Friday, May 17 th 3.L.1 Understand human body
advertisement
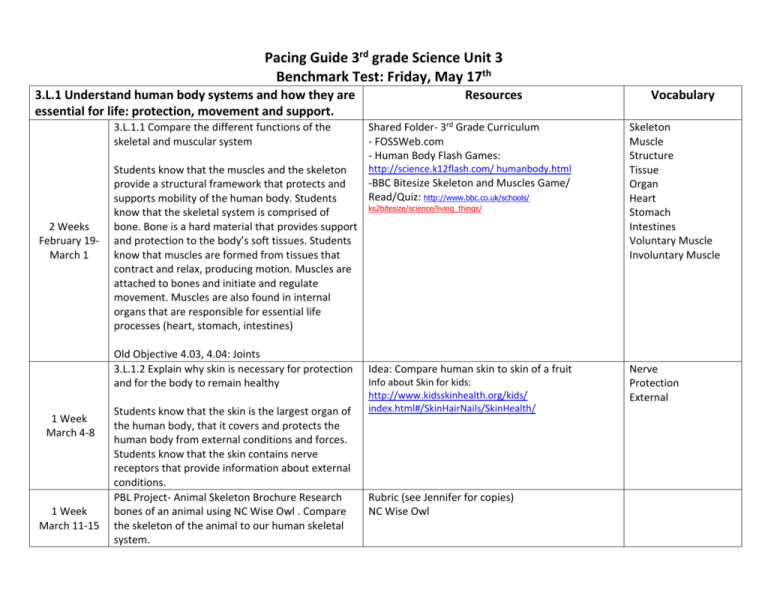
Pacing Guide 3rd grade Science Unit 3 Benchmark Test: Friday, May 17th 3.L.1 Understand human body systems and how they are essential for life: protection, movement and support. 3.L.1.1 Compare the different functions of the skeletal and muscular system 2 Weeks February 19March 1 1 Week March 11-15 Shared Folder- 3rd Grade Curriculum - FOSSWeb.com - Human Body Flash Games: http://science.k12flash.com/ humanbody.html Students know that the muscles and the skeleton -BBC Bitesize Skeleton and Muscles Game/ provide a structural framework that protects and Read/Quiz: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ supports mobility of the human body. Students ks2bitesize/science/living_things/ know that the skeletal system is comprised of bone. Bone is a hard material that provides support and protection to the body’s soft tissues. Students know that muscles are formed from tissues that contract and relax, producing motion. Muscles are attached to bones and initiate and regulate movement. Muscles are also found in internal organs that are responsible for essential life processes (heart, stomach, intestines) Old Objective 4.03, 4.04: Joints 3.L.1.2 Explain why skin is necessary for protection and for the body to remain healthy 1 Week March 4-8 Resources Students know that the skin is the largest organ of the human body, that it covers and protects the human body from external conditions and forces. Students know that the skin contains nerve receptors that provide information about external conditions. PBL Project- Animal Skeleton Brochure Research bones of an animal using NC Wise Owl . Compare the skeleton of the animal to our human skeletal system. Idea: Compare human skin to skin of a fruit Info about Skin for kids: http://www.kidsskinhealth.org/kids/ index.html#/SkinHairNails/SkinHealth/ Rubric (see Jennifer for copies) NC Wise Owl Vocabulary Skeleton Muscle Structure Tissue Organ Heart Stomach Intestines Voluntary Muscle Involuntary Muscle Nerve Protection External 3.L.2 Understand how plants survive in their environments 3.L.2.1 Remember the functions of the following plant structures as it relates to the survival of plants in their environments: Root- absorb nutrients, Stems-provide support, leavessynthesize food, flowers- attract pollinators and produce seeds for reproduction. Students know the names and functions of major plant parts (roots, leaves, stems, flowers). 8 Weeks March 18May 17 3.L.2.2 Explain how environmental conditions determine how well plants survive and grow Students know that how well plants grow and survive is determined by a combination of environmental conditions. For example, drought conditions will tend to diminish plant health and growth. 3.L.2.3 Summarize the distinct stages of the life cycle of seed plants -Magic School Bus: Gets Planted -Students will use Magic School Bus worksheet to complete in pairs (one question per group) -Bill Nye Video: Plants, Flowers -PBIS Kids: Wild Kratts Pollinators -Brain Pop Jr.: Parts of a Plant (Root, Stem, Leaves, Flowers, Seed) -Celery Project http://www.learningtreasures.com/plant_salad.htm: parts of a plant you can eat http://plants.pppst.com/plantparts.html: Parts of Plant power point -“Parts of a Plant” by Wiley Blevins -“Amazing Plants” by Sally Hewitt -“The ABCs of Plants” by Bobbie Kalman -“Oh Say Can You Seed?” by Bonnie Worth -“Flowering Plants” by Chris Oxlade -“Primarily Plants” by Carol Gossett -Magic School Bus Plants a Seed -Plant lima beans to compare to amaryllis bulb -Free PowerPoints http://plants.pppst.com/growthcycles.html -Study Jams “Plants with Seeds” and “Plants without Seeds” -“The Lorax” by Dr. Suess Roots Stem Leaves Flowers Nutrients Absorb Synthesis Pollen Pollination Reproduction Photosynthesis -BBC Bitesize Plant Life Cycle Game/ Read/Quiz: http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ ks2bitesize/science/living_things/ Seed Seedling Adult Survival Ecosystem Adaptation Habitat Environment Students know the distinct stages of the life cycle of seed plants (seed, germination, seedling, adult) Old Objective 1.05: Bees pollinating 3.L.2.4 Explain how the basic properties (texture and capacity to hold water) and components (sand, clay and humus) of soil determine the ability of soil to support the growth and survival of many plants. -Brain Pop Jr. “Plant Life Cycle” -“A Parade of Plants” by Melissa Stewart Germination Pollination Life Cycle -Shared Folder- 3rd Grade Curriculum -Flash Interactive Games: Particle Sand Clay Humus Texture Absorb Nutrients Capacity http://science.k12flash.com/soil.html -Brain Pop Jr. “Soil” -Study Jams “Soil” Students know that different soils possess different textures and capacities for the retention of water and nutrients. Students know that soil consists of different components. Students know that these characteristics of soil influence the growth and survival of plants. Old Objective 2.05, 2.06: Composting PBL- Amaryllis Project. Unit project will take the entire 8 weeks to complete (Begin the week of March 18, and end the week of May 17) Shared Folder, 3rd Grade Curriculum - Amaryllis Activity Project