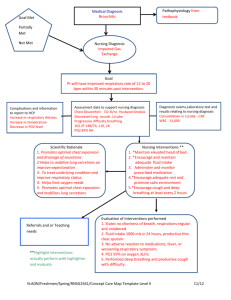
Respiratory: Age related changes: Loss of elasticity Enlarged
advertisement

Respiratory: Age related changes: Loss of elasticity Enlarged/relaxed bronchioles Decreased vital capacity Dry/bleeding of nose Decrease sense of smelled Curved spine Abdomen extension *know the anatomy of respiratory * Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures: Chest x-ray and Fluoroscopy- (and the difference) x ray is a static picture. Fluoroscopy is like an x-ray but live. ABG’s What are they? (Arterial blood gas) measure and maintains your PH. involves respiratory and urinary system Allen Test- to ensure adequate circulation. Normals: PH- 7.35-7.45 CO2- 35-45 CO3-22-26 Pneumonia puts you in respiratory acidosis Hyperventilating puts you in alkalosis When ABG’s drawn, how long to hold pressure (normally and if on coags) apply pressure dressing and hold pressure for 5 minutes . if they are on Heparin or Coumadin 20 minutes Practice: PH- 7.32 CO2- 48 CO3-21 *Respiratory acidosis (ex: COPD- OVER ABUNDANCE OF CO2) PH-7.46 CO2-45 CO3-30 * Metabolic Alkalosis PH-7.35 CO2-47 CO3-24 *Respiratory Acidosis PH-7.50 CO2-50 *Respiratory Alkalosis CO3-24 PH-7.30 CO2- 47 CO3-28 *BOTH acidosis O2 administration: What is the difference between: NC-(nasal cannula, most common) used for mild 2-4 liters of O2. Connedected to a humidifier for people with long term O2 Face mask- gives more O2 Non-rebreather mask- if NC and mask doesn’t work . get 40-50% O2 Venturi mask- seals your mouth and nose and get 70-90% O2 Why must you use caution using O2 on a patient with COPD? You will kill them because it is registering too much O2 and the body will read little CO2, stopping your breathing to regain O2 What is normal flow rate for a NC? 2-4 Suctioning: Explain oropharyngeal Suctioning- (what do you use?) Use yonkers for their mouth to clear pharynx .NOT sterile. Explain endotracheal suctioning- (the differences and time) It is sterile. Deep suction. You oxygenate the patient ,put saline down their trachea down into their lungs ( to liquefy the stuff) put the tube down in and suck. Never suction longer than 10 seconds . no suction going in . suction on when pulling out. Concern of hypoxia and Breath sounds: (types and where to listen) Crackles- deep in alveoli. Fluid in the sacks, wheezes-where the bronchus shrinks, rochiThroat culture: (How to obtain and why) Get a cotton swab and swipe the pharynx looking for bacteria Bronchoscopy: Explain the procedure: scope to examine the respiratory system. Can also be for biopsy Describe any nursing implications before, during, and after the procedure- pre; sign consent .explain procedure. NPO. Vitals. During- assess airways. After- Vitals. Gag reflex. Sputum sample: (how to collect and when) Get spit from deep within. Get it right in the morning before mouth care since things settle .Take a deep breath and cough. Don’t touch it Chest Tubes: What are they used for? Why is the water seal so important? Should the water seal fluctuate and/or bubble? Thoracentesis: What is this procedure? Pre-vitals,lung sounds Post-vitals and lung sounds to make sure you didn’t hit or damaged anything. Document how much is in there or “Small,Moderate,Large” Exp “pt had thoracentesis with large amount of serosanguiness fluid “ Why would it be used? Removes excess fluid that are in the lungs to help with breathing Serous is clear Serosanquiness is pink Anguiness is red Tracheostomy: Why is this done to patients? Cancer, trauma Explain the difference between cuffed and uncuffed- Cuff is on the inside with balloon to blow up, meaning that there is no breathing on their own and no talking because it is sealed no air movement except through the pipe. Uncuffed is where the pipe just sits there since there is no balloon, they can talk and breathe on their own. Why do you keep an extra handy? What do you do if it accidentally is removed? 1. Try to put it right back in and call it as an emergency Mechanical ventilation: What is this? Breathing on a machine Explain some of the different type settings patients can be on- only inspiration: lets the patient exhale. Only expiration: where patient does inhale. On demand(like a pacemaker): turns on when your breathing gets unbalanced Explain CPaP and BiPaP- Continuous Positive Pressure – mask that goes over your nose ONLY where you wear at night that blows continuous pressure in usually for people with sleep apnea (no breathing). BiPap- covers the mouth AND the nose worn all the time to give good pressure of air in. Diseases: AsthmaWhat is it- inflammation of the bronchi (when bronchi gets inflamed, it shrinks which results into expatory wheezes) caused it by allergy auto immune S&S- wheezing Treatment- bronchodilator, steroids prednisone *if you do not treat it, it will get worse causing respiratory distress/failure COPDWhat is it- there are 2 diseases that make COPD. (Emphysema and chronic bronchitis) Bronchitis is obstruction of your bronchi with stuff inside .sounds are rhonchi (mucous).Emphysema have floppy sacks? Smoker’s disease. Crackle sounds hear on in and expiration. COPD will usually knock you into CHF which means more fluids in the lungs and edema. S&S-(bronchitis- Rhonchi, SOB, hypoxemia) Treatment- (Bronchitis-Antibiotics, steroids, fluids) (Emphysema- oxygen, diuretic at times) PFT’s – Pulmonary Function Tests: vital capacity (how much you can breathe out and in) , tidal capacity (how much you normally breathe) . Reserve (the difference in between your vital and your tidal). In COPD the reserve shrink on both sides (in and out) PneumoniaWhat is it- fluids in the lungs caused by bacteria and viral S&S- Shortness of breath. Hypoxemia. Crackles . sometimes cough up blood Treatment- antibiotic for bacterial. Antivirals for viral. Oxygen . fluids . TuberculosisWhat is it- respiratory infection . S&S- Night sweats, coughing, low grade fever Treatment- isolation, antivirals for about two years antiturburculants Laryngeal cancerWhat is it- cancer of the larynx S&S- loss of voice, hoarseness Treatment- chemo, radiation, surgery LARYNGECTOMY: keep them on semi fowlers. Sense for bleeding . keep hydrated. Lung cancerWhat is it- cancer of the lung Staging- 1-4 . 1: just the tumor in the lung ; easy removal by taking it out then radiation to make sure you got everything out. 2: is a tumor but is by the lymph nodes, starts to spread. 3: goes from your lymph to the body 4: everywhere S&S- Coughing, hemoptysis, chest pain Treatment- chemo, radiation , surgery if possible Pulmonary embolismWhat is it- embolism: something foreign in your body. Pulmonary Embolism : clotting that travels through your heart and into your lung and blocks S&S- pain, SOB Treatment- Removal surgery, anticoagulants , thrombolytic, oxygen, sit up , Treatment to Prevent: ASA, platelets arrogates , ambulate, ROM , TED hoes , ARF/ARDS- Acute Respiratory Distress/Failure What is it- someone goes into complete distress and can’t breathe S&S- SOB, chest tightness, lung sounds, Treatment- Oxygen , treat the cause, (fluid: diuretics, bacterial: antibiotic , viral: antivirals) Hemothorax/pneumothoraxWhat is it- Air/blood in the plural space S&S- SOB Treatment- oxygen, Thoracentesis, chest tube SinusitisWhat is it- sinus infection/inflammation S&S- Toothache, stuffy/fullness (can lead to severe fever, which leads to seizures) Treatment- Antibiotic, anti-inflammatory (prednisone), fluids TonsillitisWhat is it- inflammation of the tonsils S&S- sore throat, redness, swelling Treatment- antibiotic, anti-inflammatory surgery- asses for bleeding If you get a sore throat more than three times in less than 6 months then it results into a tonsillectomy If you have an apses on your tonsils they have to come out There is bacterial and viral. Viral: when it progresses (slow/long) Bacterial: when you wake up and it hurts right away (fast) Influenza/common cold- both are viruses What is itS&S- flu: fatigue, ache and pains, high fevers cold: no high fevers, no cramps , cough , shorter Treatment- flu: anti-viral, fluids, rest, Tylenol (anti-pyretic) cold: antibiotic (amoxicillin) If you start on anti-viral within the first two days you can cut it down to half , problem: no one does it How is the flu and common cold spread: droplet Rib fracture- why is Resp.? Can puncture lung and restrict how much you inhale and exhale which can lead to pneumonia What is it- fracture of a rib S&S- SOB, pain Treatment- oxygen , analgesics , deep breathing Nasal Surgery Post op- semi fowlers, always asses for bleeding (by frequent swallowing) , main nursing DX – social isolation *do not mess with the tampons in the nose (used to measure drainage) Respiratory Vocabulary: Pulmonary toileting- used for COPD pts when they have an acute attack where they get drained of fluids (diuretics, antibiotics) Stupor- drowsiness due to lack of oxygen Tachypnea-fast breathing, over 20. TCDB- Turn Cough Deep Breathe. How you prevent pneumonia by turning the patient every 2 hours. Encourage to cough and deep breathe Hypoxia- low oxygen Hypoxemia- low oxygen in the blood Ventilation- breathing. One in and one out is 1 Perfusion- how good your circulation is of the blood Aspiration- choking. When it goes in the trachea instead of the esophagus Valsalva maneuver- forcing (ie: pushing when giving birth, or when using the restroom) when getting a chest tube out you ask pt to valsalva Empyema- accumulation of pus in the body Crackles- nonmusical sound of fluids in the alveoli Barrel chest- when chest extends and turns round, almost like a barrel Chest physiotherapy- 1. Percussion – take the hands or cups and tap the chest to break up stuff in lungs (mostly for kids) 2. Postural drainage- just turning them to keep the fluids to clear Pursed-lip breathing- where they breathe in through their nose and out through their mouth . it slows your breathing and CO2 Clubbing- (fingers)- people with long term respiratory issues have it Dyspnea- difficulty breathing Cyanosis- turning blue Pleural effusion- when you get liquid in your pleural area and it starts to crush Spirometer- plastic thing that they suck on to exercise the lungs spirometry : ventilation Cheyne-Stokes Respirations- breathing pattern . nice deep breathe and then short and then stop, then after 30 seconds they do it again . when they are dying Alveoli- sacks in your lungs Laryngitis- inflammation of the larynx Flail chest- where one side of your chest will rise and the other one stay when you inhale/exhale Echinacea- herbal remedies to help prevent from getting a cold or getting sick Blue Bloater- patient with COPD who has chronic bronchitis. they have obstruction in their bronchus so they don’t get good air in their air exchange so they start to turn blue and they get barrel chest Pink Puffer- patient with COPD who have emphysema .they have good perfusion they look fine but they are still dying. Atelectasis- when your alveoli shut down . when you stop producing surfactant (helps open your alveoli) Babies who are born early die usually because they haven’t produced any surfactant MedicationsBronchodilators- albuterol (they dilate your bronchi) Antibiotics- anything with “cillin” in it ie: amoxicillin . kill bacteria Steroids- prednisone; help inflammation Decongestants- stop mucous production but have bad SE such as raised BP . most decongestants are like “Speed” AntiTussive- robatusin . for cough . AntiVirals- fights viruses. Need to be taken in the first two days Top 5 nursing diagnosis for Respiratory and 1 intervention for each1. impaired gas exchange 2. activity intolerance 3. anxiety/fear 4. ineffective air clearance 5. impaired nutrition less than body requirements