The Circular Flow of Economics
advertisement

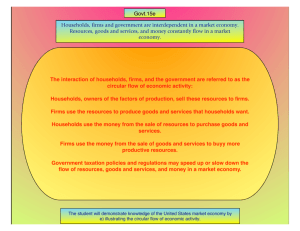
1. Which would be a likely cause of an increase in the price of pizza? A) a decreased interest in take-out and fast-food dining B) a decrease in the price of hamburgers, a substitute food C) an increase in the price of cheese, a complement D) a health report showing eating pizza reduces stress 2. Which of the following best describes the relationship between price and quantity demanded shown by the demand curve? A) as the product's price falls, consumers buy less of the good. B) there is a direct relationship between price and quantity demanded. C) as a product's price rises, consumers buy less of other goods. D) there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. 3. An improvement in the technology used in the production of automobiles will most likely cause the price and quantity of automobiles to change in which of the following ways? Price Quantity A) Increase Increase B) Increase Decrease C) Decrease Decrease D) Decrease Increase 4. An increase in the popularity of Good X will most likely cause the equilibrium price and quantity of Good X to change in which of the following ways? Price Quantity A) Increase Increase B) Increase Decrease C) Decrease Increase D) Decrease Decrease 5. A drought will most likely cause the equilibrium price and quantity of oranges to change in which of the following ways? Price Quantity A) Increase Increase B) Increase Decrease C) Uncertain Increase D) Decrease Decrease The Circular Flow of Economics 6.1 6.1 IDENTIFY THE PARTS OF THE CIRCULAR FLOW OF ECONOMICS ACTIVITY what do you think? In a capitalist economy, what is the goal? What do businesses want? What do all individuals want? Why do you care about your salary or wages? Households Firms THE CIRCULAR FLOW SIMULATION First, a few simple questions. 1. Who are the 2 players in our nation’s economy based on the circular flow model? 2. What is it that firms want from households? 3. What is it that households want from firms? Now you will be divided! • Half of you are HOUSEHOLDS • Half of you are FIRMS – You are Entrepreneurs! – You are consumers! • Your goal: – Buy as many products as possible – ECONOS are products – But to buy ECONOS you’ll need to sell your land, labor, and capital! • Your goal: – Make a profit selling ECONOS – But to make 1 ECONO you need the other 3 factors of production! • Land, labor, capital Now, let’s distribute the wealth! • Entrepreneurs you will start with money. • Households you own all the factors of production – Land, labor, capital • Unfortunately, some of you will have less than others! • ENTREPRENEURS count your money and record how much you start with! • Your goal is to make a profit THE RESOURCE MARKET FIRMS • You are a buyer in the resource market. • 1 Econo = 1 land, 1 labor, 1 capital. • Get these 3 factors of production as cheaply as you can! • Your goal is to make as many ECONOS as you can with your money. HOUSEHOLDS • You are selling your labor, land, and capital in the resource market. • Of course, you want a lot of income, so sell your factors at the highest rate you can! • Your goal is to get as much money as you can for your factors. FIRMS report to the factory • 1 Econo = 1 land, 1 labor, and 1 capital • I will trade these out for you • Once you’ve received your Econos, return to your seat. • DO NOT SELL ANY ECONOS YET! THE PRODUCT MARKET FIRMS HOUSEHOLDS • YOUR GOAL: MAKE A PROFIT! • YOUR GOAL: BUY AS MANY ECONOS AS POSSIBLE! • Sell your ECONOS at high prices • Just like the real world, buy at as low a price as you can! Analyzing the Results 1. Firms count your money. Did you make a profit, lose money, or break even? 2. Households did you have money left over, unable to buy ECONOS? What was flowing in the circular flow? • Resources flowed from households to firms and were turned into goods and services, then sold back to the households. • Money flowed from firms to households as wages. Then it went from households back to firms as they bought goods and services. This money is called revenue. Think about it • If households had unused resources, these represent unemployment. You needed to sell your labor, but couldn’t find a buyer. • If firms had unused resources, they represent inefficiency. You wasted money on them. • Unsold Econos represent a surplus. If firms ran out of Econos and households have money left over, it is a shortage. What about inequality in the distribution of income? • Firms with the most money at the beginning probably did the best when it came to making a profit or revenue! • Households with the most factors of production probably made a higher income, and therefore were able to afford more econos! • Some people are born with an advantage over others. It’s part of life! • What would happen if the money given to firms was doubled in the next round? • What if it was cut in half? What about the Government? Goods and Services TAXES SUBSIDIES OR REGULATION Households (Want income to buy products) ENTITLEMENTS Government Land, Labor, Capital Firms TAXES (want Profit) Let play again