unit 3 test topics answer key
advertisement

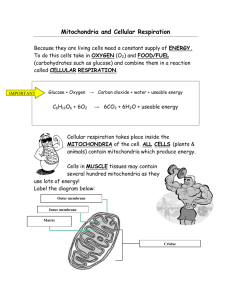
UNIT 3 TEST TOPICS: 1. Function of cell parts/organelles 2. Facts about the four organic compounds (lipids, carbs, proteins and nucleic acids) 3. Diffusion/osmosis and active transport 4. Cellular Respiration 5. Photosynthesis 6. Glossary words Review Questions – answer in your notebook 1. Is glucose a waste product of photosynthesis? Explain. Glucose is NOT a waste product; rather, the making of glucose is the purpose of photosynthesis. Plants use the energy from the sun to combine water and carbon dioxide into glucose molecules. The glucose is then used by the plant in its own cellular respiration and for the making of new plant parts. 2. What is the role of the sun in photosynthesis? The sun provides the energy needed for the chemical reaction between water and carbon dioxide to take place. 3. What are the two ways that plants use glucose after they make it via photosynthesis? Plants use glucose for cellular respiration and to make more plant parts. 4. What does a cell have to do to move glucose inside it? A cell must actively transport glucose through the membrane. 5. The reactants for CR are oxygen and glucose. How do you get each of the reactants into your body and then into the cells that make up your body? Glucose – by eating food; food is broken down in the stomach and small intestine and then glucose molecules are transported to the blood and carried to all cells. oxygen – breathing air into the lungs; oxygen diffuses through the lung tissue and into the blood; since the blood has more oxygen than the cells, oxygen naturally diffuses into the cells where it is immediately used for CR. 6. Why did water move out of the carrot that was placed in salt water? Explain. In this situation there is more water in the carrot cells than in the surrounding salt water due to the fact that the salt is taking up a lot of space; therefore, water diffuses out of the carrot cells and into the bowl. 7. What is the difference between active transport and diffusion? Diffusion does not require additional energy to move molecules through a membrane, the natural motion of molecules causes them to move into areas of lower concentration – these are small molecules that can easily move through the pores in the cell membrane. Large molecules cannot fit through the pores so cells must use energy and specially designed mechanisms, such as transport proteins, to move these large molecules through the membrane. 8. Explain the job of the following cell parts: a. Rough ER - Provides passageways for moving materials and aids the ribosomes in making proteins. b. Smooth ER - Produces lipids (fats) and breaks down toxins. Provides passageways for moving materials through the cell. c. Ribosomes – assembles proteins as instructed by RNA molecules d. Cell membrane - Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell. e. Vesicle - A membrane-bound container that moves materials around the cell. 9. Name a cell parts that you do find in plants but NOT in fungi cells. Fungi cells do NOT have chloroplasts; fungi are heterotrophs that absorb glucose from their surroundings while plants are autotrophs that make their own glucose. 10. What does it mean to say that a substance has reached equilibrium? When a substance has an equal amount of molecules within and outside of a membrane it is at equilibrium. 11. How heterotrophs get glucose into their bodies? Heterotrophs get glucose by either absorbing it through membranes (such as fungi, protists and non-photosynthetic bacteria) or they get it via eating (animals). 12. What is the purpose of photosynthesis? The purpose of photosynthesis is for the organism to be able to make its own glucose; this is done by plants, algae and photosynthetic bacteria. 13. List the organic compound that does the following: a. Provides instructions to cells what to do – nucleic acids b. Stores energy for later use - lipids c. Are a quick source of energy for cells - carbohydrates d. Make up most of a cell membrane - lipids e. Are made of amino acids - proteins f. Are enzymes and hormones - proteins g. Fats and waxes are examples - lipids h. Starch and sugars are examples - carbohydrates 14. Why is glucose NOT a waste product of photosynthesis? As stated above, the making of glucose is the goal of photosynthesis. The leftover oxygen molecules are the waste product and they are released through the stomata of the leaves so that toxic levels of oxygen do not build up in the cells. 15. How do plants use the glucose that they make? Another repeat! Plants use glucose for cellular respiration and to make more plant parts. REMEMBER TO STUDY THE GRADED REVIEWS AND KNOW THE CHEMICAL EQUATIONS FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS STUDY, STUDY AND STUDY!!!