How to View Advertisements
advertisement

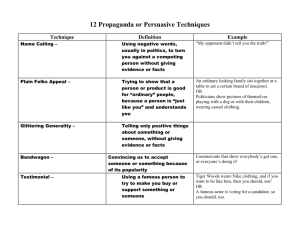
Advertisements Characteristics: Advertisements play up the good aspects of products. Any bad aspects are downplayed through careful omission of information. Advertising confirms consumer satisfaction so that those who have already purchased a product feel good about themselves. Advertisers must show how the product or service offers a clear benefit, appealing to the beliefs, attitudes, fears, and biases of the audience. Ads must be eye-catching. Ads need to be a strong combination of visuals and language. Propaganda takes advertising one step further: it attempts to sway popular opinion and beliefs through distortions of the truth and outright lies. Propaganda frequently makes use of doublespeak, which is vague, imprecise language that often means the opposite of what it seems to mean. Terms and Techniques Testimonial: The endorsement of a product by a well-known person or organization. Transfer: The shifting of qualities from one thing to another. Plain Folks: Talking down to the viewers in order to appear just like them. Bandwagon: The suggestion that everyone is using or doing something. Snob Appeal: The association of a product with a desirable lifestyle. Facts and Figures: The implication that figures and statistics prove a point beyond dispute. How can facts and figures be biased or slanted? Hidden Fears: The exploitation of an individual’s fears and insecurities. Repetition: The constant statement of an idea to fix the image of a product in the viewer’s mind. Magic Ingredients: The implication that a product’s effectiveness is scientifically based. Weasel Words: The use of vague terms to mislead the viewer into thinking the product is better than it really is. Spin: The attempt to turn negative evidence into something that the public will perceive positively. How to View Advertisements First, view the advertisement as a whole, considering: Your first impression of the ad Its overall look Its tone and atmosphere The storyline, if any; is there a climax and resolution? Possible target audiences. Think about the target audience more carefully, trying to narrow it down as much as possible. Is the ad placed properly to reach its intended audience? What are the connections between the ad, its placement, and the target audience? Study the content of the advertisement to determine what message it is trying to send. What is the setting? What kind of atmosphere does it convey? Are there any people in the ad? If so, what kind of people are they(age, sex, race, social and economic status)? What are they doing? What is being communicated by the body language? Is there any stereotyping? Does the ad feature celebrities? Is the celebrity a credible spokesperson for the product? What benefits does the celebrity’s appearance provide? Is there a story being told? Is there something more to the ad than what is visible? Does it look like something just happened or is about to happen? Is there anything in the advertisement that could be considered a symbol? Does the content imply a certain lifestyle? Examine the language used in the ad. What message does the name of the product communicate? Identify key words and phrases. What claims are being made? How are they supported? What approach is being used (from terms and techniques)? Is there a hidden message? Explore the design elements. What is the focal point? What draws the eye to this position? How are the visual items arranged? Which items are being visually linked or juxtaposed? How does the print component contribute to the ad? Think about style, size, and placement. What is the colour scheme and how does it relate to the atmosphere? Does the product appear in the ad? Where is it located? Why might it have been positioned here? Is there a product logo? What does the logo communicate? Analyzing Advertisements NAME: Why? What is the effect? How does this communicate the message? Identify techniques used Your first impression, the overall look, tone, story and setting Narrow down the target audience People: what kind? What are they doing? Stereotypes? Body language? Celebrities? Symbols? Lifestyle implied? Language: what is the message? Key words and phrases? What claims are being made? Analyze the text: style, size, and placement. Effects? Design elements: focal point, arrangement of visual items, colour scheme? Product: placement? Logo? Terms and Techniques Testimonial: The endorsement of a product by a well-known person or organization. Transfer: The shifting of qualities from one thing to another. Plain Folks: Talking down to the viewers in order to appear just like them. Bandwagon: The suggestion that everyone is using or doing something. Snob Appeal: The association of a product with a desirable lifestyle. Facts and Figures: The implication that figures and statistics prove a point beyond dispute. How can facts and figures be biased or slanted? Hidden Fears: The exploitation or an individual’s fears and insecurities. Repetition: The constant statement of an idea to fix the image of a product in the viewer’s mind. Magic Ingredients: The implication that a product’s effectiveness is scientifically based. Weasel Words: The use of vague terms to mislead the viewer into thinking the product is better than it really is. Spin: The attempt to turn negative evidence into something that the public will perceive positively.