Diploid
advertisement
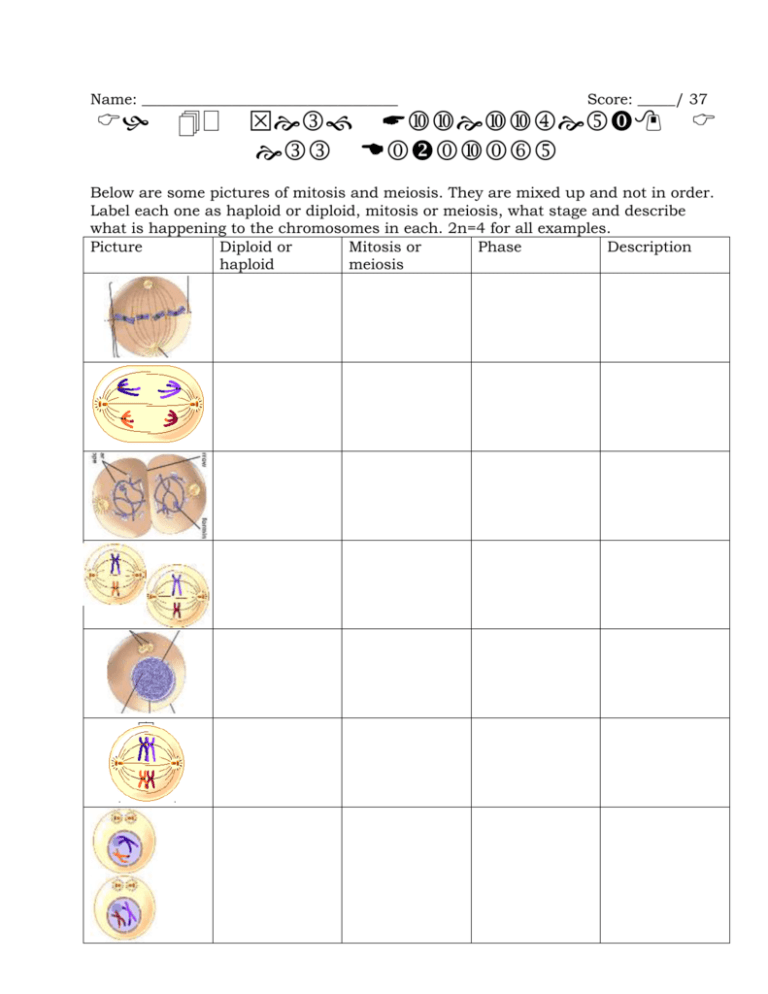
Name: __________________________________ Score: _____/ 37 Below are some pictures of mitosis and meiosis. They are mixed up and not in order. Label each one as haploid or diploid, mitosis or meiosis, what stage and describe what is happening to the chromosomes in each. 2n=4 for all examples. Picture Diploid or Mitosis or Phase Description haploid meiosis 29. – 32. Draw the cell cycle. Label the 4 stages and describe what is happening in each. 33. – 34. In meiosis, there are two ways that the gametes can be genetically different. Describe the two ways this happens and the phases in which it happens (be specific). 35. – 37. Describe prokaryotic cell division. Be sure to mention shape/location of DNA as well as the process itself. Name: __________________________________ Score: _____/ 37 Below are some picture so mitosis and meiosis. They are mixed up and not in order. Label each one as haploid or diploid, mitosis or meiosis, what stage and describe what is happening to the chromosomes in each. 2n=4 for all examples. Picture Diploid or Mitosis or Phase Description haploid meiosis Metaphase Chromosomes (2 chromatids) line up in middle of cell Diploid Mitosis Diploid* Meiosis (will be haploid) Diploid Mitosis Anaphase I Homologs separate (centromeres do not split) Telophase Haploid Meiosis Metaphase II Nucleus reforms, chromosomes unwind, cytokinesis Chromosomes (2 chromatids) line up in middle of cell Diploid Neither/ both Interphase Chromosomes replicate, cell does cell things Diploid Meiosis Metaphase I Homologs line up in middle of cell Haploid Meiosis Prophase II Chromosomes (2 chromatids) start to move towards center, nuclear membrane breaks down 29. – 32. Draw the cell cycle. Label the 4 stages and describe what is happening in each. M G1 G2 S G1 growth, cell does cell things S synthesis, DNA copies G2 growth, cell does cell things M mitosis & cytokinesis, nucleus divides, followed by cytoplasm and contents 33. – 34. In meiosis, there are two ways that the gametes can be genetically different. Describe the two ways this happens and the phases in which it happens (be specific). Crossing over: genes from one chromosome switch places with the same genes on its homolog. This means some of Mom’s genes and Dad’s genes will be on the same chromosome, instead of separate ones. Prophase I Independent assortment: Which side of the cell homologs line up on is random. It’s not Mom’s on one side and Dad’s on the other. Metaphase I 35. – 37. Describe prokaryotic cell division. Be sure to mention shape/location of DNA as well as the process itself. DNA in prokaryotes (bacteria) is circular (rather than strands) and attached to the inside of the cell membrane (rather than in a nucleus). When prokaryotes divide, it is called binary fission. The DNA replicates and the cell merely splits in two. There is no cytokinesis, since there are no membrane bound organelles in prokaryotes.







