Haemoglobin - TASIS IB Biology
advertisement

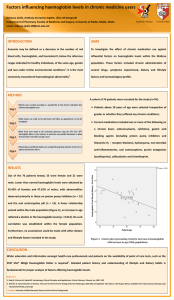
Haemoglobin By Maja & Jonathan S Protein Functions S Iron-containing oxygen-transporting metallprotein S Essential for respiration S Located in all red blood cells of vertebrates S Around 35% of our blood (including water) S Four iron atoms; can bind up to four oxygen molecules S Responsible for the red colour of blood (iron) S carries the oxygen from the lungs or gills to the cells History S Many people did research for Heamogobin S Discovered in 1840 by Hünefeld S Description of revisable oxygenation by Felix Hoppe-Seyler S 1959 Max Perutz determined protein structure; resulted in Nobel prize for Chemistry in 1962 S Role in blood determined by Claude Bernard Primary Structure S The haemoglobin molecule consists of 4 polypeptide (globin) chains. In adults there are 2 alpha chains and 2 beta chains. S Peptide bond between each amino acid called residues Secondary Structure S Joined amino acid residues coil to form sections of alpha helix, which stabilizes the structure S Structure fairly compact Tertiary Structure S Main bonding involved in stabilising the structure of each haemoglobin chain is the attachment of a haem group (a porphyrin ring containing iron) --->the yellow ball on the picture S No disulphide bridges involved in the tertiary structure of haemoglobin. Quaternary Structure S Two alpha and two beta chains are associated to form a haemoglobin molecule. S More than one peptide chain (multimeric proteins). The manner in which these chains fit together (sort of like a puzzle) is the quaternary structure. Defective function S Sickle cell anaemia S In the primary structure: a single alteration in the amino acid structure - substitution of valine GTG (non polar) for glutamic acid GAG (polar) - only in the beta chain - causes the molecule to pack differently into the red blood cells, causing sickling. S Thalassemia S inherited condition in which reduced production of one of the globin chains occurs. The unpaired other chain builds up in the cells, resulting in problems. Works Cited S http://www.austincc.edu/emeyerth/tertiary.htm S http://faculty.stcc.edu/AandP/AP/AP2pages/Units18to20 /blood/hemoglob.htm S http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/haemoglobinproteinstructur e.html