Photosynthesis Notes!
advertisement
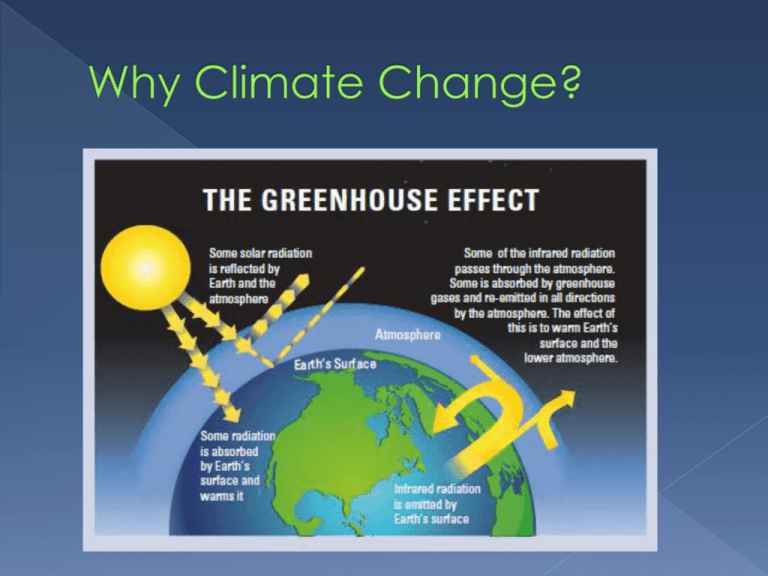
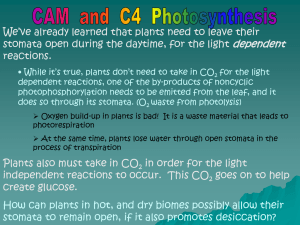
After looking at your pictures… › share what you’ve noticed about where Carbon is found… › Share what you’ve noticed about how Carbon moves from place to place… We are going to focus on some of the natural processes that move Carbon… › Photosynthesis › Cellular Respiration Using Bromothymol Blue is a pH indicator. Review: › What is pH? › How does the scale work? BTB gets bluer the more basic a solution is. When CO2 is in water, it forms Carbonic Acid, H2CO3 We will use BTB as an indicator of CO2 Purpose? › Convert light energy into stored chemical energy (=glucose) that the plant can use Who does it? › Autotrophs Where does it happen? › Choloroplasts Chloroplasts 6CO2 + 12H20 C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20 Note** water on product side is NEW, formed from different combination of H’s and O’s. Purpose › Convert stored chemical energy into useable energy (=ATP) Who does it? › ALL organisms (even plants!) Where? › Mitochondria C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Heat + ATP Enzymes involved in both reactions (PS &CR) › Different enzymes = specificity › Increase speed of chem rxns › Lower activation energy (so cell won’t fry) ATP= chemical energy used to do WORK › Usable Energy stored in bonds (AT-P-P~P) that is released when bonds are broken › Used for movement & breakdown of molecules › Comes from glucose breakdown! › Energy not recycled, but nutrients and matter are Go back to your Elodea / Fishy Models. Fix and add to your explanations. Different types of plants “trap” CO2 for photosynthesis in slightly different ways. At Tucker Prairie, there is competition between these C3 & C4 Plants › C3 Plants trap CO2 with one enzyme › C4 Plants trap CO2 with two enzymes and require a little bit of extra energy ~85% of all plants are C3 Examples—rice, wheat, barley, most trees and many grasses › Grasses of Tucker Prairie Stomata are open during day and closed at night—this is important because they can get CO2 for photosynthesis Do best in Temperate environments ~3% of all land plants Examples—corn, sugarcane, and many grasses › Forbs of Tucker Prairie Stomata are open during day and closed at night—BUT…stomata can close if the plant is losing too much water during the day. › › When stomata close, CO2 concentration in leaves go down. Plant can still do photosynthesis because of the 2nd enzyme Do well in tropical, high heat intensity and drought conditions C3 Pathway Which plants have the advantage— › C3 Grasses? › C4 Forbs?