or countries together using LAN cables. WAN – WIDE AREA NETWORK Computers on LANs in one building can be connected to computers on LANs in another building usually through the telephone system, often using a modem. They can also be connected via fibre optic cables or satellite. By linking LANs together, the network is no longer local to one building, it is now spread over a wide area. It is known as a Wide Area Network (WAN) The largest WAN in existence is the Internet? WIRED CONNECTIONS A wired network is accessing the internet or network through an Ethernet cable. This transfers data between connected PCs. In a wired network, a router may be used to connect all the computers. Wired connections may also refer to peripheral devices as well. “Wired" describes input devices that connect to a USB port, such as monitors, smartphones, tablets, printers and external hard drives. WIRED NETWORKS Control of information and Security, it will only send Information to the computer if it has a wire connected. Reliability and Speed of Transfer, the users connected do not need to look for a strong signal it will always be of a good quality. Another bonus with a wired connection is the speed and reliability they offer, for a business that regularly moves a lot of data around, a wired set-up is the best way to go. WIRELESS NETWORKS A wireless network uses radio waves to transmit information, just like cell phones, televisions and radios do. Here's what happens: A computer's wireless adapter translates data into a radio signal and transmits it using an antenna. A wireless router receives the signal and decodes it. The router sends the information to the Internet using a wired/fibre optic connection. The process also works in reverse, with the router receiving information from the Internet, translating it into a radio signal and sending it to the computer's wireless adapter. WI-FI HOTSPOTS A Wi-Fi hotspot is simply an area with an accessible wireless network. The term is most often used to refer to wireless networks in public areas like airports and coffee shops. Being able to connect to the Internet in public hotspots is extremely convenient. Wireless home networks are convenient as well. They allow you to easily connect multiple computers and to move them from place to place without disconnecting and reconnecting wires. CONNECTING TO WI FI When connecting to Wi-Fi, these rough steps are needed; which are similar for most devices. BENEFITS OF WIRELESS CONNECTION Having lots of wires running throughout a building can be costly and awkward to maintain. Any breakages in the wired connection will also have to be manually fixed. Freedom to move around the office, roads or houses. Freedom to work at any time of the day not just when the office is open. ADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Excellent for wireless internet services. Compact (keyboard and touchpad are built-in). Bluetooth and wireless built-in. ADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Portability (great if you travel a lot), Small and light in size. Apps can add more functions. Many of the same features you'll find on a desktop. ADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES GPS for navigation. Longer battery life than most laptops. Increased Productivity. Photograph issues with cable boxes or peoples TV boxes. ADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Can access networks or browse the Internet through 3G/4G. Saves time, travel to and from Cable Ties Ltd offices. ADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Use of Cloud Computing, can save money and space. Cable Ties Ltd can easily get in touch with staff if issues arise (Telephone call, email, SMS message) DISADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Data Security - Cable Ties Ltd need to keep their data safe while letting mobile devices of workers access all the data necessary. Cost Having to pay for the device and also the data plans and the devices can raise the cost for Cable Ties Ltd. Creating guidelines and security for the devices can cost money. % of companies using devices reported a security breach in the past year. DISADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES Easy to lose, or to be stolen. Lost/stolen devices account for a significant amount of lost data for companies/Cable Ties Ltd. DISADVANTAGES OF MOBILE DEVICES For transferring data a high quality of connectivity is needed to be able to send the data. This may not be available for all workmen of Cable Ties Ltd depending on the area they are working. If the worker for Cable Ties Ltd is in a situation where there is no source of power for charging then that will lead to lost work and tracking for the company. BLUETOOTH A wireless technology which allows one device to talk and connect to another. It wirelessly transmits a signal that can be received by any device using the software. Can transmit through walls and other non-metal barriers. It can be used in anything (phones, computers, even TVs). It is secure and has a long battery life. BLUETOOTH USES Bluetooth headset can be used by drivers to talk on the phone while travelling to a job. Sending/Receiving files to the phones with information about a new job or when a job is finished. To allow for Wireless controllers when working with wires underground.. INFRA-RED Like Bluetooth it connects two devices together, it then sends and receives the information through electromagnetic waves. Widely used in most audio and video remote controls Advantages Cheap to install Uses little power. Secure, as the items need to be pointed at each other. Disadvantages Both devices have to be in a straight line Both devices need to be close to each other to pass the signals.