16.1 Water in the Air
advertisement

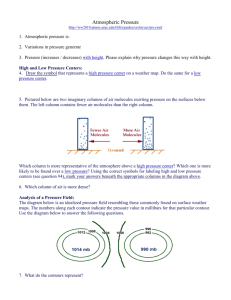
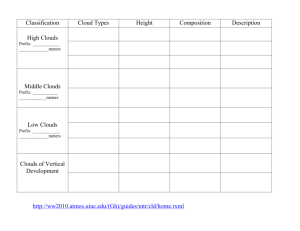
Chapter 16.1 Water in the Air Team Work! • In you team of 4 people…diagram the water cycle in your composition book. (section 16.1) • Label each part of the water cycle • Define each label as you go Water Cycle • Definition: –The continuous movement of water from Earth’s surface (oceans and rivers) into the air (atmosphere), onto and over the land, into the ground, and back to the surface. Illustration http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Water_cycle.png Evaporation • Water from the Earth’s surface to the air, the process by which water changes from a liquid (water) to a gas (water vapor). • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/evap.rxml Transpiration • Evaporation of water into the Atmosphere from plants. • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/trsp.rxml Condensation • Process by which water changes from a gas (water vapor) into a liquid (water). • Cloud Formation. • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/cond/home.rxml Precipitation • Process by which water moves from the Atmosphere (clouds) to the Earth’s surface. • May be in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or hail. • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/prcp.rxml Runoff • The movement of water that flows across land and collects in rivers and streams and eventually ends up in the oceans. • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/run.rxml Putting it all together • The Water Cycle • http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides /mtr/hyd/smry.rxml The Water Cycle Humidity • The amount of water vapor in the air • Relative Humidity= The amount of water vapor in the air The maximum amount of water vapor the air can hold at a given temperature. Relative Humidity • This graph shows that as air gets warmer, the amount of water vapor that the air can hold increases. • When air hold all of the water vapor that it can at any given temperature, it is said to be saturated. • Saturated air has a relative humidity of 100%. Factors Affecting Relative Humidity • 1) Amount of Water Vapor • 2) Temperature • Relative Humidity changes if either one (or both) changes Measuring Relative Humidity • Psychrometer – Instrument used to measure relative humidity. – Made of wet-bulb and dry-bulb thermometers. http://www.usatoday.com/weather/wsling.htm Sling Psychrometer Determining Relative Humidity • Once you have both thermometer readings, you use the chart to find the relative humidity. Dew Point • The temperature at which the air becomes completely saturated= 100% • Temperature of air must cool to become saturated • Thermal Energy travels from hot to cold • At this temperature gas → liquid – (Water vapor condenses into water) Clouds • Definition – A collection of small water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air, which forms when air is cooled and condensation occurs. • Clouds are classified by form and altitude. Convective Cooling… How to make a cloud! • • • • 1. Air rises 2. Molecules move apart 3. Uses potential energy 4. Lowers temperature Condensation Level • The level in the atmosphere where condensation occurs. • The temperature is lower than the dew point of the air, therefore condensation occurs. • The base of the cloud is the level in the atmosphere where it’s cold enough to condense! Cumulus Clouds • Means “heap” • Puffy, white clouds with flat bottoms • Usually indicate fair weather http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/wwhlpr/fair_cumulus.rxml?hret=/guides/mtr/cld/cldtyp/home.rxml Cumulonimbus Clouds • Nimbus means “rain” • Thunderstorm clouds • Tall, dense, usually dark http://www.answers.com/topic/cumulonimbus-cloud-1 Stratus Clouds • Means “layered”- form in layers • Covers large area of the sky • May bring dull and grey weather http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/Weather/Older/Stratus_Clouds.html Cirrus Clouds • Means “curl of hair” • High level clouds • Made of ice crystals http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/wwhlpr/cirrus.rxml?hret=/guides/mtr/cld/cldtyp/home.rxml Altitude CirroHigh clouds AltoMiddle Clouds StratoLow clouds fog Cloud Types Precipitation RAIN SNOW SLEET HAIL Hail Precipitation • • • • Rain 0.5 – 5 mm diameter Drizzle < 0.5 mm diameter Snow = ice particles Sleet = ice pellets form when rain falls through a layer of freezing air • Hail = solid lumps of ice form in cumulonimbus clouds