dvt & varicose veins
advertisement

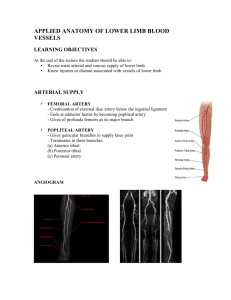
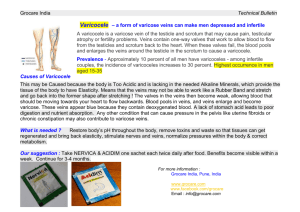
DVT & VARICOSE VEINS DVT It is the most common venous disorders result from incompetent valves in the veins and obstruction of venous return to the heart, usually as a result of thrombus. ETIOLOGY Venous stasis Vessel wall injury Hypercoagulability RISK FACTORS • Older age • Major surgery and orthopedic surgery • Cancers • Immobilization • Pregnancy and the postpartum period Cont… • • • • Trauma and minor leg injury Previous VTE Oral contraceptives Hormonal replacement therapy Central venous catheters • Obesity • Infection PATTERNS OF DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS Popliteal thrombosis Femoral thrombosis Iliac thrombosis PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Clot formation Clot can enlarged and extend Venous valves are damaged(Inflammatory response) Postphlebitic syndrome Cont… Muscle spasm and changes in intravascular pressure Developing thrombus to dislodge & moves towards heart and lungs Obstruct perfusion to the lung segments Cont… Pulmonary arteries partially or totally obstructed by embolus Circulation of the lung segment affected Lung may undergo severe infarction with massive tissue destruction Clinical manifestations Calf thrombosis • Calf tenderness • Distal swelling Femoral thrombosis • Tenderness & pain in distal thigh & popliteal regions • Swelling • Calf vein thrombosis Cont… Iliofemoral thrombosis • Massive swelling • Tenderness & pain in entire extremity Upper extremity thrombosis • Swelling of affected extremity • Dilated superficial veins • Tenderness & pain • Impaired mobility • Local warmth Cont… • Mild fever • Possible venous cord in the popliteal area DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION History collection Physical examination Color flow duplex ultrasound imaging D- Dimer test Cont…. Venography CT venography MR venography Treatment Goals To prevent propagation of the clot Prevent the development of new thrombi Prevent pulmonary emboli Limit venous valvular damage Cont… Bed rest Leg elevation Compression stockings Pharmacological measures – Heparin – Warfarin – Thrombolytic therapy Cont… Unfractionated heparin • Initial-5000U OR 80U/kg - IV • Followed by maintain the APTT between 1.5 & 2.5 times the control. • It given as 5 to 7 days Cont…. LMWH Dosage – 250U/ kg every 12 hours. Eg; enoxaparin, dalteparin. Warfarin Dose of 5 mg per day Cont… Thrombolytic therapy Eg;streptokinase, urokinase, recombinant tissue plasminogen(reteplase, alteplase) Surgical management Thrombectomy- transvenous filtration device • Greenfield filter • Bird’s nest filter Guidelines for safe practice Green field filter Bird’s nest filter Varicose veins These are swollen,twisted and sometimes painful veins that have filled with an abnormal collection of blood. Causes Hereditary Thrombophelebitis Risk factors Prolonged standing Obesity & distended belly Pregnancy Cont… Straining-chronic constipation, urinary retention, chronic cough. Prior surgery age Pathophysiology Generally blood flow from the superficial veins to the deep veins To the large veins to the heart Venous blood flow work against gravity This is assisted by unidirectional intraluminal valves in the veins Cont… Activity causes intermittent compression of the veins by muscles Pressure increases in the vein valves Incompetent valves Valve failure Cont…. Veins become swollon and enlarged Become hard & tortuous Feeling of heaviness & pressure Clinical manifestations Aching ,heavy legs Appearance of spider veins Ankle swelling Brownish blue shiny skin discolouration Redness, dryness, itching of the affected area Cont… Cramps while standing Bleeding during minor injuries Hard swollon area Whitened irregular scar like patches in the ankles. Diagnostic evaluation History collection Physical examination Tourniquet test Doppler ultrasound MRI TREATMENT Conservative Elevation of legs Regular exercises Compression stockings Anti inflammatory medications Cont…. Active Stripping - Removal of all or part of the saphenous vein . Endovascular laser surgery – uses a laser to destroy the veins. Radiofrequency ablation – heat to destroy the affected veins. Cont… Ligation – it is usually involved in an incision at the groin .here they tied saphenous vein to the femoral vein just at the entrance of the incision. Laser therapy Ablation therapy Non surgical Sclerotherapy - Injecting the chemical inside the vein . Sclerosant agent-polidocanal, sclerodex. Lasers – it is used in case of small veins with vacosity. Sclerotherapy Complications Varicose ulsers Severe bleeding Acute necrosis