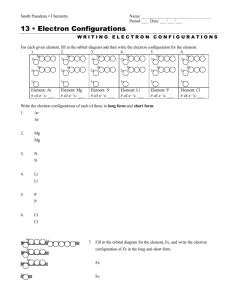
Chemistry Unit 2 Warm Ups

Mrs. Hilliard
1.
Valence electron
2.
Period
3.
Alkaline earth metal
4.
Halogen
5.
Metalloid
6.
Hund’s Rule
7.
Representative element
8.
Energy sublevel
9.
Transition element
10.
Electronegativity
11.
Ion
12.
Octet rule
13.
Nuclear Fusion
14.
Nuclear fission
15.
Cation
16.
Photon
17.
Wavelength
18.
Atomic Orbital
19.
Noble Gas
20.
Ground State
21.
Principle Energy Level
22.
Alkali Metal
23.
Group
24.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
25.
Anion
26.
Aufbau Principle
1.
Valence electron- the electrons in an atom’s 8.
Energy sublevel- the energy levels outermost orbitals; determines the chemical contained within a principle energy level.
2.
3.
properties of an element.
Period- a horizontal row of elements in the modern periodic table.
Alkaline earth metal- group 2 elements in the modern periodic table and are highly
9.
10.
Transition element- elements in groups 3-
12 of the modern periodic table.
Electronegativity- indicates the relative ability of an element’s atoms to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
reactive.
4.
Halogen- a highly reactive group 17 (7A) element.
5.
Metalloid- an element that has physical and
11.
Ion- an atom or bonded group of atoms with a positive or negative charge.
12.
Octet rule- states that atoms lose, gain, or share electrons in order to acquire the chemical properties of both metals and nonmetals.
stable electron configuration of a noble gas.
6.
Hund’s Rule- states that single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equalenergy orbital before additional electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals. (bus seat rule, single first then double)
13.
Nuclear Fusion- the process of binding smaller atomic nuclei into a single, larger, and more stable nucleus.
14.
Nuclear fission- the splitting of a nucleus into smaller, more stable fragments, accompanied by a large release of energy.
7.
Representative element- elements from groups 1, 2, and 13-18 in the modern periodic table.
15.
Cation- An ion that has a positive charge.
16.
Photon- A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy.
22.
Alkali Metal- Group 1 elements, except for hydrogen, they are reactive and usually exist as compounds with other elements.
17.
Wavelength- The shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave.
23.
Group- A vertical column of elements in the periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number, also called a family.
18.
Atomic Orbital- A three-dimensional region around the nucleus of an atom that describes an electron’s probable location.
24.
Pauli Exclusion Principle- States that a maximum of two electrons can occupy a single atomic orbital but only if the electrons have opposite spins.
19.
Noble Gas- An extremely unreactive group 18 element.
25.
Anion- An ion that has a negative charge.
20.
Ground State- The lowest allowable energy state of an atom.
26.
Aufbau Principle- States that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. (hog hilton, lazy)
21.
Principal Energy Levels- The major energy levels of an atom.
1.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in electronegativity?
2.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in first ionization energy?
3.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in ionic radius?
4.
What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state called?
5.
What is the measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself?
1.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in electronegativity?
2.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in first ionization energy?
3.
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in ionic radius?
4.
What is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state called?
5.
What is the measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself?
6. Which of the following elements is a metal?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Ne
7. Which of the following elements is a metalloid?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Ne
8. Which of the following elements is a non-metal?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Te
9. What is the halogen that is in Period 3?
10.Which region contains the alkali metals?
11. Which region contains the noble gases?
12. Which scientist arranged the modern periodic table?
6. Which of the following elements is a metal?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Ne
7. Which of the following elements is a metalloid?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Ne
8. Which of the following elements is a non-metal?
a. K b. C c. Si d. Te
9. What is the halogen that is in Period 3? Cl
10.Which region contains the alkali metals? A
11. Which region contains the noble gases? D
12. Which scientist arranged the modern periodic table?
Mendeleev
Element Block Characteristics
A
B
C
?
p d
Very Reactive, soft shiny metal
Very electronegative, liquid at room temperature
Liquid metal
13. What category of elements have the property of being malleable and ductile?
14. What category of elements have the property of being gases or dull solids and poor conductors of electricity?
15. Which block is element A most likely found in?
16. What is the most important characteristic in determining an element’s chemical properties?
17. What do we know about elements in the same group?
Element Block Characteristics
A
B
C
?
p d
Very Reactive, soft shiny metal
Very electronegative, liquid at room temperature
Liquid metal
13. What category of elements have the property of being malleable and ductile?
Metals
14. What category of elements have the property of being gases or dull solids and poor conductors of electricity?
nonmetals
15. Which block is element A most likely found in?
S block
16. What is the most important characteristic in determining an element’s chemical properties?
The number of valence electrons it contains (group #)
17. What do we know about elements in the same group?
They have the same number of valence electrons and the same charge for the ions (Ca +2 , Mg +2 , etc)
B
C
18. Which region is called the s-block on the diagram?
19. Which region is called the p-block on the diagram?
20. Which region is called the d-block on the diagram?
21. Which region is called the f-block on the diagram?
22. What will an atom that loses an electron form?
23. What will an atom that gains an electron form?
B
18. Which region is called the s-block on the diagram?
A
19. Which region is called the p-block on the diagram?
D
20. Which region is called the d-block on the diagram?
B
21. Which region is called the f-block on the diagram?
C
22. What will an atom that loses an electron form?
A cation (positive ion)
23. What will an atom that gains an electron form?
An anion (negative ion)
C
D
C
B
A
24. Which label identifies the trough of the wave?
25. Which label identifies the crest of the wave?
26. Which label identifies the amplitude of the wave?
27. Which label identifies the wavelength of the wave?
D
C
B
A
24. Which label identifies the trough of the wave? A
25. Which label identifies the crest of the wave? B
26. Which label identifies the amplitude of the wave? C
27. Which label identifies the wavelength of the wave?
D
28. Which element has the electron configuration
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 8 ?
29. What is the electron configuration for the element
Ruthenium (Ru)?
30. Which elements have 7 valence electrons?
31. What is the correct number of valence electrons in the element aluminum (Al)?
32. How many valence electrons does carbon (C) have?
33. How many valence electrons does oxygen (O) have?
28. Which element has the electron configuration
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 8 ? Nickel
29. What is the electron configuration for the element
Ruthenium (Ru)?
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 6
30. Which elements have 7 valence electrons? Fluorine,
Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, Astatine
31. What is the correct number of valence electrons in the element aluminum (Al)? 3
32. How many valence electrons does carbon (C) have? 4
33. How many valence electrons does oxygen (O) have? 6
34. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Germanium (Ge)?
35. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Phosphorus (P)?
36. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Chlorine (Cl)?
A
B
37. What type of orbital is shown in A?
38. What type of orbital is shown in B?
39. Which block contains 7 orbitals?
40. Which region contains elements with 6 valence electrons?
41. The octet rule states that atoms will ___________ electrons to achieve a complete set of eight valence electrons.
34. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Germanium (Ge)?
35. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Phosphorus (P)?
36. What is the correct electron dot configuration (Lewis Dot
Structure) for Chlorine (Cl)?
A
B
37. What type of orbital is shown in A? P
38. What type of orbital is shown in B? D
39.Which block contains 7 orbitals? F
40. Which region contains elements with 6 valence electrons? D
41. The octet rule states that atoms will _ gain or lose _ electrons to achieve a complete set of eight valence electrons.
42. Which region contains elements with an electron configuration that ends with p1?
43. What is the noble gas configuration for barium (Ba)?
44. How many valence electrons are present in barium (Ba)?
45. What is the complete electron configuration for Ruthenium (Ru)?
46. What is the noble gas electron configuration for Selenium (Se)?
47. What is the correct electron dot diagram for Carbon (C)?
A. B. C. D.
48. What is the period and group number of the element with the electron configuration of [Ne] 3s 2 3p 5 ?
42. Which region contains elements with an electron configuration that ends with p1? B
43. What is the noble gas configuration for barium (Ba)? [Xe]6s 2
44. How many valence electrons are present in barium (Ba)? 2
45. What is the complete electron configuration for Ruthenium (Ru)?
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 6
46. What is the noble gas electron configuration for Selenium (Se)? [Ar]
4s 2 3d 10 4p 4
47. What is the correct electron dot diagram for Carbon (C)?
A. B.
C. D.
48. What is the period and group number of the element with the electron configuration of [Ne] 3s 2 3p 5 ? Period 3, Group 17 or 7A
49. What is the splitting of nuclei called?
50. What is the combining of nuclei called?
51.What is the correct orbital box diagram and electron configuration for Sulfur (S)?
52.What is the orbital box diagram and electron configuration for Iodine (I)?
53. What is the orbital box diagram and electron configuration for Selenium (Se)?
54. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a single orbital according to the Pauli Exclusion
Principle?
49. What is the splitting of nuclei called? Nuclear Fission
50. What is the combining of nuclei called? Nuclear Fusion
51.What is the correct orbital box diagram and electron configuration for Sulfur (S)?
52.What is the orbital box diagram and electron configuration for
Iodine (I)?
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 10 5p 5
53. What is the orbital box diagram and electron configuration for Selenium (Se)?
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 4
54. What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a single orbital according to the Pauli Exclusion Principle? 2
1.
Endothermic reaction
2.
Ionic compound
3.
Formula unit
4.
Metallic bond
5.
Monatomic ion
6.
Chemical Bond
7.
Oxyanion
8.
Polyatomic ion
9.
Delocalized electron
10.
Oxidation number
11.
Electrolyte
12.
Ionic bond
13.
Covalent bond
14.
Exothermic reaction
15.
Polar covalent bond