DO/Temp Training Agenda
advertisement

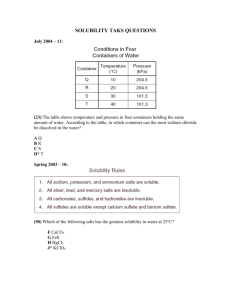
Temperature and DO Temperature A measure of heat Dissolved Oxygen (DO) The concentration of oxygen (gas) which is dissolved in water. Both are important individually and to one another Why is Temperature Important? Most aquatic organisms are poikilothermic (“cold-blooded”), which means they don’t internally regulate their core body temperature. The rate of many chemical reactions increases at higher temperatures. Oxygen solubility Temperature - Units Fahrenheit (°F), Celsius (°C), Kelvin (K) Celsius (°C) used for most science (SI unit) – a.k.a. centigrade, where “centi-” = hundredth Water Freezes at 0°C = 32°F = 273.15 K Water Boils at 100°C = 212°F = 373.15 K 0°C 100°C 32°F 212°F Temperature - Units Conversion Factors (°F – 32) °C = 1.8 °F = (°C x 1.8) + 32 Temperature – Q10 Rule General rule which predicts: Growth rates of cold-blooded aquatic organisms and many biochemical reaction rates will double for every 10°C (18°F) temperature increase within their "preferred" range. Temp – Biological Effects Growth Rate Optimum Lethal 0 10 20 30 40 Temperature (Celsius) 50 Max weekly AVG temp for spawning 35 Max temp for embryo spawning 25 20 15 Max weekly AVG for juvenile growth 10 Atlantic Salmon Sockeye Salmon Brook Trout Rainbow Trout Smallmouth Bass Largemouth Bass Bluegill 0 Common Carp 5 Channel Catfish Temperature 30 Max temp for survival of short exposure (juveniles) Temperature Standards Temperature All waters 64°F (17.8°C) Salmon spawning, egg 55°F (12.8°C) incubation, and fry emergence Bull Trout 50°F (10°C) Columbia River (to RM 309) 68°F (20°C) Willamette River (to RM 50) 68°F (20°C) Rolling 7-day average of maximum daily temperatures Temperature – Deep Cr (Clack) 22 21.3 20.9 21.0 20.9 20.9 20.5 20 19.4 18 16 7-day max AVG = 20.6°C 8/2 8/2 8/1 8/1 7/31 7/31 7/30 7/30 7/29 7/29 7/28 7/28 7/27 7/27 7/26 14 7/26 Temperature (*C) 20.2 Temperature – Causes Loss of riparian shading Warm water inputs – Retention ponds – Municipal or industrial wastewater – Stormwater runoff Groundwater inputs Weather – Air temperature, cloud cover, day length Turbidity Dissolved Oxygen O2 gas dissolved in water Atmosphere Water O2 CO2 21 % 0.035 % 0% 20 % Required by nearly all aquatic life DO – Solubility Inverse, non-linear relationship to temperature Decreases with decreasing barometric pressure – Weather, elevation High salinity reduces solubility DO – Solubility 15.00 Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) 14.00 13.00 12.00 11.00 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 0 5 10 15 20 Temperature (Degrees C) 25 30 DO – Units Concentration: mg/L = µg/mL = ppm (parts per million) Percent Saturation: Measured DO (mg/L) DO % Sat. = Solubility (mg/L) DO – Sources Photosynthesis – Influenced by sunshine, temperature, water velocity Atmospheric Re-aeration – Turbulent mixing • Water velocity and depth • Oxygen deficit Inflow of oxygenated water DO – Sinks Respiration – Greatest source of DO loss in summer Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) – Decomposition of organic wastes – Standard measure is 5-day BOD = BOD5 Nitrification (NBOD) – NH3 + O2 = NO3 Dissolved Oxygen DO – Diel Fluctuations PM AM Time of Day DO – Standards Salmonid Spawning thru Fry Emergence unless or Water Quality Standard > 11 mg/L Intergravel Standard > 6 mg/L Intergravel DO > 8 mg/L > 9 mg/L Natural conditions > 95% sat. Cold-water Aquatic Resources Natural conditions > 8 mg/L > 90% sat. Cool-water Aquatic Resources > 6.5 mg/L Warm-water Aquatic Resources > 5.5 mg/L DO and Temp Data Quality Temperature Dissolved Oxygen Accuracy Precision + 0.5°C + 1.0°C + 0.3 mg/L + 0.5 mg/L Measuring DO and Temp Measure Immediately - In Field Measure Both at Same Time Recording Time is Crucial Sample Collection – Below surface ~ 4 inches (or ½ way to bottom of shallow stream) – Cap DO bottle underwater