Homeostasis and Endocrine Signaling
advertisement

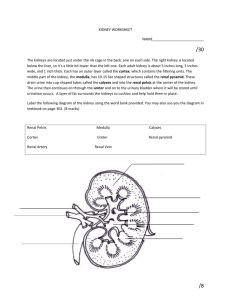
Homeostasis and Endocrine Signaling Tissues • Figure 32.2 • 4 major types: • Epithelial – found on outside of the body and lining organs and cavities. • Muscle – 3 types • Cardiac – heart tissue, involuntary • Smooth – involuntary actions in body, organs, blood vessels • Skeletal – muscle that moves, attaches to bone, voluntary • Nervous tissue – the neuron, sends impulses, communication • Glia cells are nerve helping cells to the neurons • Connective tissue – diverse group of tissues scattered throughout body and extracellular matrix • • • • • • Bone – calcified hard matrix Blood – liquid matrix Cartilage – ear, nose, gel like matrix Dense fibrous – tendons and ligaments Adipose - fat Areolar – loose fibrous connecting tissue Regulator or Conformer? • Animals that are regulators uses internal mechanisms to control internal change – endothermic, homeothermic, warm blooded • Animals that are conformers – internal condition changes in accordance with external changes, ectothermic, cold blooded • Homeostasis – maintenance of a constant internal balance • examples,- body temp, blood glucose levels… • Negative feedback – when body is out of homeostasis and it is brought back. • Positive feedback – when body is brought out of homeostasis purposely for a short period of time, childbirth and oxytocin Thermoregulation (heat) • Figure 32.3 Figure 32.4 Response: Heating stops. Room temperature decreases. Sensor/ control center: Thermostat turns heater off. Stimulus: Room temperature increases. Set point: Room temperature at 20C Stimulus: Room temperature decreases. Room temperature increases. Response: Heating starts. Sensor/ control center: Thermostat turns heater on. Endocrine system • Endocrine system – communication via hormones that are released by endocrine glands into the blood stream. • Hormones – chemical messengers • Exocrine glands – figure 32.11 • Exocrine glands – integumentary system, release product to cavity or outside the body, sweat. • Nervous system – rapid communication using neurons and nerve impulses • All run by Stimulus/Response mechanism Figure 32.11a Major Endocrine Glands and Their Hormones Pineal gland Melatonin Thyroid gland Thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) Calcitonin Parathyroid glands Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Ovaries (in females) Estrogens Progestins Testes (in males) Androgens Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary Posterior pituitary Oxytocin Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone, ADH) Adrenal glands (atop kidneys) Adrenal medulla Epinephrine and norepinephrine Adrenal cortex Glucocorticoids Mineralocorticoids Pancreas Insulin Glucagon Figure 32.8 Sensor/control center: Thermostat in hypothalamus Response: Sweat Response: Blood vessels in skin dilate. Stimulus: Increased body temperature Body temperature decreases. Homeostasis: Internal body temperature of approximately 36–38C Body temperature increases. Stimulus: Decreased body temperature Response: Blood vessels in skin constrict. Response: Shivering Sensor/control center: Thermostat in hypothalamus Figure 32.9 (a) Signaling by hormones (b) Signaling by neurons Stimulus Stimulus Endocrine cell Cell body of neuron Nerve impulse Hormone Axon Signal travels to a specific location. Signal travels everywhere. Blood vessel Nerve impulse Axons Response Response Osmoregulation (fluids) • How animals control solute concentrations in the interstitial fluid and balance water gain and loss • Excretory system – releasing of nitrogenous and metabolic waste products (kidney) • Osmoconformer – being isoosmotic with its surroundings, marine animals • Osmoregulator – to control internal osmolarity independent of the environment. Allows animals to live in freshwater/terrestrial habitats. Nitrogenous wastes in animals • 32.16 Figure 32.16 Proteins Nucleic acids Amino acids Nitrogenous bases Amino groups Most aquatic animals, including most bony fishes Ammonia Mammals, most amphibians, sharks, some bony fishes Urea Many reptiles (including birds), insects, land snails Uric acid Figure 32.16a Most aquatic animals, including most bony fishes Ammonia Mammals, most amphibians, sharks, some bony fishes Urea Many reptiles (including birds), insects, land snails Uric acid The excretory process • Urine formation: 32.17 Figure 32.17 Filtration Capillary Filtrate Excretory tubule Reabsorption Secretion Urine Excretion The Kidney – figure 32.19 Figure 32.19b Kidney Structure Renal cortex Renal medulla Renal artery Nephron Organization Renal vein Afferent arteriole from renal artery Ureter Proximal tubule Renal pelvis Nephron Types Peritubular capillaries Distal tubule Cortical nephron Efferent arteriole from glomerulus Branch of renal vein Renal cortex Collecting duct Renal medulla Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Juxtamedullary nephron Vasa recta Descending limb Loop of Henle Ascending limb Figure 32.19bc Nephron Organization Afferent arteriole from renal artery Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Proximal tubule Peritubular capillaries Distal tubule Efferent arteriole from glomerulus Branch of renal vein Collecting duct Vasa recta Descending limb Loop of Henle Ascending limb Figure 32.20 1 Proximal tubule NaCI Nutrients HCO3− H2O K H CORTEX NH3 4 Distal tubule H2O NaCI K HCO3− H Interstitial fluid 3 Thick segment Filtrate H2O Salts (NaCI and others) HCO3− H Urea Glucose, amino acids Some drugs 2 Descending limb of loop of Henle of ascending limb NaCI H2O OUTER MEDULLA NaCI 3 Thin segment of ascending limb 5 Collecting duct Urea NaCI Key Active transport Passive transport INNER MEDULLA H2O Adaptations • Based on where you live, there are adaptations to the kidney • Hyperosmotic urine (dessert animals) – long loops of Henle that extend deep into the medulla • Birds – shorter loop of Henle, les concentrated urine compared to mammals – uric acid is product to help conserve water. Homeostatic regulation of kidney • 32.23 antidiruretic hormone Figure 32.23-3 Osmoreceptors trigger release of ADH. Thirst Drinking of fluids ADH Increased permeability Distal tubule STIMULUS: Increase in blood osmolarity H2O reabsorption Collecting duct Homeostasis