Active Transport
advertisement

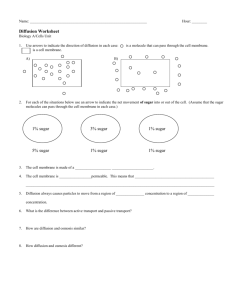
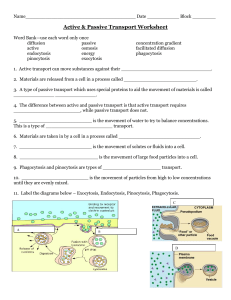
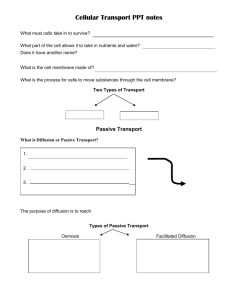
Active Transport For each: 1. Identify the type of solution 2. Describe what will move, and where 3. Explain why this occurs 4. Describe how the cell’s volume will change 1. 2. A cell contains a solution that is 88% water, and it is sitting in a solution that is 20% water. A cell contains a solution that is 43% sugar, and it is sitting in a solution that is 99% sugar. Homework Review #12. Distilled water has a lower concentration of protein than does human blood. Imagine that Ms. SCHERBEN is in the hospital and she needs a blood transfusion. Unfortunately, the doctor messes up and gives Ms. SCHERBEN distilled water instead of blood! LOWER H2O Lower protein HIGHER H2O HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC “LYSIS” Goal By the end of the period, we can… Compare active and passive transport Identify whether cellular transport is diffusion, active transport, or osmosis Passive Transport Key Point #1: Passive transport takes no energy and always moves towards equilibrium. The goal is equal concentration (equilibrium) High Low concentration Happens naturally (no energy) Diffusion AND osmosis In DIFFUSION The solutes are permeable to the membrane and move H L. In OSMOSIS Only water (solvent) is permeable to the membrane. 75% water 20% water Active Transport Key Point #2: Active transport takes energy to move all solutes in or out of the cell. The goal is to move against equilibrium Low High concentration Happens on purpose (takes energy) Question: What form of energy would the cell use for active transport? In ACTIVE TRANSPORT The solutes are permeable to the membrane and move L H Active Transport Why would the cell do this? To store food inside the cell To eliminate wastes To get rid of toxins NO ENERGY Comparing the Three DIFFUSION PASSIVE TRANSPORT OSMOSIS ACTIVE TRANSPORT SOLUTES SOLUTES WATER EQUILBRIUM EQUILBRIUM ENERGY Helpful Hints How can you tell if something is active or passive? How do you know if it diffusion or osmosis? Ask yourself: Is the solute moving, or is water moving? What is permeable to the membrane? Are we moving H L or L H? Guided Practice State whether this is Active Transport or Passive Transport Active or Passive? Active or Passive? Active or Passive? Water moving to equalize concentrations Active or Passive? Cell uses ATP to get as much sugar as possible Active or Passive? Happens naturally with no use of energy Active or Passive? ALL solutes being moved out of the cell Active or Passive? Takes energy Active or Passive? Moving toward equilibrium Changing Gears Now I will give you two cells. I will tell you what is moving and where. You tell me if it is DIFFUSION, OSMOSIS, OR ACTIVE TRANSPORT. If solutes are moving from L R If solutes are moving from L R If water is moving from R L Water is moving from inside outside A cell has a 40% sugar concentration inside is in a solution of 50% sugar concentration. The cell membrane is permeable to water. HINT: IT MIGHT HELP YOU TO DRAW THE SITUATION Solutes are moving from inside outside A cell has a 10% sugar concentration inside is in a solution of 50% sugar concentration. The cell membrane is permeable to solutes. Solutes are moving from outside inside A cell has a 10% sugar concentration inside is in a solution of 80% sugar concentration. The cell membrane is permeable to solutes. Solutes are moving from outside inside A cell has a 40% sugar concentration inside is in a solution of 20% sugar concentration. The cell membrane is permeable to solutes. Independent Practice Work INDIVIDUALLY to complete the worksheet. Yeaaaaaaaaahhhhh! Key Point Wrap-Up Key Point #1: Passive transport takes no energy and always moves towards equilibrium. Both diffusion and osmosis Key Point #2: Active transport takes energy to move all solutes in or out of the cell. Exit Question 1. Match each of the following statements to either ACTIVE or PASSIVE transport. (You do not have to write complete sentences!) (1) Requires energy (2) Movement of solute or solvent in/out of a cell (3) Moves toward equilibrium 2. A cell containing 20% sugar solution is placed in 80% sugar solution. What will happen if ACTIVE transport occurs?